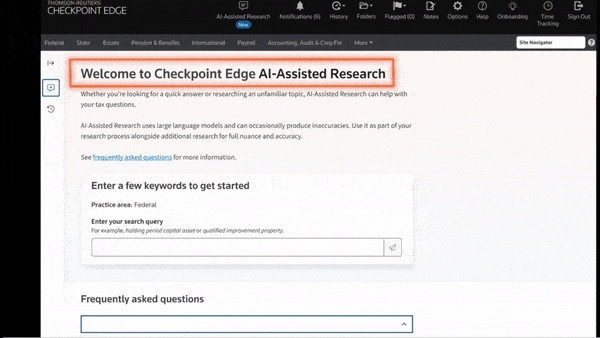
Do You Have a Process for Inspecting and Ensuring Safety When Using Tools and Equipment?
Do You Have A Process For Inspecting And Ensuring Safety When Using Tools And Equipment? Absolutely! Implementing a thorough inspection process is critical for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing accidents. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of workplace safety, and our comprehensive range of tools and equipment is designed to help you uphold the highest safety standards. Let’s dive into the essential steps and best practices for conducting effective safety inspections, enhancing accident prevention, and optimizing your overall safety program.
1. Why is Safety Inspection of Tools and Equipment Important?
Regular safety inspections of tools and equipment are essential for several compelling reasons. Compliance with safety regulations is paramount, and while organizations like the Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) may not mandate specific inspection procedures, they strongly recommend them. According to OSHA, employers are responsible for providing a safe and healthful workplace. Safety inspections are a proactive way to identify and mitigate potential hazards, ensuring compliance with OSHA’s guidelines.
Beyond regulatory requirements, regular inspections are a vital component of a robust health and safety program. Here’s why:
- Accident and Injury Prevention: Inspections identify potential hazards before they lead to accidents, reducing the risk of workplace injuries.
- Improved Workplace Morale: Demonstrates a commitment to employee well-being, fostering a culture of safety and security.
- Enhanced Property Insurance: Detailed inspection reports and certifications can assist with property insurance claims, providing valuable documentation of safety measures.
Source: OSHA – Employer Responsibilities
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Effective Safety Inspections
To create a safe working environment, treat safety inspections as part of a continuous improvement cycle. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to streamline your process:
2.1. Develop an Inspection Strategy
 Person holding a clipboard while conducting safety inspections
Person holding a clipboard while conducting safety inspections
Before conducting an inspection, it’s vital to have a well-defined strategy. A comprehensive safety inspection plan includes:
- Inspection Schedule: Determine the frequency of inspections, ideally every six months. Ensure all shifts and less-frequented areas are covered.
- Inspector Team: Assemble a team with diverse skills, including safety professionals, equipment experts, and supervisors. Distribute responsibilities to prevent omissions.
- Inspection Checklist: Create a detailed checklist tailored to your workplace. Categorize items by equipment safety, fall protection, accident risk, etc. Include people, equipment, and environmental factors.
- Reference Guidelines: Consult relevant standards and guidelines. For instance, the National Fire Protection Association’s (NFPA) Life Safety Code 101 provides minimum design, operation, and maintenance requirements for fire safety.
For example, the ANSI Z244.1 standard provides guidelines for lockout/tagout procedures, essential for electrical safety. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of lockout/tagout devices to help you comply with this standard and ensure worker safety during maintenance.
2.2. Conduct the Safety Inspection Thoroughly
Execute the inspection meticulously, adhering to your strategic plan. The inspection team must closely observe all work processes and equipment, identifying potential hazards. Some key areas to watch out for include:
- Inadequate machine guards
- Malfunctioning safety equipment
- Absence of a well-stocked first aid kit
- Biological hazards such as parasites
- Environmental issues like fumes or radiation
- Physical hazards such as wear and tear of equipment, heat, electrical hazards, etc.
- Risks to the mental health of workers such as stress or workplace bullying
- Poor work practices like using machinery without adequate safety training, overloading equipment, using defective tools, repairing or adjusting equipment while it’s on, and more
It’s best to use an inspection form to record all data, which is especially helpful for insurance purposes. Even when not required, these forms ensure a detailed record of your findings. Remember, the goal is not merely compliance but the genuine safety of your workforce.
Keep these best practices in mind:
- Communicate any immediate danger to the relevant authorities without delay.
- Never operate equipment without proper training.
- Take comprehensive notes, detailing each hazard and the conditions under which it occurs.
- Solicit information from workers regarding specific processes or equipment.
- Record equipment readings, emissions inspections, hazardous conditions, and other relevant data through notes, sketches, photographs, and videos.
