**How to Fix a Handbrake on a Car: A Comprehensive Guide**

Fixing a car handbrake involves diagnosing the issue, adjusting cables, or replacing worn parts. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers the tools and expertise to ensure your handbrake functions flawlessly, enhancing vehicle safety and control. This article provides a detailed guide to resolving handbrake problems, focusing on practical solutions and professional insights.
1. What is the Purpose of a Handbrake and How Does It Work?
The handbrake, also known as the emergency brake or parking brake, serves primarily as a safety mechanism to keep a vehicle stationary when parked, especially on inclines. It also functions as a backup braking system in case of hydraulic brake failure. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), a properly functioning handbrake can significantly reduce the risk of rollaway accidents (NHTSA, 2021).
- Mechanical Operation: The handbrake typically works through a cable system that mechanically applies the brakes, bypassing the hydraulic system.
- Types of Handbrakes: These include lever-operated, button-activated, and foot-pedal systems, each applying the brakes differently.
- Essential Safety Feature: Ensures the vehicle remains stationary when parked and provides an alternative braking method in emergencies.
2. What are the Common Symptoms of a Faulty Handbrake System?
Recognizing the symptoms of a faulty handbrake system early can prevent more significant issues. Common indicators include:
- Loose Handbrake Lever: The lever pulls up too high without engaging the brakes effectively.
- Weak Holding Power: The car moves or rolls when the handbrake is applied, especially on hills.
- Unusual Noises: Squealing, grinding, or clicking sounds when the handbrake is used.
- Difficulty Releasing: The handbrake is hard to release or doesn’t fully disengage.
- Dashboard Warning Light: The handbrake warning light remains on even when the handbrake is disengaged.
3. What Tools and Materials Do You Need to Fix a Handbrake?
Having the right tools and materials is crucial for effectively fixing a handbrake. Here’s a comprehensive list:
| Tool/Material | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Wrench Set | Metric or SAE wrenches to adjust and tighten nuts and bolts. | Adjusting cable tension and securing components. |
| Socket Set | Various sizes of sockets to fit different fasteners. | Removing and installing brake components. |
| Screwdrivers | Both flathead and Phillips head screwdrivers for removing screws and adjusting mechanisms. | Accessing and adjusting internal components. |
| Pliers | Standard and needle-nose pliers for gripping, bending, and cutting. | Manipulating cables and small parts. |
| Jack and Jack Stands | To safely lift and support the vehicle. | Accessing the handbrake system underneath the car. |
| Wheel Chocks | To prevent the vehicle from rolling. | Ensuring safety while working. |
| Penetrating Oil | To loosen rusted or seized nuts and bolts. | Facilitating the removal of stubborn parts. |
| Brake Cleaner | To clean brake components and remove dirt and grease. | Maintaining brake efficiency and preventing contamination. |
| Handbrake Cable | Replacement cable if the existing one is stretched or damaged. | Restoring proper handbrake function. |
| Gloves | To protect hands from dirt and chemicals. | Ensuring personal safety. |
| Safety Glasses | To protect eyes from debris. | Ensuring personal safety. |
| Torque Wrench | To tighten nuts and bolts to the manufacturer’s specified torque. | Preventing over-tightening or loosening of components. |
| Multimeter | To check electrical connections and diagnose issues with electronic parking brakes. | Diagnosing electrical problems in modern handbrake systems. |
| Brake Adjustment Tool | Specifically designed for adjusting drum brakes. | Ensuring proper brake shoe adjustment. |
| Service Manual | Vehicle-specific manual for detailed instructions and torque specifications. | Providing accurate guidance for the repair process. |
| Replacement Brake Pads/Shoes | To replace worn-out brake pads or shoes. | Restoring proper braking performance. |
4. How to Inspect the Handbrake System for Damage?
A thorough inspection is the first step in fixing a handbrake. Follow these steps:
- Cable Inspection: Check the entire length of the handbrake cable for signs of stretching, fraying, or corrosion. According to a study by the Vehicle Safety Research Centre at Loughborough University, cable degradation is a common cause of handbrake failure (VSRC, 2019).
- Lever Mechanism: Examine the handbrake lever for smooth operation. Look for any binding or excessive play.
- Brake Components: Inspect the brake pads or shoes for wear and damage. Check the brake discs or drums for scoring or rust.
- Connectors and Linkages: Ensure all connectors, linkages, and springs are intact and functioning correctly.
- Equalizer: If your system has an equalizer, check it for damage and proper movement.
