Mercedes ESP Failure: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Addressing a Mercedes Esp Failure can be perplexing. This guide from CARDIAGTECH.NET provides clarity, offering comprehensive information on diagnosing and resolving ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz, ensuring optimal vehicle stability and safety with specialized auto repair tools. Unlock peak performance – connect with us today.
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz is a critical safety feature designed to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving conditions. This sophisticated system integrates various sensors and actuators to monitor and adjust vehicle dynamics, ensuring stability and preventing accidents. Understanding its function is the first step in addressing any mercedes esp failure.
1.1 What is Mercedes-Benz ESP?
ESP, or Electronic Stability Program, is an active safety system designed to help drivers maintain control of their vehicle during adverse driving conditions. It works by monitoring the vehicle’s direction and comparing it to the driver’s intended path. If a discrepancy is detected, such as the vehicle beginning to skid, ESP intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power to help steer the vehicle back on course.
According to Mercedes-Benz, ESP can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, particularly in situations involving sudden maneuvers, slippery surfaces, or evasive actions.
1.2 Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several key components that work together to ensure optimal performance. These include:
-
Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing data used to detect wheel slip or lock-up.
-
Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
-
Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis, detecting any deviation from the intended path.
-
Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration, providing information about the forces acting on the vehicle.
-
Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU processes data from all sensors and determines the appropriate corrective actions, such as applying brakes or adjusting engine power.
-
Hydraulic Unit: This unit controls the brake pressure applied to individual wheels, as directed by the ECU.
1.3 How ESP Works to Prevent Skidding
When the ESP system detects a potential loss of control, it takes immediate action to stabilize the vehicle. Here’s how it works:
-
Detection: Sensors continuously monitor wheel speed, steering angle, yaw rate, and lateral acceleration to detect any deviation from the driver’s intended path.
-
Analysis: The ECU analyzes the sensor data to determine if the vehicle is beginning to skid or lose control.
-
Intervention: If a loss of control is detected, the ESP system intervenes by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power. For example, if the vehicle is oversteering (rear end sliding out), the ESP system may apply the brake to the outer front wheel to help steer the vehicle back on course.
-
Correction: By applying precise braking force to individual wheels, the ESP system helps to counteract the skid and maintain vehicle stability.
1.4 Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
A properly functioning ESP system offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Enhanced Safety: ESP helps prevent accidents by maintaining vehicle stability and control during challenging driving conditions.
-
Reduced Risk of Skidding: By selectively applying brakes and adjusting engine power, ESP minimizes the risk of skidding, particularly on slippery surfaces.
-
Improved Handling: ESP enhances vehicle handling by ensuring that the vehicle responds predictably to the driver’s inputs.
-
Increased Driver Confidence: Knowing that ESP is there to assist in critical situations can increase driver confidence and reduce stress behind the wheel.
2. Identifying a Mercedes ESP Failure
Recognizing the symptoms of a mercedes esp failure is crucial for timely intervention and repair. The most common indicator is the ESP warning light illuminating on the dashboard. However, other symptoms may include reduced stability, erratic braking, and unusual handling.
2.1 Common Symptoms of ESP Failure
Several symptoms can indicate a mercedes esp failure. Being aware of these signs can help you address the issue promptly and prevent further complications. Key symptoms include:
-
ESP Warning Light Illumination: The most obvious sign of an ESP issue is the illumination of the ESP warning light on the dashboard. This light may stay on continuously or flash intermittently.
The ESP warning light illuminated on a Mercedes-Benz dashboard signals a potential issue with the Electronic Stability Program.
-
Reduced Stability: A noticeable decrease in vehicle stability, particularly during turns or on uneven surfaces, can indicate an ESP malfunction.
-
Erratic Braking: Unusual or unexpected braking behavior, such as the brakes engaging without driver input, may be a sign of ESP problems.
-
Unusual Handling: Difficulty controlling the vehicle or a sensation of the vehicle pulling to one side can suggest an issue with the ESP system.
-
ABS Light Illumination: In some cases, a mercedes esp failure can also trigger the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) warning light, as the two systems are interconnected.