- Remember that even minor oversights can pose significant hazards.
2.3. Review and Analyze Collected Data
Upon gathering the inspection data, thoroughly review and analyze it to identify gaps and formulate actions to mitigate hazards and improve workplace practices. Detecting trends in the data can help pinpoint the root causes of issues, enabling enterprise-level changes to prevent future occurrences. For instance, repeated issues with a specific tool may indicate a need for updated equipment or additional training.
2.4. Implement Corrective Actions
 Person wearing a hard hat while conducting inspections
Person wearing a hard hat while conducting inspections
The data gathered in the safety inspection must be utilized to prevent risks. Include a section in your inspection report that proposes corrective actions for each identified hazard. For instance, if a work practice poses a safety risk, suggest reforms to the practice. If a data trend is concerning, establish a team to further investigate the matter.
Your proposed actions should be comprehensive, including the delegation of work, deadlines for completion, and a method for reporting progress. Providing teams responsible for corrective actions with stakeholder contact information facilitates effective communication.
2.5. Follow Up Diligently
Schedule regular follow-ups to ensure actions are taken on the safety inspection findings. After deadlines pass, request progress reports from relevant teams and check with stakeholders to confirm the effectiveness of the solutions. If a hazard persists despite corrective action, the root cause may not have been eliminated, requiring further analysis.
Remember, safety inspection is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. Continuous monitoring and improvement are essential to maintaining a safe workplace.
3. Essential Tools for Effective Safety Inspections
To conduct comprehensive safety inspections, consider equipping your team with the following tools and equipment:
| Tool/Equipment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection Checklists | Detailed lists of items to inspect, tailored to specific equipment and work areas. | Ensures consistent and thorough inspections, prevents overlooking critical safety aspects. |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Safety glasses, gloves, hard hats, and other protective gear. | Protects inspectors from potential hazards during the inspection process. |
| Multimeter | Measures voltage, current, and resistance in electrical systems. | Identifies electrical hazards and ensures equipment is functioning safely. |
| Sound Level Meter | Measures noise levels in the workplace. | Identifies areas where noise levels exceed safe limits, allowing for implementation of noise reduction measures. |
| Gas Detector | Detects the presence of hazardous gases. | Ensures safe air quality, particularly in confined spaces or areas with potential gas leaks. |
| Thermal Imaging Camera | Detects heat signatures to identify potential overheating or electrical issues. | Enables early detection of equipment malfunctions and potential fire hazards. |
| Digital Camera/Video Recorder | Documents inspection findings with photos and videos. | Provides visual evidence of hazards and corrective actions, facilitating clear communication and documentation. |
| Lockout/Tagout Devices | Locks out equipment during maintenance to prevent accidental startup. | Ensures equipment is safely de-energized before maintenance or repairs, preventing injuries. |
| Ladders and Scaffolding | Provides safe access to elevated areas for inspection. | Ensures inspectors can safely reach and inspect high areas without risking falls. |
| Measuring Tape | Measures distances and dimensions to ensure compliance with safety standards. | Verifies proper clearances and adherence to safety regulations. |
| Light Meter | Measures the intensity of light. | Ensures that the working environment has enough light. |
You can find a wide range of these essential tools and equipment at CARDIAGTECH.NET, designed to meet the highest safety standards.
4. Legal Standards and Guidelines for Tool and Equipment Safety
Adhering to legal standards and guidelines is critical for ensuring workplace safety and compliance. Here are some key standards and guidelines to be aware of:
4.1. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
OSHA provides comprehensive regulations and standards for workplace safety, including specific requirements for tools and equipment. Employers are responsible for ensuring that tools and equipment are safe to use, properly maintained, and used according to manufacturer instructions.
Source: OSHA – Regulations
4.2. American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
ANSI develops voluntary consensus standards for a wide range of products, processes, and systems, including those related to tool and equipment safety. Compliance with ANSI standards demonstrates a commitment to best practices and can help reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
Source: ANSI – Standards
4.3. National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
NFPA develops codes and standards for fire safety, including requirements for fire extinguishers, fire suppression systems, and electrical safety. Compliance with NFPA standards is essential for preventing fires and protecting workers and property.
Source: NFPA – Codes and Standards
4.4. European Union (EU) Directives
For companies operating in the European Union, compliance with EU directives such as the Machinery Directive and the Personal Protective Equipment Directive is mandatory. These directives set out essential health and safety requirements for tools, equipment, and PPE.
Source: EU Directives
4.5. State and Local Regulations
In addition to federal and international standards, many states and local jurisdictions have their own regulations for workplace safety. Employers should be aware of and comply with all applicable regulations in their area.
