Luz Esp Mercedes: Diagnosing & Fixing ESP Issues
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the frustration of seeing that “Luz Esp Mercedes” light illuminate on your dashboard. This article will explore the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) system in your Mercedes-Benz, delve into the common causes of ESP malfunctions, and provide actionable steps to diagnose and resolve the issue, getting you back on the road safely with confidence. We’ll cover everything from faulty brake light switches to sensor issues, helping you understand the intricacies of your vehicle’s safety system and how to keep it running smoothly.
1. Understanding the Mercedes ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP), a crucial safety feature in your Mercedes-Benz, works in tandem with other systems like ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), traction control, and hill start assist. ESP’s primary function is to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving situations. By monitoring various sensors throughout the vehicle, the system detects when the car is not moving in the direction the driver intends. This comprehensive system, designed to enhance vehicle stability, relies on interconnected technologies, proper maintenance, and precise diagnostic tools.
1.1. How ESP Works
ESP utilizes sensors that are strategically placed throughout your Mercedes-Benz to continuously monitor its behavior. These sensors include:
- Steering wheel angle sensor: Measures the driver’s intended direction.
- Brake pedal sensor: Detects when the brakes are applied.
- Accelerator pedal sensor: Monitors the driver’s acceleration input.
- Yaw rate sensor: Measures the car’s rotation around its vertical axis.
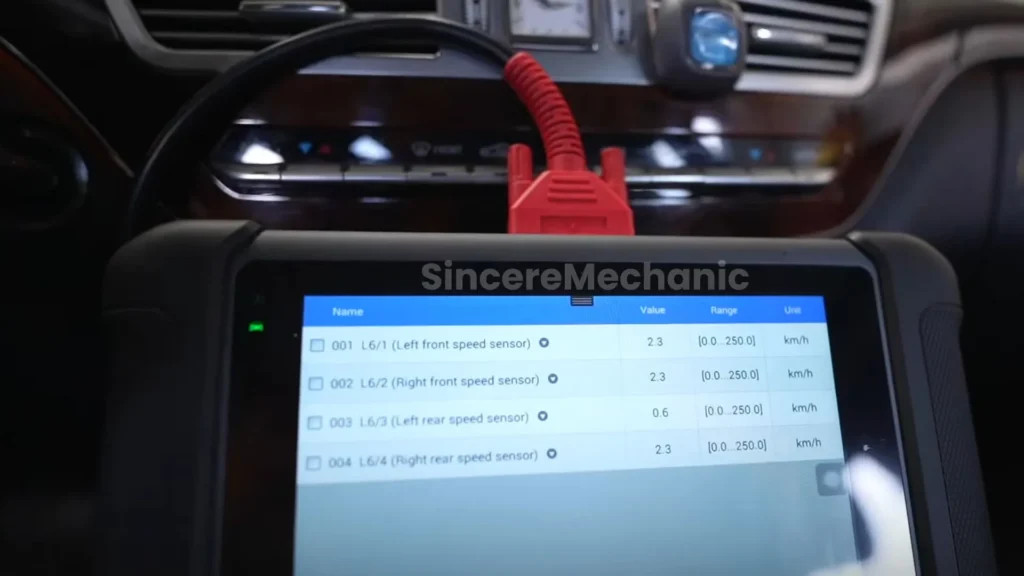
- Wheel speed sensors: Monitor the speed of each individual wheel.
This information is then fed into the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), which analyzes the data and determines if the vehicle is behaving as expected. If the ECU detects a discrepancy between the driver’s intended direction and the car’s actual movement, it intervenes to stabilize the vehicle. ESP functions by applying brakes to individual wheels, reducing engine power, or both, to counteract oversteer or understeer and help the driver regain control. According to a study by Mercedes-Benz, ESP can prevent up to 80% of skidding-related accidents.