 Handbrake cable inspection showing signs of wear
Handbrake cable inspection showing signs of wear
5. How to Adjust a Handbrake Cable on a Car?
Adjusting the handbrake cable is a common fix for a loose or ineffective handbrake. Here’s how to do it:
- Locate the Adjuster: Find the handbrake cable adjuster, usually located under the car near the center or inside the cabin near the handbrake lever.
- Loosen the Lock Nut: Use a wrench to loosen the lock nut on the adjuster.
- Tighten the Adjuster Nut: Turn the adjuster nut to tighten the cable, increasing tension. A general guideline is to adjust until the handbrake engages fully within 3-5 clicks of the lever.
- Test the Handbrake: Apply and release the handbrake several times, checking that it holds the car securely on an incline and releases fully without dragging.
- Secure the Lock Nut: Once the adjustment is correct, tighten the lock nut to secure the adjuster in place.
6. What are the Different Types of Handbrake Adjusters?
Different vehicles use various types of handbrake adjusters. Here are a few common types:
- Threaded Rod Adjuster: Features a threaded rod with nuts to adjust cable tension.
- Screwed Sleeve Adjuster: Uses a screwed sleeve to lengthen or shorten the cable.
- Bowden Cable Adjuster: Found on enclosed Bowden cables, this adjuster is typically located on a bracket.
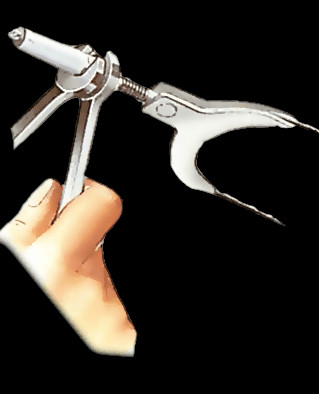 Screwed sleeve adjuster for handbrake cable
Screwed sleeve adjuster for handbrake cable
7. How to Adjust a Twin-Cable Handbrake System?
Some vehicles use a twin-cable system, requiring a slightly different adjustment procedure:
- Access the Adjusters: Remove the rubber cover or carpeting to access the adjusters, usually located at the base of the handbrake lever.
- Loosen the Locknuts: Hold the adjuster nut with a spanner and loosen the locknut a few turns.
- Adjust Each Cable: Use pliers to hold the lower end of one rod and turn the lower nut clockwise to draw the rod forward. Adjust until the handbrake lever pulls up only three to five clicks. Repeat for the other cable.
- Balance the Tension: Ensure both rear wheels have equal resistance when the handbrake is applied. Adjust the cables until they are balanced.
- Secure the Adjusters: Tighten the locknuts to secure the adjusters.
8. What is the Procedure for Adjusting Primary and Secondary Handbrake Cables?
Some handbrake systems have primary and secondary cables, each requiring specific attention:
- Identify Cables: Locate the primary cable running from the handbrake lever to the relay lever and the secondary cable going from the relay lever to the brakes.
- Set Handbrake Position: Set the handbrake lever one or two clicks on.
- Tighten Slack Cables: Free any locknuts, then tighten the cable with the most slack until it is taut. Repeat with the second cable.
- Secure Locknuts: Tighten the locknuts to secure the adjustments.
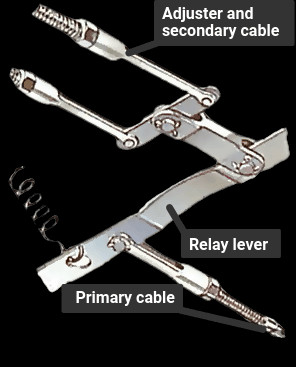 Adjusting primary and secondary handbrake cables
Adjusting primary and secondary handbrake cables
9. How to Handle an Equalizing Cable System?
Equalizing cable systems require a different approach to ensure balanced braking:
- Release the Fork: Pull out the split pin and remove the clevis pin to release the fork.
- Set Handbrake Position: Pull the handbrake lever until it engages on the second notch.
- Adjust the Nut: Loosen the locknut and screw back the adjuster nut until the clevis-pin holes in the fork align with the hole in the lever on the backplate.
- Secure the Components: Tighten the locknut and refit the clevis pin with a new split pin.
 Releasing the fork on an equalizing cable system
Releasing the fork on an equalizing cable system
10. How to Adjust a Disc-Pad Handbrake?
For vehicles with disc brakes, the handbrake operates on the rear discs, requiring specific adjustment steps:
- Loosen the Locknut: With a large, open-ended spanner, loosen and unscrew the large, thin locknut on the back of the brake caliper a few turns.