2.2 Understanding ESP Warning Lights
The ESP warning light can appear in different forms, each indicating a specific situation:
-
Solid ESP Light: A continuously illuminated ESP light typically indicates that the ESP system has been deactivated, either manually by the driver or due to a malfunction.
-
Flashing ESP Light: A flashing ESP light indicates that the ESP system is actively engaged, working to stabilize the vehicle during a skid or loss of traction.
-
ESP and ABS Lights On: If both the ESP and ABS lights are illuminated, it suggests a more complex issue affecting both systems.
2.3 Using Diagnostic Tools to Confirm ESP Issues
To accurately diagnose a mercedes esp failure, it’s essential to use professional diagnostic tools. These tools can read error codes stored in the vehicle’s computer, providing valuable information about the nature and location of the problem. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
-
OBD-II Scanners: These handheld devices can read generic error codes related to the ESP system, providing a starting point for diagnosis.
-
Mercedes-Benz Specific Scanners: These advanced scanners offer more detailed diagnostic information, including specific error codes, live data, and system tests.
-
Software-Based Diagnostics: Some diagnostic solutions involve software that runs on a laptop or tablet, providing comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and access to repair information.
2.4 Interpreting Error Codes Related to ESP
Error codes can provide valuable clues about the cause of a mercedes esp failure. Here are some common error codes related to ESP and their potential meanings:
| Error Code | Description | Potential Cause |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | Control Unit N47-5 (ESP, Electronic Stability Program Control Unit) is defective. | Faulty ESP control unit, wiring issues, or sensor malfunction. |
| C1101 | ASR function is faulty. | Issues with the acceleration skid control (ASR) system, which works in conjunction with ESP. |
| C1120 | Component N49 (Steering angle sensor) is defective. | Faulty steering angle sensor, misaligned steering wheel, or wiring problems. |
| C1140 | Component B24/15 (Lateral acceleration sensor) is defective. | Faulty lateral acceleration sensor, wiring issues, or sensor misalignment. |
| C1142 | Component B24/3 (Yaw rate sensor) is defective. | Faulty yaw rate sensor, wiring problems, or sensor misalignment. |
| C1172 | CAN signal fault from control unit N93 (Central gateway control unit). | Communication issues between the ESP control unit and the central gateway control unit. |
| C1176 | Fault in CAN communication with control unit N80 (Steering column module). | Communication problems between the ESP control unit and the steering column module, affecting steering angle data. |
2.5 Recognizing Intermittent ESP Issues
Intermittent ESP issues can be particularly challenging to diagnose. These problems may occur sporadically, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact cause. Common signs of intermittent ESP issues include:
-
ESP Light Comes On and Off: The ESP warning light illuminates intermittently, without any apparent pattern.
-
ESP Function Works Sporadically: The ESP system functions correctly at times but fails to engage during other situations.
-
Error Codes Appear and Disappear: Diagnostic scans reveal error codes that disappear upon clearing, only to reappear later.
To diagnose intermittent ESP issues, it’s essential to gather as much information as possible about the conditions under which the problem occurs. This may involve noting the time of day, weather conditions, road surface, and driving maneuvers that trigger the issue.
3. Common Causes of Mercedes ESP Failure
Several factors can contribute to a mercedes esp failure. These range from sensor malfunctions to wiring issues and problems with the control unit. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective repair.
3.1 Sensor Malfunctions
Faulty sensors are a common cause of ESP problems. The ESP system relies on accurate data from various sensors to function correctly. If a sensor malfunctions, it can provide incorrect or incomplete information, leading to ESP failure.
-
Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors can fail due to physical damage, contamination, or electrical issues.
A wheel speed sensor is crucial for monitoring wheel rotation and detecting potential skidding.
-
Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor can malfunction due to wear and tear, misalignment, or electrical problems.
-
Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor can fail due to impact damage, contamination, or electrical issues.
-
Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor can malfunction due to physical damage, contamination, or electrical problems.
