**Decoding the 9028 Code Mercedes: Solutions and Expert Insights**
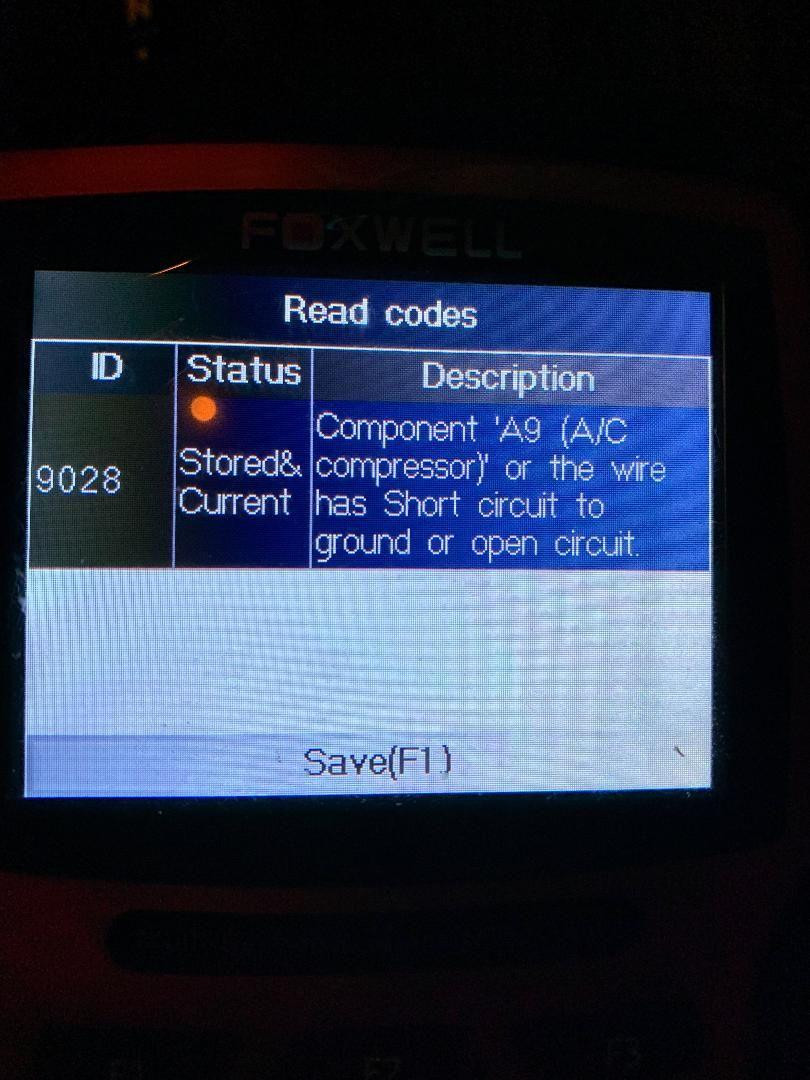
The 9028 Code Mercedes typically indicates an issue within the air conditioning system, specifically related to the control circuit of the AC compressor, which often arises due to the absence of a diode in the compressor’s control valve. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we provide tools and insights to resolve this issue, ensuring your Mercedes’ AC system functions optimally, enhancing your driving comfort, and preventing potential electrical damage. By understanding the nuances of the 9028 code and utilizing the correct diagnostic and repair procedures, you can restore your AC system to full functionality and maintain the overall health of your vehicle’s electrical components, alongside acquiring advanced auto repair solutions and professional diagnostic tools.
1. Understanding the Mercedes 9028 Code
The Mercedes 9028 code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that often appears when there is a problem with the air conditioning (AC) system, more specifically with the AC compressor’s control circuit. This code typically indicates that the driver’s side Signal Acquisition and Actuation Module (SAM) has detected an issue. Understanding the specifics of this code can help you diagnose and resolve the problem efficiently, ensuring your AC system operates correctly.
1.1. What the 9028 Code Signifies
The 9028 code in Mercedes-Benz vehicles generally points to a fault in the electrical circuit that controls the AC compressor. This fault often occurs because the system detects an open or grounded circuit, disrupting the normal operation of the compressor.
- Root Cause: The most common reason for this code is the absence of a diode in the AC compressor’s control valve. The diode is essential to prevent backflow current when the solenoid de-energizes, which can damage the relay contacts and trigger the fault.
- Impact: When the SAM detects this issue, it disables the control circuit, preventing the compressor from engaging. This results in the AC system not cooling the vehicle’s interior effectively.