- Tighten the Adjustment Nut: With a smaller open-ended spanner, turn the adjustment nut clockwise until it becomes stiff.
- Check Wheel Movement: The heel of the cast-metal lever arm should press against the back of one pad, and the wheel should be hard to turn by hand.
- Secure the Adjuster: Hold the adjuster nut steady while tightening the locknut.
 Adjusting a disc-pad handbrake system
Adjusting a disc-pad handbrake system
11. How Do Electronic Parking Brakes (EPB) Work and How to Troubleshoot Them?
Electronic Parking Brakes (EPB) are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles. They use an electronic control unit (ECU) and actuators to apply and release the parking brake.
- Working Mechanism: EPBs use electronic signals to engage the brake calipers, providing precise and consistent braking force.
- Troubleshooting: Common issues include sensor failures, actuator malfunctions, and ECU problems. Diagnostic tools are necessary to read error codes and identify the specific problem.
- Resetting EPB: After replacing brake pads or other components, the EPB system often needs to be reset using a diagnostic tool to ensure proper calibration.
12. What are the Safety Precautions to Take When Working on a Handbrake?
Safety should always be a priority when working on a handbrake system:
- Secure the Vehicle: Always use jack stands to support the vehicle after lifting it with a jack. Never work under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
- Chock the Wheels: Use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear safety glasses and gloves to protect your eyes and hands.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical accidents, especially when working on EPB systems.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Use brake cleaner and penetrating oil in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
13. How Often Should You Check and Maintain Your Handbrake System?
Regular maintenance can prevent handbrake issues and ensure optimal performance:
- Regular Inspections: Check the handbrake system at least twice a year or during routine maintenance checks.
- Cable Lubrication: Lubricate the handbrake cable and linkages to prevent corrosion and ensure smooth operation.
- Brake Component Checks: Inspect brake pads, shoes, and rotors regularly for wear and damage.
- Professional Service: Have the handbrake system professionally inspected and adjusted every 2-3 years, or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
14. What are the Consequences of Neglecting Handbrake Maintenance?
Neglecting handbrake maintenance can lead to serious consequences:
- Rollaway Accidents: A faulty handbrake can fail to hold the vehicle, leading to rollaway accidents, especially on inclines.
- Brake Failure: A poorly maintained handbrake can compromise the overall braking system, increasing the risk of brake failure.
- Increased Wear and Tear: Neglecting the handbrake can cause increased wear and tear on other braking components, leading to costly repairs.
- Safety Risks: A malfunctioning handbrake poses significant safety risks to the driver, passengers, and other road users.
15. How to Diagnose a Handbrake that Won’t Engage?
If your handbrake won’t engage, follow these diagnostic steps:
- Check Cable Tension: Ensure the handbrake cable is properly tensioned and not stretched or broken.
- Inspect Linkages: Check all linkages and connectors for damage or disconnection.
- Examine Brake Components: Inspect the brake pads or shoes for excessive wear.
- Test Lever Mechanism: Ensure the handbrake lever mechanism is functioning correctly.
- Check EPB System: For vehicles with EPB, use a diagnostic tool to check for error codes and system malfunctions.
16. How to Diagnose a Handbrake that Won’t Release?
A handbrake that won’t release can be equally problematic. Here’s how to diagnose the issue:
- Check Cable Binding: Ensure the handbrake cable is not binding or corroded, preventing it from releasing properly.
- Inspect Springs: Check the return springs on the brake calipers or drums to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Examine Lever Mechanism: Ensure the handbrake lever mechanism is releasing fully.
- Check EPB System: For vehicles with EPB, use a diagnostic tool to check for error codes and system malfunctions.
- Manually Release: Attempt to manually release the handbrake mechanism at the brake calipers or drums.
17. Can a Stretched Handbrake Cable be Repaired or Does it Need to be Replaced?
A stretched handbrake cable is a common issue. Whether it can be repaired or needs replacement depends on the extent of the damage:
- Minor Stretching: Minor stretching can often be compensated for by adjusting the cable tension.
- Significant Stretching or Fraying: If the cable is significantly stretched, frayed, or corroded, it should be replaced to ensure reliable handbrake performance.
- Safety Recommendation: Replacing a damaged handbrake cable is generally recommended for safety reasons.
18. What are the Signs that Brake Pads or Shoes Need to be Replaced in Relation to the Handbrake?
Worn brake pads or shoes can affect the handbrake’s performance. Here are the signs to look for:
- Reduced Handbrake Effectiveness: The handbrake requires more clicks to engage fully or doesn’t hold the vehicle securely.