5. The Role of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in Tool and Equipment Safety
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) plays a crucial role in mitigating workplace hazards and protecting workers from injuries. It is essential to ensure that workers have access to and properly use appropriate PPE when using tools and equipment.
5.1. Types of PPE
- Eye Protection: Safety glasses, goggles, and face shields protect against flying debris, chemical splashes, and other eye hazards.
- Hand Protection: Gloves protect against cuts, abrasions, chemical exposure, and extreme temperatures.
- Head Protection: Hard hats protect against head injuries from falling objects or impacts.
- Foot Protection: Safety shoes and boots protect against foot injuries from falling objects, punctures, and electrical hazards.
- Hearing Protection: Earplugs and earmuffs protect against noise-induced hearing loss.
- Respiratory Protection: Respirators protect against harmful airborne contaminants.
- Body Protection: Vests and full-body suits protect against chemical spills, extreme temperatures, and other hazards.
5.2. Ensuring Proper PPE Use
- Hazard Assessment: Conduct a thorough hazard assessment to identify potential hazards and determine the appropriate PPE for each task.
- PPE Selection: Choose PPE that is appropriate for the hazards and fits workers properly.
- Training: Provide training on how to properly use, inspect, and maintain PPE.
- Enforcement: Enforce the use of PPE and provide regular reminders to workers.
- Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain PPE to ensure it is in good condition.
6. Leveraging Technology to Enhance Safety Inspections
In today’s digital age, technology offers innovative solutions to streamline and enhance safety inspections. Here are some ways you can leverage technology to improve your safety inspection process:
6.1. Mobile Inspection Apps
Mobile inspection apps enable inspectors to conduct inspections using smartphones or tablets. These apps often include features such as:
- Customizable checklists
- Photo and video documentation
- Real-time data synchronization
- Automated reporting
- GPS tracking
6.2. Cloud-Based Inspection Management Software
Cloud-based inspection management software provides a centralized platform for managing all aspects of the inspection process, from scheduling inspections to tracking corrective actions. These systems often include features such as:
- Inspection scheduling
- Automated notifications
- Data analytics and reporting
- Integration with other business systems
6.3. Drones and Robotics
Drones and robotics can be used to conduct inspections in hazardous or hard-to-reach areas. These technologies can capture high-resolution images and videos, detect potential hazards, and reduce the risk to human inspectors.
6.4. Wearable Technology
Wearable technology, such as smart glasses and smartwatches, can provide real-time information and support to inspectors in the field. These devices can display inspection checklists, provide access to technical documentation, and enable hands-free communication.
7. How CARDIAGTECH.NET Supports Your Safety Inspection Process
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the critical importance of safety in your daily operations. That’s why we offer a range of high-quality tools and equipment designed to meet the highest safety standards. Here’s how our products and services can support your safety inspection process:
7.1. High-Quality Tools and Equipment
We provide a wide selection of tools and equipment that are durable, reliable, and designed for safe operation. Our products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet or exceed industry safety standards.
7.2. PPE Solutions
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive range of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to protect your workers from workplace hazards. From safety glasses and gloves to hard hats and respirators, we have the PPE you need to ensure worker safety.
7.3. Inspection and Maintenance Tools
We provide a variety of inspection and maintenance tools to help you keep your equipment in top condition. Our multimeters, thermal imaging cameras, and gas detectors enable you to identify potential hazards and ensure equipment is functioning safely.
7.4. Training and Support
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers training and support to help you properly use and maintain your tools and equipment. Our team of experts can provide guidance on safety best practices and help you develop a comprehensive safety program.
7.5. Customized Solutions
We understand that every workplace is unique, so we offer customized solutions to meet your specific safety needs. Our team can work with you to develop a tailored safety program that addresses the specific hazards in your workplace.
By choosing CARDIAGTECH.NET, you’re investing in the safety and well-being of your workforce. Our high-quality tools, PPE solutions, and expert support can help you create a safer, more productive workplace.