3.2 Wiring and Electrical Issues
Wiring and electrical problems can also cause a mercedes esp failure. Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring can disrupt the communication between sensors and the ESP control unit, leading to system malfunction. Common wiring issues include:
-
Damaged Wiring Harnesses: Physical damage to wiring harnesses can interrupt the flow of signals.
-
Corroded Connectors: Corrosion can build up on electrical connectors, preventing proper contact and signal transmission.
-
Loose Connections: Loose connections can cause intermittent problems and lead to ESP failure.
3.3 ESP Control Unit Problems
The ESP control unit (ECU) is the brain of the ESP system. If the ECU malfunctions, it can lead to a mercedes esp failure. Common ECU problems include:
-
Software Glitches: Software glitches or corruption can cause the ECU to malfunction.
-
Hardware Failures: Internal hardware failures can render the ECU inoperable.
-
Power Supply Issues: Insufficient or unstable power supply can cause the ECU to malfunction.
3.4 Brake System Issues
The ESP system relies on the braking system to apply individual brakes and correct vehicle dynamics. Problems with the braking system can therefore lead to ESP failure. Common brake system issues include:
-
Faulty ABS Pump: A malfunctioning ABS pump can prevent the ESP system from applying brakes effectively.
-
Brake Fluid Issues: Low brake fluid levels or contaminated brake fluid can affect the performance of the braking system and ESP.
-
Brake Pad Wear: Worn brake pads can reduce braking performance and affect the ability of the ESP system to control individual wheels.
3.5 Steering System Problems
The steering system is another critical component that interacts with the ESP system. Issues with the steering system can lead to inaccurate data and ESP failure. Common steering system problems include:
-
Misaligned Steering: A misaligned steering wheel can cause the steering angle sensor to provide incorrect data.
-
Faulty Power Steering: Problems with the power steering system can affect the vehicle’s handling and the ESP’s ability to maintain control.
-
Worn Steering Components: Worn steering components, such as tie rod ends or ball joints, can affect the vehicle’s stability and the ESP’s performance.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing Mercedes ESP Failure
Diagnosing a mercedes esp failure involves a systematic approach to identify the root cause. This step-by-step guide will help you troubleshoot ESP issues effectively.
4.1 Preliminary Checks and Visual Inspection
Before diving into diagnostic tools, start with a thorough visual inspection of the ESP system. Check for obvious signs of damage or wear, such as:
-
Sensor Condition: Inspect all sensors for physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Wiring Condition: Examine wiring harnesses for damage, fraying, or corrosion.
-
Brake System: Check brake fluid levels, brake pad thickness, and the condition of brake lines and hoses.
-
Steering System: Inspect steering components for wear, damage, or misalignment.
4.2 Using an OBD-II Scanner to Retrieve Error Codes
The next step is to use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve error codes from the vehicle’s computer. Connect the scanner to the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard, and follow the scanner’s instructions to read and record any error codes.
-
Record All Error Codes: Note down all error codes, as they provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem.
-
Research Error Codes: Use online resources or repair manuals to research the meaning of each error code and potential causes.
-
Clear Error Codes (Optional): After recording the error codes, you can clear them to see if they reappear, which can help identify intermittent issues.