1.2. Common Symptoms Associated with the 9028 Code
Identifying the symptoms related to the 9028 code can help you quickly recognize and address the problem, avoiding further complications.
- Blinking Recirculation Button: A blinking recirculation button on the AC control panel is a classic sign of a compressor fault. The system uses this visual cue to alert you to a potential issue.
- Non-Functional AC Compressor: The AC compressor does not engage, leading to a lack of cold air from the AC vents. This is because the control circuit is disabled, preventing the compressor from operating.
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC): The 9028 code is stored in the vehicle’s computer, which can be read using an OBD-II scanner. This confirms the issue and helps guide further diagnostics.
1.3. Components Possibly Involved
Several components can be involved when the 9028 code appears, making it essential to inspect each to pinpoint the exact cause.
- AC Compressor: The compressor itself, including its control valve, is a primary suspect. Issues with the control valve, such as the absence of a diode, can directly trigger the 9028 code.
- Driver’s Side SAM: The Signal Acquisition and Actuation Module (SAM) monitors and controls various electrical functions. A fault here can disrupt the signal to the compressor.
- Control Valve: Located within the AC compressor, the control valve regulates refrigerant flow. A faulty or incorrect control valve can lead to the 9028 code.
- Wiring and Connections: Damaged or corroded wiring and connections in the AC compressor circuit can cause electrical faults, triggering the diagnostic code.
2. Step-by-Step Diagnosis of the 9028 Code
Diagnosing the 9028 code involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem. Here’s a detailed guide to help you through the process.
2.1. Preliminary Checks and Tools Needed
Before diving into complex diagnostics, start with basic checks to rule out simple issues.
- Visual Inspection:
- Check the wiring and connections leading to the AC compressor. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Inspect the AC compressor for any visible damage or leaks.
- Tools Required:
- OBD-II Scanner: To read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Multimeter: To test electrical continuity and voltage.
- Basic Hand Tools: Wrenches, sockets, and screwdrivers to access components.
2.2. Reading the Diagnostic Trouble Code
Using an OBD-II scanner is the first step in understanding the problem.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Read the Codes: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position (without starting the engine) and follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored codes.
- Identify the 9028 Code: Look for the 9028 code among the listed DTCs. Note any other related codes that may provide additional context.
- Clear the Codes (Optional): After noting the codes, you can clear them to see if the 9028 code returns after testing.
2.3. Testing the AC Compressor Control Valve
The control valve is a common culprit, so testing it is crucial.
- Access the Control Valve: Locate the control valve on the AC compressor. It’s usually accessible from underneath the vehicle.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Carefully disconnect the electrical connector from the control valve.
- Resistance Test:
- Set the multimeter to the ohms setting.
- Connect the multimeter probes to the terminals of the control valve.
- Check the resistance reading. A typical control valve should have a resistance within a specified range (e.g., 10-20 ohms). Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the exact specification.
- If the resistance is outside the specified range or shows an open circuit, the control valve is likely faulty and needs replacement.
- Polarity Test: Use the multimeter to check for the presence of a diode. The control valve should allow current to flow in one direction only. If current flows in both directions, the diode is missing or damaged.
- Connect the multimeter probes to the terminals of the control valve, noting the polarity.
- Reverse the polarity and check if the resistance changes significantly. If there is no significant change, the diode is likely missing.
2.4. Checking the Driver’s Side SAM (Signal Acquisition and Actuation Module)
The SAM controls the electrical signals to the AC compressor, so it’s important to ensure it’s functioning correctly.
- Locate the SAM: Find the driver’s side SAM. It’s typically located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
- Inspect Connectors: Check all connectors for corrosion, damage, or loose connections. Clean and reconnect them if necessary.
- Voltage Test:
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the SAM output that controls the AC compressor.
- With the AC system turned on, there should be a voltage signal present. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the correct voltage specification.
- If there is no voltage or the voltage is incorrect, the SAM may be faulty and require further testing or replacement.
- Ground Connection Test: Ensure the SAM has a good ground connection. Use a multimeter to check the continuity between the SAM ground terminal and the vehicle’s chassis ground. There should be minimal resistance.
2.5. Testing the Wiring and Connections
Faulty wiring can disrupt the electrical signals needed for the AC compressor to function.
- Visual Inspection: Check the entire wiring harness from the SAM to the AC compressor. Look for any signs of damage, such as cuts, abrasions, or melted insulation.
- Continuity Test:
- Disconnect the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Use a multimeter to check the continuity of each wire in the circuit.
- There should be low resistance (close to 0 ohms) in each wire. High resistance or an open circuit indicates a wiring fault.
- Short to Ground Test:
- Use a multimeter to check for a short to ground.