- Grinding or Squealing Noises: These noises indicate that the brake pads or shoes are worn down to the metal.
- Visible Wear: Inspect the brake pads or shoes for visible wear, such as reduced thickness or damage.
- Dashboard Warning Light: Some vehicles have a warning light that indicates when the brake pads or shoes are worn.
19. How Does Rust and Corrosion Affect the Handbrake System and How to Prevent It?
Rust and corrosion can significantly impact the handbrake system:
- Cable Seizing: Rust can cause the handbrake cable to seize, preventing it from moving freely.
- Linkage Damage: Corrosion can damage linkages and connectors, leading to handbrake failure.
- Reduced Effectiveness: Rust on brake components can reduce the handbrake’s effectiveness.
Prevention Methods:
- Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean the handbrake system to remove dirt, salt, and other contaminants.
- Lubrication: Lubricate the handbrake cable and linkages to prevent corrosion.
- Protective Coatings: Apply protective coatings to brake components to prevent rust.
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect the handbrake system for signs of rust and corrosion.
20. What Role Does the Handbrake Play in Vehicle Safety Inspections?
The handbrake is a critical component in vehicle safety inspections. Inspectors typically check:
- Handbrake Effectiveness: The handbrake must hold the vehicle securely on an incline.
- Lever Travel: The handbrake lever should engage fully within the specified number of clicks.
- Cable Condition: The handbrake cable must be in good condition, without stretching, fraying, or corrosion.
- Release Mechanism: The handbrake must release fully without dragging.
21. How to Choose the Right Replacement Handbrake Cable?
Choosing the right replacement handbrake cable is essential for proper handbrake function:
- Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure the replacement cable is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- OEM vs. Aftermarket: Consider whether to use an Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) cable or an aftermarket cable. OEM cables are generally more reliable but can be more expensive.
- Material Quality: Look for cables made from high-quality materials that are resistant to stretching, fraying, and corrosion.
- Proper Length: Ensure the replacement cable is the correct length for your vehicle.
22. What is the Difference Between a Drum Brake Handbrake and a Disc Brake Handbrake?
The primary difference lies in how the braking force is applied:
- Drum Brake Handbrake: Uses brake shoes that press against the inside of a drum to create friction and stop the vehicle.
- Disc Brake Handbrake: Uses brake pads that clamp against a rotor to create friction and stop the vehicle. Some disc brake systems use a separate, smaller drum brake system specifically for the handbrake.
 Drum brakes and disc brakes
Drum brakes and disc brakes
23. How to Properly Break-In New Brake Pads or Shoes After Handbrake Repairs?
Properly breaking in new brake pads or shoes is crucial for optimal performance and longevity:
- Initial Bedding: After installing new brake pads or shoes, perform several moderate stops from low speeds to bed the pads or shoes against the rotors or drums.
- Avoid Hard Stops: Avoid hard stops during the first 200 miles to prevent overheating and glazing of the brake pads or shoes.
- Gradual Increase: Gradually increase the intensity of braking over the first few hundred miles.
- Listen for Noises: Pay attention to any unusual noises, such as squealing or grinding, which may indicate a problem.
24. What are the Best Practices for Parking on Hills Using the Handbrake?
Parking on hills requires extra caution. Follow these best practices:
- Engage the Handbrake: Always engage the handbrake fully when parking on a hill.
- Turn the Wheels: Turn the wheels towards the curb when parking downhill and away from the curb when parking uphill.
- Use the Gear: If parking uphill, put the car in first gear (for manual transmissions) or park (for automatic transmissions). If parking downhill, put the car in reverse (for manual transmissions) or park (for automatic transmissions).
- Chock the Wheels: For added safety, especially on steep hills, use wheel chocks.
25. How Does Cold Weather Affect the Handbrake System and What Can Be Done to Mitigate These Effects?
Cold weather can have several adverse effects on the handbrake system:
- Cable Freezing: Moisture can freeze inside the handbrake cable, preventing it from moving freely.
- Rust and Corrosion: Cold weather and road salt can accelerate rust and corrosion.
- Reduced Effectiveness: Cold temperatures can reduce the effectiveness of brake pads and shoes.
Mitigation Measures:
- Regular Lubrication: Regularly lubricate the handbrake cable to prevent freezing.
- Protective Coatings: Apply protective coatings to brake components to prevent rust.
- Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean the handbrake system to remove salt and contaminants.