4.3 Testing Individual Sensors with a Multimeter
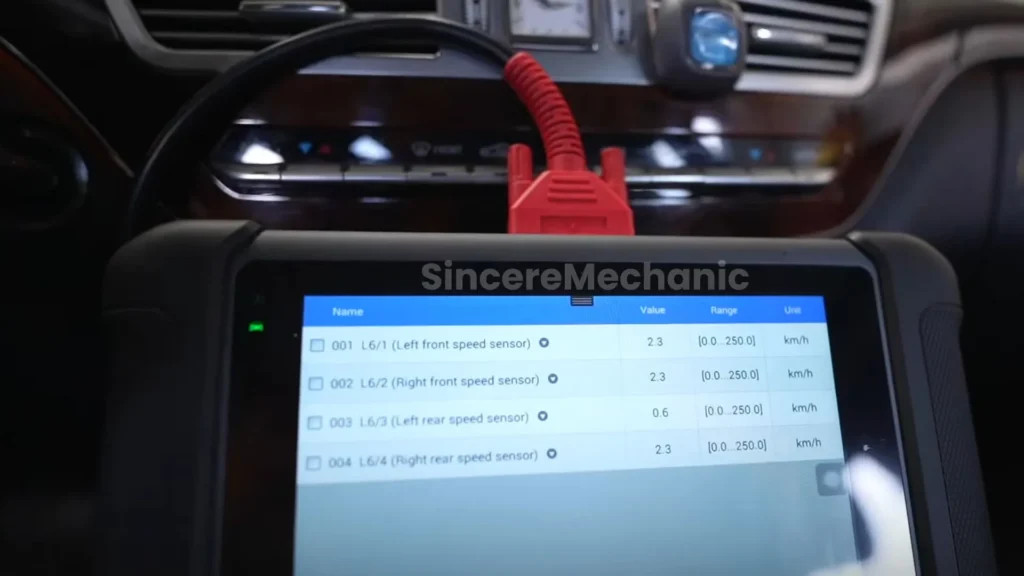
To verify the functionality of individual sensors, use a multimeter to measure their resistance, voltage, or signal output. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the correct testing procedures and specifications for each sensor.
-
Wheel Speed Sensors: Measure the resistance of each wheel speed sensor and compare it to the specified range.
-
Steering Angle Sensor: Measure the voltage output of the steering angle sensor while turning the steering wheel.
-
Yaw Rate Sensor: Measure the signal output of the yaw rate sensor while moving the vehicle.
-
Lateral Acceleration Sensor: Measure the signal output of the lateral acceleration sensor while applying lateral force to the vehicle.
4.4 Checking Wiring Continuity and Voltage
Use a multimeter to check the continuity and voltage of the wiring connected to the ESP system. This can help identify damaged wires, corroded connectors, or loose connections.
-
Continuity Test: Disconnect the battery and use the multimeter to check the continuity of each wire, ensuring that there are no breaks or shorts.
-
Voltage Test: With the ignition on, use the multimeter to measure the voltage at each connector, ensuring that the correct voltage is present.
4.5 Inspecting and Testing the ABS Pump
The ABS pump is a critical component of the ESP system. Inspect the ABS pump for leaks, damage, or corrosion. Use a diagnostic scanner to perform a functional test of the ABS pump, ensuring that it is operating correctly.
-
Visual Inspection: Check the ABS pump for any signs of damage or leaks.
-
Functional Test: Use a diagnostic scanner to activate the ABS pump and verify that it is pumping fluid correctly.
4.6 Analyzing Live Data from the ESP System
Advanced diagnostic scanners can provide live data from the ESP system, allowing you to monitor the performance of various components in real-time. This can help identify subtle issues that may not trigger error codes.
-
Monitor Sensor Data: Observe the live data from each sensor, ensuring that the values are within the expected range.
-
Analyze System Response: Monitor the ESP system’s response to different driving maneuvers, ensuring that it is functioning correctly.
5. Repairing a Mercedes ESP Failure
Once you have identified the cause of the mercedes esp failure, the next step is to perform the necessary repairs. This may involve replacing faulty sensors, repairing damaged wiring, or replacing the ESP control unit.
5.1 Replacing Faulty Sensors
If a sensor is found to be faulty, it should be replaced with a new, high-quality sensor. Follow these steps to replace a sensor:
-
Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the battery to prevent electrical damage.
-
Locate the Sensor: Identify the location of the faulty sensor.
-
Disconnect the Wiring: Disconnect the wiring connector from the sensor.
-
Remove the Sensor: Remove the sensor from its mounting location.
-
Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring that it is properly aligned and secured.
-
Connect the Wiring: Connect the wiring connector to the new sensor.
-
Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the battery.
-
Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any error codes and verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
5.2 Repairing Damaged Wiring
If damaged wiring is causing the mercedes esp failure, it should be repaired or replaced. Follow these steps to repair damaged wiring:
-
Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the battery to prevent electrical damage.