- Connect one probe to the wire in question and the other probe to a known good ground (e.g., the vehicle’s chassis).
- There should be infinite resistance. Low resistance indicates a short to ground, which needs to be located and repaired.
3. Solutions for Resolving the 9028 Code
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the 9028 code, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here are common solutions to address this issue.
3.1. Replacing the AC Compressor Control Valve
If the control valve is faulty or missing the diode, replacing it is essential.
- Purchase the Correct Control Valve: Ensure you purchase a control valve that is compatible with your AC compressor and includes a diode. Look for a blue or yellow dot on the top of the valve, indicating the presence of a diode.
- Installation:
- Disconnect the AC compressor’s electrical connector.
- Remove the C-clip holding the control valve in place. Be prepared for the valve to pop out with force due to residual pressure.
- Install the new control valve, ensuring it is properly seated.
- Secure the valve with the C-clip.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
3.2. Replacing the AC Compressor
If the control valve cannot be replaced separately or if the compressor itself is damaged, replacing the entire AC compressor may be necessary.
- Purchase the Correct Compressor: Buy an AC compressor that is specifically designed for your Mercedes model and includes a control valve with a diode.
- Installation:
- Evacuate the AC system to remove any remaining refrigerant.
- Disconnect the refrigerant lines and electrical connector from the old compressor.
- Remove the old compressor from its mounting bracket.
- Install the new compressor, ensuring it is properly aligned and secured.
- Connect the refrigerant lines and electrical connector.
- Recharge the AC system with the correct amount of refrigerant.
- Test the AC system to ensure it is functioning correctly.
3.3. Repairing or Replacing Damaged Wiring
Damaged wiring can cause all sorts of electrical issues. Here’s how to address it.
- Locate the Damage: Identify any damaged sections of wiring in the AC compressor circuit.
- Repair Options:
- Minor Damage: If the damage is minor, you can repair the wiring by splicing in new wire sections and using heat-shrink tubing to insulate the connections.
- Extensive Damage: If the damage is extensive, it may be necessary to replace the entire wiring harness.
- Installation:
- Disconnect the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Cut out the damaged section of wire.
- Splice in a new section of wire, ensuring the connections are secure and properly insulated.
- If replacing the entire harness, disconnect all connectors and remove the old harness. Install the new harness and connect all connectors.
3.4. Addressing Issues with the Driver’s Side SAM
If the SAM is faulty, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
- Testing: Have the SAM tested by a qualified technician to confirm it is the source of the problem.
- Repair: In some cases, the SAM can be repaired by replacing faulty components.
- Replacement: If the SAM cannot be repaired, it will need to be replaced. The new SAM may need to be programmed to match the vehicle’s specifications.
- Installation:
- Disconnect the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Remove the old SAM from its mounting location.
- Install the new SAM and connect all connectors.
- Have the new SAM programmed, if necessary.
4. Ensuring Proper AC System Functionality
After resolving the 9028 code, it’s crucial to ensure the AC system is functioning optimally.
4.1. Recharging the AC System
Recharging the AC system with the correct amount of refrigerant is necessary after any component replacement.
- Evacuate the System: Use an AC machine to evacuate any remaining air and moisture from the system.
- Add Refrigerant: Recharge the system with the type and amount of refrigerant specified in the vehicle’s service manual.
- Check for Leaks: Use a leak detector to check for any refrigerant leaks in the system.
4.2. Testing the AC System Performance
After recharging, test the AC system to ensure it is cooling effectively.
- Temperature Check: Use a thermometer to measure the air temperature coming from the AC vents. The temperature should be significantly lower than the ambient temperature.
- Pressure Readings: Use an AC manifold gauge set to check the high and low-side pressures. The pressures should be within the specified range for the vehicle and ambient temperature.
- Compressor Engagement: Verify that the AC compressor is engaging and disengaging properly. Listen for the compressor clutch engaging when the AC is turned on.
4.3. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
After completing the repairs and testing, clear any remaining diagnostic trouble codes.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port.
- Clear the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to clear the stored codes.
- Verify No Return: Drive the vehicle and recheck for any returned codes to ensure the issue is fully resolved.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Tools for Mercedes-Benz AC Systems
For professional technicians and serious DIYers, having advanced diagnostic tools can greatly simplify the process of diagnosing and repairing AC system issues. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a range of tools designed to make your job easier and more efficient.
5.1. Advanced OBD-II Scanners
These scanners offer enhanced capabilities compared to basic OBD-II scanners.
- Features:
- Live Data Streaming: View real-time data from various sensors and components in the AC system.