- Avoid Prolonged Engagement: Avoid engaging the handbrake for extended periods in freezing conditions to prevent the brake pads or shoes from sticking to the rotors or drums.
26. What are the Key Differences Between Adjusting a Manual Handbrake and an Electronic Parking Brake?
Adjusting a manual handbrake involves mechanical adjustments to the cable and linkages. In contrast, adjusting an Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) requires electronic diagnostic tools to reset and calibrate the system. EPB adjustments often involve recalibrating the actuators and sensors to ensure proper braking force and release.
27. How Can You Test the Effectiveness of Your Handbrake After Making Adjustments?
After making adjustments, testing the handbrake’s effectiveness is crucial:
- Incline Test: Park the vehicle on a moderate incline and engage the handbrake. Ensure the vehicle does not roll.
- Lever Travel Check: Check that the handbrake lever engages fully within the specified number of clicks (usually 3-5 clicks).
- Release Check: Ensure the handbrake releases fully without dragging.
- Driving Test: Drive the vehicle at a low speed and gently apply the handbrake to ensure it engages smoothly and evenly.
28. What Types of Lubricants are Best for Maintaining the Handbrake Cable and Linkages?
Using the right lubricants can significantly extend the life of the handbrake system:
- Cable Lubricants: Use a cable lubricant specifically designed for brake cables. These lubricants are typically Teflon-based and resist moisture and corrosion.
- Grease: Use a high-quality lithium grease for lubricating linkages and connectors.
- Penetrating Oil: Use penetrating oil to loosen rusted or seized parts before lubricating.
29. How Does the Condition of the Rear Brake Calipers or Wheel Cylinders Affect Handbrake Performance?
The condition of the rear brake calipers or wheel cylinders directly affects handbrake performance:
- Seized Calipers/Cylinders: If the calipers or cylinders are seized, they may prevent the handbrake from engaging or releasing properly.
- Leaking Calipers/Cylinders: Leaks can reduce the braking force applied by the handbrake.
- Proper Function: Ensuring the calipers or cylinders are in good working order is essential for optimal handbrake performance.
30. What Are Some Advanced Techniques for Diagnosing Intermittent Handbrake Problems?
Intermittent handbrake problems can be challenging to diagnose. Here are some advanced techniques:
- Data Logging: Use a diagnostic tool to log data from the EPB system while driving to identify any anomalies.
- Visual Inspection: Perform a thorough visual inspection of all components, looking for subtle signs of damage or wear.
- Component Testing: Test individual components, such as sensors and actuators, to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Consult a Specialist: If you are unable to diagnose the problem, consult a qualified mechanic specializing in brake systems.
31. Where Can You Find Reliable Parts and Tools for Handbrake Repair?
Finding reliable parts and tools is essential for a successful handbrake repair. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality tools and parts to meet your needs.
- Online Retailers: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a comprehensive selection of automotive tools and parts.
- Local Auto Parts Stores: Support local businesses and get immediate access to parts.
- Specialty Tool Suppliers: Suppliers specializing in automotive tools often carry high-quality, specialized equipment.
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to providing top-notch tools and equipment, ensuring your handbrake repairs are done efficiently and effectively.
32. What are the Best Practices for Safely Disposing of Old Handbrake Components?
Proper disposal of old handbrake components is essential for environmental safety:
- Brake Pads/Shoes: Dispose of used brake pads and shoes according to local regulations. Many auto parts stores offer recycling programs.
- Brake Fluid: Dispose of used brake fluid at a designated recycling center.
- Cables and Metal Parts: Recycle metal parts at a local recycling facility.
33. How to Upgrade Your Handbrake System for Improved Performance?
Upgrading your handbrake system can improve performance, especially for vehicles used in demanding conditions:
- Performance Brake Pads/Shoes: Install performance brake pads or shoes for increased stopping power.
- Stainless Steel Cables: Upgrade to stainless steel handbrake cables for improved durability and resistance to corrosion.
- EPB Upgrades: For vehicles with EPB, consider upgrading the ECU or actuators for improved performance and reliability.
34. What Government Regulations and Standards Apply to Handbrake Systems?
Handbrake systems are subject to various government regulations and standards to ensure safety:
- Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS): These standards set minimum performance requirements for handbrake systems.
- State Vehicle Inspections: Many states require handbrake systems to pass inspection to ensure they meet safety standards.
- Environmental Regulations: Regulations govern the disposal of brake components and fluids to protect the environment.