-
Locate the Damage: Identify the location of the damaged wiring.
-
Repair or Replace the Wiring: Repair the damaged wiring using appropriate techniques, such as splicing or soldering. If the damage is extensive, replace the entire wiring harness.
-
Insulate the Wiring: Insulate the repaired wiring with electrical tape or heat-shrink tubing.
-
Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the battery.
-
Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any error codes and verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
5.3 Replacing the ESP Control Unit
If the ESP control unit is faulty, it should be replaced with a new or remanufactured unit. Follow these steps to replace the ESP control unit:
-
Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the battery to prevent electrical damage.
-
Locate the ECU: Identify the location of the ESP control unit, typically under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
-
Disconnect the Wiring: Disconnect the wiring connectors from the ESP control unit.
-
Remove the ECU: Remove the ESP control unit from its mounting location.
-
Install the New ECU: Install the new ESP control unit, ensuring that it is properly aligned and secured.
-
Connect the Wiring: Connect the wiring connectors to the new ESP control unit.
-
Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the battery.
-
Program the ECU: In some cases, the new ESP control unit may need to be programmed to match the vehicle’s specifications. Use a diagnostic scanner to perform the programming procedure.
-
Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any error codes and verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
5.4 Addressing Brake System Issues
If brake system issues are contributing to the mercedes esp failure, they should be addressed. This may involve replacing worn brake pads, flushing the brake fluid, or repairing the ABS pump.
-
Replace Worn Brake Pads: Replace worn brake pads to ensure optimal braking performance.
-
Flush the Brake Fluid: Flush the brake fluid to remove contaminants and ensure proper hydraulic function.
-
Repair the ABS Pump: Repair or replace the ABS pump if it is found to be faulty.
5.5 Resolving Steering System Problems
If steering system problems are contributing to the mercedes esp failure, they should be resolved. This may involve realigning the steering wheel, repairing the power steering system, or replacing worn steering components.
-
Realign the Steering Wheel: Realign the steering wheel to ensure that the steering angle sensor provides accurate data.
-
Repair the Power Steering System: Repair or replace the power steering pump or other components if they are found to be faulty.
-
Replace Worn Steering Components: Replace worn steering components, such as tie rod ends or ball joints, to improve the vehicle’s stability and handling.
6. Preventive Measures to Avoid ESP Failures
Preventing a mercedes esp failure involves regular maintenance and proactive care. By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of ESP problems and ensure the continued safety and reliability of your Mercedes-Benz.
6.1 Regular Maintenance of Sensors
Regularly inspect and maintain the sensors of the ESP system to ensure they are functioning correctly. This includes:
-
Cleaning Sensors: Clean the sensors regularly to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants.
-
Checking Connections: Check the wiring connections to the sensors to ensure they are secure and free from corrosion.
-
Replacing Sensors: Replace sensors as needed, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
6.2 Checking and Maintaining Wiring
Regularly inspect and maintain the wiring of the ESP system to prevent damage and corrosion. This includes:
-
Inspecting Wiring: Inspect the wiring harnesses for damage, fraying, or corrosion.
-
Securing Wiring: Secure loose wiring harnesses to prevent them from rubbing against other components.
-
Protecting Wiring: Protect wiring from exposure to extreme temperatures, chemicals, and moisture.
6.3 Keeping the Brake System in Good Condition
Maintaining the brake system in good condition is essential for the proper functioning of the ESP system. This includes:
-
Checking Brake Fluid Levels: Check brake fluid levels regularly and add fluid as needed.
-
Flushing Brake Fluid: Flush the brake fluid every two years to remove contaminants and ensure proper hydraulic function.
-
Replacing Brake Pads: Replace brake pads as needed to maintain optimal braking performance.
6.4 Ensuring Proper Tire Maintenance
Proper tire maintenance is crucial for the ESP system to function correctly. This includes:
-
Maintaining Correct Tire Pressure: Maintain the correct tire pressure as specified by the manufacturer.
-
Checking Tire Tread Depth: Check tire tread depth regularly and replace tires as needed to ensure adequate traction.