1.2. ESP Indicator Light: What It Tells You
The ESP indicator light on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard serves as a communication tool, alerting you to the system’s status. It is designed to keep you informed. In most cases, the light remains off during normal driving conditions. However, the light may illuminate for the following reasons:
- System activation: The ESP light flashes when the system is actively working to stabilize the vehicle. This is normal and indicates that ESP is doing its job.
- System deactivation: In some Mercedes-Benz models, you can manually deactivate ESP. If deactivated, the ESP light will remain on to indicate that the system is not active.
- Malfunction: If the ESP light stays on continuously and doesn’t flash during driving, it could signal a malfunction within the system. This requires further investigation to identify and resolve the underlying issue.
Ignoring a persistent ESP light can compromise your safety and potentially lead to more extensive and costly repairs. Addressing the issue promptly ensures that your ESP system is functioning correctly and provides the intended level of protection.
2. Common Causes of “Luz ESP Mercedes” Illumination
When the ESP warning light illuminates in your Mercedes, it’s essential to address the issue promptly. Understanding the root causes is the first step toward effective resolution. Here are some of the most common reasons why you might encounter the “luz ESP Mercedes” warning:
2.1. Faulty Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch is a common culprit behind ESP warning lights. This switch communicates to the vehicle’s system when the brakes are applied. When the switch fails, it can send incorrect signals, causing the ESP system to activate erroneously.
| Component | Description | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Brake Light Switch | A sensor that detects when the brake pedal is pressed, activating the brake lights and sending a signal to the ESP. | ESP light on, intermittent brake light function, cruise control malfunction, difficulty shifting out of park (for automatics). |
A faulty brake light switch can manifest in several ways, including:
- The ESP light illuminating on the dashboard.
- Brake lights not functioning correctly (either staying on or not activating).
- Cruise control malfunctions.
- Difficulty shifting out of park in automatic transmission vehicles.
Replacing a faulty brake light switch is often a straightforward and relatively inexpensive repair.
2.2. ABS Module Issues
The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) module works in conjunction with the ESP system. The ABS ensures the tires don’t lock up during braking, preventing skidding. The ESP system relies on the ABS to apply brakes to individual wheels for stability control.
| Component | Description | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| ABS Module | Controls the anti-lock braking system, preventing wheel lockup during braking. | ESP light on, ABS light on, reduced braking performance, longer stopping distances, erratic braking behavior, unusual noises from the brakes. |
| ABS Wheel Sensor | Measures the speed of each wheel, providing data to the ABS module for controlling braking force. | ESP light on, ABS light on, traction control issues, speedometer malfunction, unstable braking. |
| ABS Pump | Supplies hydraulic pressure to ABS modulator unit | ABS and traction control light on, hard brake pedal, ABS not working, grinding noise |
Common ABS module issues that can trigger the ESP light include:
- Sensor Malfunctions: Faulty wheel speed sensors provide inaccurate data, disrupting both ABS and ESP functions.
- Module Failure: The ABS module itself can fail due to electrical problems or internal component damage.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring connecting the ABS module and sensors can also lead to communication errors and trigger the ESP light.
Addressing ABS module issues requires a thorough diagnostic process.
2.3. Traction Control Module Problems
The traction control module is another critical component that works in harmony with the ESP system. The traction control system prevents wheel spin during acceleration, maximizing grip and stability. Like the ABS, ESP relies on the traction control system to manage wheel speed and prevent loss of control.
| Component | Description | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Traction Control Module | Manages engine power and braking to prevent wheel spin during acceleration. | ESP light on, traction control light on, reduced acceleration, wheel spin, difficulty driving on slippery surfaces. |
| Wheel Speed Sensors | Measure the speed of each wheel, providing data to the traction control module for regulating wheel spin. | Malfunctioning traction control, ABS issues, speedometer problems. |
If the traction control module malfunctions, it can disrupt the ESP system, leading to the warning light appearing on your dashboard. Common issues include:
- Sensor Failures: Faulty wheel speed sensors can cause the traction control system to miscalculate wheel spin, triggering the ESP light.