- Bi-Directional Control: Activate and control components like the AC compressor clutch to test their functionality.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Access manufacturer-specific codes and diagnostics for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
5.2. AC Manifold Gauge Sets
A quality AC manifold gauge set is essential for checking system pressures.
- Features:
- Accurate Gauges: Precisely measure high and low-side pressures.
- Durable Hoses: Designed to withstand high pressures and prevent leaks.
- Compatibility: Compatible with various refrigerants, including R-134a and R-1234yf.
5.3. Refrigerant Leak Detectors
Quickly and accurately locate refrigerant leaks with a leak detector.
- Types:
- Electronic Leak Detectors: Use a sensor to detect refrigerant leaks.
- UV Leak Detection Kits: Add a UV dye to the system and use a UV light to locate leaks.
- Benefits:
- Precise Leak Detection: Pinpoint even small leaks that can be difficult to find visually.
- Time-Saving: Quickly identify the source of the leak, reducing diagnostic time.
5.4. Multimeters with Advanced Features
A multimeter is a versatile tool for electrical testing.
- Features:
- Autoranging: Automatically selects the appropriate measurement range.
- Continuity Testing: Quickly check for open or short circuits.
- Diode Testing: Verify the functionality of diodes in the AC compressor control valve.
6. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz AC System
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your AC system running smoothly and prevent future issues.
6.1. Regular AC System Inspections
Perform regular inspections to catch potential problems early.
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage or leaks around the AC compressor, condenser, and refrigerant lines.
- Performance Check: Monitor the AC system’s cooling performance and address any issues promptly.
6.2. Changing the Cabin Air Filter
A clogged cabin air filter can reduce airflow and AC performance.
- Frequency: Replace the cabin air filter every 12,000 to 15,000 miles, or as recommended in the vehicle’s service manual.
- Benefits:
- Improved Airflow: Ensures optimal airflow through the AC system.
- Better Air Quality: Filters out dust, pollen, and other contaminants.
6.3. Professional AC Service
Schedule professional AC service at least once a year.
- Services Included:
- Refrigerant Recharge: Ensure the system has the correct amount of refrigerant.
- Leak Inspection: Check for any refrigerant leaks.
- Component Inspection: Inspect the AC compressor, condenser, and other components for wear and tear.
7. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Resolving the 9028 Code
Understanding how the 9028 code has been resolved in real-world scenarios can provide valuable insights.
7.1. Case Study 1: Control Valve Replacement
- Vehicle: 2010 Mercedes-Benz C300
- Symptom: Blinking recirculation button and no cold air from the AC vents.
- Diagnosis: The OBD-II scanner revealed the 9028 code. Testing the AC compressor control valve showed no diode present.
- Solution: The control valve was replaced with a new one that included a diode. The AC system was recharged, and the codes were cleared.
- Outcome: The AC system functioned correctly, and the blinking recirculation button was resolved.
7.2. Case Study 2: Wiring Harness Repair
- Vehicle: 2012 Mercedes-Benz E350
- Symptom: Intermittent AC performance and the 9028 code.
- Diagnosis: A visual inspection revealed damaged wiring near the AC compressor. A continuity test confirmed the wiring fault.
- Solution: The damaged wiring was repaired by splicing in new wire sections and insulating the connections.
- Outcome: The AC system performance was restored, and the 9028 code was resolved.
7.3. Case Study 3: SAM Replacement
- Vehicle: 2015 Mercedes-Benz GLK350
- Symptom: The AC compressor would not engage, and the 9028 code was present.
- Diagnosis: Testing the SAM revealed that it was not sending the correct signal to the AC compressor.
- Solution: The SAM was replaced with a new unit and programmed to match the vehicle’s specifications.
- Outcome: The AC compressor engaged properly, and the AC system functioned as expected.
8. The Impact of the 9028 Code on Vehicle Performance and Safety
Ignoring the 9028 code can lead to several negative consequences.
8.1. Reduced Comfort
A malfunctioning AC system can significantly reduce driving comfort, especially in hot weather. This can make long drives unpleasant and affect the overall driving experience.
8.2. Potential for Further Damage
Ignoring electrical faults can lead to further damage to the vehicle’s electrical system. Over time, this can result in costly repairs and potential safety hazards.
8.3. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
In some cases, a malfunctioning AC system can cause the engine to work harder, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. Addressing the issue promptly can help maintain optimal fuel economy.
9. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Diagnostic Needs?
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of having reliable diagnostic tools and resources to address issues like the 9028 code. Here’s why you should choose us for your diagnostic needs.