-
Rotating Tires: Rotate tires regularly to promote even wear and extend tire life.
6.5 Avoiding Aggressive Driving Habits
Aggressive driving habits, such as hard braking, rapid acceleration, and sharp turns, can put extra stress on the ESP system and increase the risk of failure. Avoid these driving habits to prolong the life of the ESP system and maintain vehicle stability.
7. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Complex ESP Issues
For complex mercedes esp failure cases that cannot be resolved with basic diagnostic techniques, advanced diagnostic methods may be required. These techniques involve specialized tools and expertise to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
7.1 Using Oscilloscopes to Analyze Sensor Signals
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the signals from the ESP sensors in real-time. This can help identify subtle issues, such as signal distortion or noise, that may not be apparent with a multimeter.
-
Connect the Oscilloscope: Connect the oscilloscope to the sensor’s wiring connector.
-
Monitor the Signal: Monitor the sensor’s signal while operating the vehicle under various conditions.
-
Analyze the Signal: Analyze the signal for any signs of distortion, noise, or other anomalies.
7.2 Performing Component-Level Testing
Component-level testing involves testing individual components of the ESP system, such as the ABS pump or ESP control unit, to verify their functionality. This may require specialized testing equipment and procedures.
-
Isolate the Component: Isolate the component to be tested from the rest of the ESP system.
-
Connect the Testing Equipment: Connect the testing equipment to the component.
-
Perform the Test: Perform the test according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
-
Analyze the Results: Analyze the results of the test to determine if the component is functioning correctly.
7.3 Utilizing Factory Diagnostic Software
Factory diagnostic software, such as Mercedes-Benz’s XENTRY or Vediamo, provides advanced diagnostic capabilities and access to detailed repair information. This software can be used to perform system tests, program control units, and access technical documentation.
-
Install the Software: Install the factory diagnostic software on a laptop or tablet.
-
Connect to the Vehicle: Connect the laptop or tablet to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
-
Perform Diagnostics: Use the software to perform system tests, read error codes, and access technical documentation.
7.4 Seeking Professional Assistance
In some cases, diagnosing and repairing a mercedes esp failure may require the expertise of a trained professional. If you are unable to resolve the issue on your own, seek assistance from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
-
Contact a Qualified Technician: Contact a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician with experience in diagnosing and repairing ESP systems.
-
Provide Detailed Information: Provide the technician with detailed information about the symptoms, error codes, and diagnostic steps you have already taken.
-
Follow the Technician’s Recommendations: Follow the technician’s recommendations for further diagnosis and repair.
8. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Solving Mercedes ESP Failures
CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner in solving mercedes esp failures. We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, repair equipment, and technical support to help you address ESP issues effectively.
8.1 Providing High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a comprehensive selection of high-quality diagnostic tools specifically designed for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Our tools include:
-
OBD-II Scanners: Handheld devices for reading generic error codes.
-
Mercedes-Benz Specific Scanners: Advanced scanners for detailed diagnostics.
-
Software-Based Diagnostics: Software solutions for comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
8.2 Offering Essential Repair Equipment
We also offer a range of essential repair equipment to help you perform ESP repairs efficiently. Our equipment includes:
-
Multimeters: For testing sensor signals and wiring continuity.
-
Oscilloscopes: For analyzing sensor signals in real-time.
-
Brake Service Tools: For servicing brake systems.
-
Steering System Tools: For repairing steering systems.
8.3 Delivering Expert Technical Support
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to providing expert technical support to our customers. Our team of experienced technicians can help you troubleshoot ESP issues, interpret error codes, and perform repairs.
-
Phone Support: Contact our technical support team for assistance via phone.
-
Online Support: Access our online knowledge base and support forums for answers to common questions.
-
Remote Diagnostics: In some cases, we can provide remote diagnostic assistance to help you troubleshoot ESP issues.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of ESP Failure
To illustrate the diagnostic and repair process, here are a few case studies of real-world mercedes esp failure examples:
9.1 Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
-
Symptoms: ESP warning light illuminated, reduced stability during turns.