35. What is the Cost of Hiring a Professional Mechanic to Fix a Handbrake Issue?
The cost of hiring a professional mechanic to fix a handbrake issue can vary:
- Labor Costs: Labor costs typically range from $75 to $150 per hour.
- Parts Costs: Parts costs vary depending on the type of components needed and the vehicle’s make and model.
- Total Cost: The total cost can range from $150 to $500 or more, depending on the complexity of the repair.
By using CARDIAGTECH.NET tools and following this guide, you can save money and ensure the job is done right.
36. How Do Different Driving Conditions Affect the Wear and Tear on the Handbrake System?
Different driving conditions can significantly affect wear and tear:
- City Driving: Frequent use of the handbrake in stop-and-go traffic can increase wear and tear.
- Hilly Terrain: Driving in hilly terrain can put extra strain on the handbrake system.
- Off-Road Driving: Off-road driving can expose the handbrake system to dirt, mud, and other contaminants.
- Coastal Areas: Driving in coastal areas can accelerate rust and corrosion due to exposure to salt air.
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to mitigate these effects.
37. How Does Tire Size and Condition Affect Handbrake Performance?
Tire size and condition can affect handbrake performance:
- Tire Size: Larger tires require more force to hold the vehicle, potentially reducing handbrake effectiveness.
- Tire Condition: Worn tires provide less grip, making it harder for the handbrake to hold the vehicle.
- Proper Inflation: Ensuring tires are properly inflated is crucial for optimal handbrake performance.
38. What are the Environmental Considerations When Maintaining a Handbrake System?
Environmental considerations are important when maintaining a handbrake system:
- Brake Dust: Brake dust contains harmful materials. Use a brake cleaner that minimizes dust dispersion.
- Fluid Disposal: Dispose of brake fluid properly at a recycling center.
- Component Recycling: Recycle old brake components whenever possible.
39. How to Document Your Handbrake Repair Process for Future Reference?
Documenting your repair process can be helpful for future reference:
- Take Photos: Take photos of each step of the repair process.
- Keep Records: Keep records of the parts used, tools used, and adjustments made.
- Write Notes: Write notes about any challenges encountered and how they were resolved.
- Use a Repair Log: Use a repair log or journal to track all maintenance and repairs performed on the vehicle.
40. How to Get Expert Advice and Support for Complex Handbrake Repairs?
For complex handbrake repairs, seeking expert advice and support is invaluable. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides resources and assistance to help you succeed.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums dedicated to automotive repair.
- Professional Mechanics: Consult a qualified mechanic specializing in brake systems.
- CARDIAGTECH.NET Support: Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET for expert advice and support.
By following these detailed steps and utilizing the resources available at CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can effectively fix your car’s handbrake, ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for immediate assistance and expert advice. Let CARDIAGTECH.NET help you get the job done right!
FAQ: Handbrake System
1. What is the main function of a handbrake?
The primary function of a handbrake is to keep a vehicle stationary when parked, especially on inclines, and to serve as a backup braking system.
2. How do I know if my handbrake needs adjustment?
Signs include a loose handbrake lever, weak holding power, unusual noises, and difficulty releasing the handbrake.
3. Can I adjust my handbrake myself, or should I see a mechanic?
Simple adjustments can be done yourself with the right tools and knowledge, but complex issues are best left to a professional mechanic.
4. What tools are needed to adjust a handbrake cable?
Common tools include wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, pliers, a jack, jack stands, and penetrating oil.
5. How often should I check my handbrake?
Check your handbrake at least twice a year or during routine maintenance checks.
6. What causes a handbrake to fail?
Common causes include stretched cables, worn brake pads or shoes, rust, and corrosion.
7. Is it dangerous to drive with a faulty handbrake?
Yes, driving with a faulty handbrake can lead to rollaway accidents and compromise the overall braking system.
8. What is an electronic parking brake (EPB)?
An EPB is an electronic system that uses actuators to apply and release the parking brake.
9. How do I maintain an electronic parking brake?
Maintenance involves regular inspections, using diagnostic tools to check for error codes, and resetting the system after replacing brake components.
10. Where can I buy reliable handbrake repair tools and parts?
You can find reliable tools and parts at CARDIAGTECH.NET, local auto parts stores, and specialty tool suppliers.
This comprehensive guide, enhanced with insights from CARDIAGTECH.NET, aims to provide you with the knowledge and tools necessary to maintain and repair your car’s handbrake system effectively. Remember to prioritize safety and consult with professionals when needed. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for immediate assistance and expert advice.