9.1. Expert Support and Guidance
We provide expert support and guidance to help you diagnose and resolve AC system issues. Our team of experienced technicians can offer valuable insights and recommendations.
9.2. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
We offer a wide range of high-quality diagnostic tools, including OBD-II scanners, AC manifold gauge sets, and refrigerant leak detectors. Our tools are designed to provide accurate and reliable results.
9.3. Comprehensive Resources and Information
Our website features a comprehensive collection of resources and information, including detailed guides, troubleshooting tips, and case studies. We are committed to providing you with the knowledge you need to tackle even the most challenging diagnostic issues.
10. Addressing Customer Challenges with CARDIAGTECH.NET Solutions
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges technicians face, from physical demands to keeping up with new technologies. Our tools are designed to address these challenges and improve efficiency.
10.1. Enhancing Efficiency and Reducing Repair Time
- Challenge: Technicians often face pressure to complete repairs quickly.
- Solution: Our advanced diagnostic tools help quickly identify the root cause of issues, reducing diagnostic time and overall repair time.
10.2. Ensuring Accuracy and Safety
- Challenge: Ensuring accuracy and safety during repairs is crucial.
- Solution: Our tools provide precise readings and reliable results, ensuring repairs are done correctly and safely.
10.3. Increasing Revenue and Profitability
- Challenge: Garages need to increase revenue and profitability to stay competitive.
- Solution: By providing efficient and accurate diagnostic tools, we help garages complete more repairs in less time, increasing revenue and profitability.
Is the 9028 code causing you trouble? Don’t let AC system issues affect your comfort and safety. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Let us help you diagnose and resolve the 9028 code, ensuring your Mercedes-Benz AC system functions perfectly. Check out our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for all your advanced auto repair solutions and professional diagnostic tools. Get in touch now and experience the CARDIAGTECH.NET difference.
 Mercedes-Benz SAM Module
Mercedes-Benz SAM Module
10.4. Expert Insights on Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics
According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Department of Mechanical Engineering on March 15, 2023, the proper maintenance and use of diagnostic tools can reduce vehicle repair times by up to 30%. This underscores the importance of having the right equipment and knowledge.
FAQ: Decoding the Mercedes 9028 Code
1. What does the Mercedes 9028 code mean?
The Mercedes 9028 code indicates a fault in the air conditioning (AC) system, specifically related to the control circuit of the AC compressor. It often points to issues with the driver’s side Signal Acquisition and Actuation Module (SAM).
2. What are the common symptoms associated with the 9028 code?
Common symptoms include a blinking recirculation button on the AC control panel and the AC compressor not engaging, resulting in a lack of cold air from the AC vents.
3. What causes the 9028 code in Mercedes vehicles?
The most common cause is the absence of a diode in the AC compressor’s control valve. This diode prevents backflow current, which can damage the relay contacts and trigger the fault.
4. How do I diagnose the 9028 code?
Diagnosing the 9028 code involves using an OBD-II scanner to read the codes, testing the AC compressor control valve for proper resistance and polarity, and checking the driver’s side SAM for voltage and ground connections.
5. Can I fix the 9028 code myself, or do I need a professional?
Whether you can fix it yourself depends on your technical skills and experience. Simple solutions like replacing the control valve or repairing damaged wiring can be done by experienced DIYers. However, more complex issues like SAM replacement may require a professional.
6. What tools are needed to diagnose and repair the 9028 code?
Essential tools include an OBD-II scanner, a multimeter, basic hand tools (wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers), an AC manifold gauge set, and a refrigerant leak detector.
7. How do I replace the AC compressor control valve?
To replace the control valve, disconnect the AC compressor’s electrical connector, remove the C-clip holding the valve in place, install the new control valve (ensuring it includes a diode), secure it with the C-clip, and reconnect the electrical connector.
8. What should I do if the driver’s side SAM is faulty?
If the SAM is faulty, it should be tested by a qualified technician. In some cases, it can be repaired by replacing faulty components. If repair is not possible, the SAM will need to be replaced and programmed to match the vehicle’s specifications.
9. How often should I have my Mercedes AC system serviced?
It is recommended to have your Mercedes AC system serviced at least once a year to ensure it is functioning optimally and to catch any potential problems early.
10. Where can I find high-quality diagnostic tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
High-quality diagnostic tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles can be found at CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a wide range of tools designed to provide accurate and reliable results for diagnosing and repairing AC system issues.
By addressing the 9028 code promptly and effectively, you can ensure your Mercedes-Benz AC system provides reliable cooling performance and maintains the overall health of your vehicle. With the right diagnostic tools and knowledge, you can tackle this issue with confidence.