8. Addressing Common Challenges in Tool and Equipment Safety
Even with the best intentions, you may encounter challenges in maintaining tool and equipment safety. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Lack of Training | Provide comprehensive training programs that cover proper tool usage, maintenance, and safety procedures. |
| Inadequate Inspections | Implement a regular inspection schedule and use detailed checklists to ensure thorough evaluations. |
| Neglecting Maintenance | Establish a preventative maintenance program that includes regular servicing, repairs, and replacements as needed. |
| Poor Housekeeping | Promote good housekeeping practices by keeping work areas clean, organized, and free of clutter. |
| Using the Wrong Tool for the Job | Ensure that workers have access to the right tools for each task and are trained to use them properly. |
| Failure to Use PPE | Enforce the use of PPE and provide regular reminders to workers. |
| Ignoring Warning Signs | Encourage workers to report any warning signs or potential hazards immediately. |
| Overconfidence and Complacency | Regularly review safety procedures and provide refresher training to prevent overconfidence and complacency. |
| Resistance to Change | Communicate the benefits of safety improvements and involve workers in the process to foster buy-in. |
| Language Barriers | Provide training and communication materials in multiple languages to ensure that all workers understand safety procedures. |
9. Real-World Examples of Successful Safety Inspections
To illustrate the importance and effectiveness of safety inspections, here are a few real-world examples:
Example 1: Manufacturing Plant
A manufacturing plant implemented a comprehensive safety inspection program that included regular inspections of all tools and equipment. As a result, they identified and corrected several potential hazards, including frayed electrical cords, loose machine guards, and worn-out PPE. The plant saw a 40% reduction in workplace injuries in the first year of the program.
Example 2: Construction Site
A construction site implemented a daily safety inspection program that included inspections of all tools, equipment, and work areas. They identified and corrected several potential hazards, including unsafe scaffolding, damaged power tools, and improper use of PPE. The construction site saw a 50% reduction in workplace accidents in the first year of the program.
Example 3: Automotive Repair Shop
An automotive repair shop implemented a weekly safety inspection program that included inspections of all tools, equipment, and work areas. They identified and corrected several potential hazards, including damaged lifts, leaking fluid containers, and improper storage of flammable materials. The automotive repair shop saw a 30% reduction in workplace injuries in the first year of the program.
These examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of implementing a comprehensive safety inspection program. By identifying and correcting potential hazards, you can create a safer, more productive workplace.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Tool and Equipment Safety
Here are some frequently asked questions about tool and equipment safety:
- How often should tools and equipment be inspected?
- Tools and equipment should be inspected regularly, ideally before each use. Formal inspections should be conducted at least every six months, or more frequently if the equipment is used heavily or in hazardous conditions.
- Who should conduct safety inspections?
- Safety inspections should be conducted by trained personnel who are knowledgeable about the tools and equipment being inspected and the relevant safety standards.
- What should be included in a safety inspection checklist?
- A safety inspection checklist should include all critical safety aspects of the tools and equipment being inspected, such as proper guarding, electrical safety, structural integrity, and PPE requirements.
- What should be done if a hazard is identified during a safety inspection?
- If a hazard is identified during a safety inspection, it should be immediately reported to the appropriate personnel and corrected as soon as possible. The equipment should be taken out of service until the hazard is corrected.
- How can technology improve safety inspections?
- Technology can improve safety inspections by providing real-time data, automating reporting, and enabling remote inspections using drones and robotics.
- What is the role of PPE in tool and equipment safety?
- PPE plays a crucial role in mitigating workplace hazards and protecting workers from injuries. It is essential to ensure that workers have access to and properly use appropriate PPE when using tools and equipment.
- How can employers promote a culture of safety in the workplace?
- Employers can promote a culture of safety by providing comprehensive training, enforcing safety procedures, involving workers in safety planning, and recognizing and rewarding safe behavior.
- What are the legal requirements for tool and equipment safety?
- The legal requirements for tool and equipment safety vary by jurisdiction, but generally include OSHA regulations, ANSI standards, and other applicable codes and standards.
- How can CARDIAGTECH.NET support my safety inspection process?
- CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality tools and equipment designed to meet the highest safety standards, as well as PPE solutions, inspection and maintenance tools, training and support, and customized solutions to meet your specific safety needs.
- What should be done to ensure mental health safety in the workplace?
- To ensure mental health safety in the workplace, it’s important to implement policies that promote a healthy work-life balance, offer resources for mental health support, and create a culture where employees feel comfortable discussing their mental health concerns. Training managers to recognize and address signs of stress or burnout in their teams can also be very effective.
Conclusion: Prioritize Safety with CARDIAGTECH.NET
Ensuring safety when using tools and equipment is not just a regulatory requirement; it’s a moral imperative. By implementing a thorough inspection process, providing adequate training, and investing in high-quality tools and equipment, you can create a safer, more productive workplace.
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to helping you prioritize safety. Our comprehensive range of tools, PPE solutions, and expert support can help you create a safer, more efficient work environment. Don’t wait until an accident happens. Take proactive steps to protect your workers and your business today.
Ready to enhance your safety inspection process? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for a consultation. Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you create a safer, more productive workplace.