-
Error Code: C1210 – Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Faulty.
-
Diagnosis: Using a multimeter, the left front wheel speed sensor was found to have an open circuit.
-
Repair: The faulty wheel speed sensor was replaced with a new sensor.
-
Outcome: The ESP warning light was cleared, and the vehicle’s stability was restored.
9.2 Case Study 2: Damaged Wiring Harness
-
Symptoms: ESP and ABS warning lights illuminated, erratic braking behavior.
-
Error Code: C1172 – CAN Signal Fault from Central Gateway Control Unit.
-
Diagnosis: A visual inspection revealed a damaged wiring harness near the ABS pump.
-
Repair: The damaged wiring harness was repaired by splicing and insulating the damaged wires.
-
Outcome: The ESP and ABS warning lights were cleared, and the vehicle’s braking behavior was normalized.
9.3 Case Study 3: Faulty ESP Control Unit
-
Symptoms: ESP warning light illuminated, multiple sensor error codes, system not responding to diagnostics.
-
Error Codes: Multiple sensor error codes, no communication with ESP control unit.
-
Diagnosis: The ESP control unit was not responding to diagnostic commands, indicating a potential hardware failure.
-
Repair: The ESP control unit was replaced with a remanufactured unit.
-
Outcome: The ESP system was restored to normal operation after programming the new control unit.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Mercedes ESP Failure
Here are some frequently asked questions about mercedes esp failure:
Q1: What does the ESP warning light mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
A: The ESP warning light indicates that the Electronic Stability Program is either actively engaged or has a malfunction. A solid light typically means the system is disabled or has a fault, while a flashing light indicates the system is actively working to stabilize the vehicle.
Q2: Can I drive my Mercedes-Benz with the ESP warning light on?
A: It is not recommended to drive with the ESP warning light on, as it indicates a potential issue with the stability control system. Driving with a faulty ESP system can increase the risk of accidents, particularly in adverse driving conditions.
Q3: How do I reset the ESP system on my Mercedes-Benz?
A: To reset the ESP system, try turning the steering wheel lock to lock (full left to full right) while parked. If the light persists, a diagnostic scan is necessary to identify and clear any error codes.
Q4: What are the common causes of ESP failure in Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
A: Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, yaw rate sensors, lateral acceleration sensors, damaged wiring, and ESP control unit problems.
Q5: Can low tire pressure affect the ESP system?
A: Yes, low tire pressure can affect the ESP system, as it relies on accurate wheel speed data to function correctly. Ensure that your tires are properly inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended pressure.
Q6: How often should I have the ESP system checked?
A: The ESP system should be checked as part of your regular maintenance schedule, typically every 12 months or 10,000 miles.
Q7: Can I disable the ESP system on my Mercedes-Benz?
A: Yes, most Mercedes-Benz vehicles have a button to disable the ESP system. However, it is generally not recommended to disable the ESP system unless you are driving in specific conditions, such as deep snow or sand.
Q8: Is it safe to drive in the rain with the ESP light on?
A: Driving in the rain with the ESP light on is not recommended. The ESP system is crucial for maintaining stability on slippery surfaces, and a faulty system can increase the risk of accidents.
Q9: How much does it cost to repair an ESP failure on a Mercedes-Benz?
A: The cost to repair an ESP failure can vary depending on the cause of the problem. Replacing a faulty sensor may cost a few hundred dollars, while replacing the ESP control unit can cost several thousand dollars.
Q10: Where can I find reliable diagnostic tools and repair equipment for Mercedes-Benz ESP systems?
A: CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of reliable diagnostic tools and repair equipment for Mercedes-Benz ESP systems. Visit our website or contact our technical support team for assistance.
Don’t let a mercedes esp failure compromise your safety and driving experience. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880, and let our experts help you diagnose and repair your ESP system efficiently. Visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information. Let us help you enhance your work efficiency and precision with our tools, leading to increased customer satisfaction and business growth. Contact us now for a consultation on the best tools for your auto repair needs.