- Module Malfunctions: The traction control module itself can fail due to electrical issues or internal damage.
- Software Glitches: Software glitches within the traction control module can also cause it to function improperly.
Diagnosing and resolving traction control module issues requires specialized tools and expertise.
2.4. Low Battery Voltage
The electronic systems in modern vehicles, including the ESP, are sensitive to voltage fluctuations. A weak or failing battery can cause a variety of electrical problems, including the illumination of the ESP light. When the battery voltage drops below a certain threshold, the ESP system may not function correctly, triggering the warning light.
| Component | Description | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Battery | Provides electrical power to start the engine and run the vehicle’s systems. | ESP light on, difficulty starting the engine, dimming headlights, electrical system malfunctions. |
| Alternator | Charges the battery and provides power to the vehicle’s electrical systems. | ESP light on, battery light on, dimming lights, engine stalling, slow cranking, electrical system issues. |
2.5. Incorrect Wheel Size or Tire Pressure
The ESP system relies on accurate wheel speed data to function correctly. If the wheels on your Mercedes-Benz are not the correct size or if the tire pressures are significantly different, it can disrupt the ESP system and trigger the warning light.
| Component | Description | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Wheels | The metal discs on which the tires are mounted. | ESP light on, uneven tire wear, handling problems, vibrations. |
| Tires | The rubber coverings that provide traction and cushioning for the vehicle. | ESP light on, poor handling, reduced fuel efficiency, uneven wear. |
| Tire gauge | Instrument used to measure pressure of tires | Incorrect tire pressure |
Here’s how incorrect wheel size or tire pressure can affect the ESP system:
- Wheel Size Mismatch: If the wheels on your Mercedes-Benz are not the same size, the wheel speed sensors will send conflicting data to the ESP system, triggering the warning light.
- Tire Pressure Differences: Significant differences in tire pressure can also cause inaccurate wheel speed readings, leading to ESP malfunctions.
Ensuring that your Mercedes-Benz has the correct wheel size and that the tire pressures are properly maintained is essential for optimal ESP system performance.
2.6. Throttle Body Issues
The throttle body controls the amount of air that enters the engine. The ESP system uses throttle control to modulate engine power during a skid. A malfunctioning throttle body can affect the ESP system’s ability to control engine output, leading to the ESP light illuminating.
| Component | Description | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Throttle Body | Controls the amount of air entering the engine. | ESP light on, rough idling, stalling, poor acceleration, reduced fuel efficiency, check engine light. |
| Sensors | Throttle position sensor, airflow sensor | Idling issues, acceleration problems, rough running |
| Actuator | Regulates throttle plate | The car cannot maintain idle speed; therefore, the engine stalls. |
| Valve | Prevents carbon buildup, ensuring proper throttle operation | Whistling noise, reduced performance, check engine light |
Common throttle body issues that can trigger the ESP light include:
- Carbon Buildup: Over time, carbon deposits can accumulate in the throttle body, restricting airflow and affecting engine performance.
- Sensor Malfunctions: The throttle position sensor (TPS) can fail, sending inaccurate data to the engine control unit (ECU).
- Actuator Problems: The throttle body actuator, which controls the throttle plate, can also malfunction, leading to ESP issues.
Cleaning the throttle body regularly and replacing faulty sensors or actuators can help prevent ESP-related problems.
2.7. Steering Angle Sensor Failure
The steering angle sensor is another critical component of the ESP system. It measures the angle of the steering wheel, providing data to the ESP system about the driver’s intended direction. If the steering angle sensor malfunctions, it can send incorrect data to the ESP system, causing the warning light to illuminate.
| Component | Description | Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Steering Angle Sensor | Measures the angle of the steering wheel, providing data to the ESP system. | ESP light on, power steering problems, difficulty steering, inaccurate steering input, stability control malfunction. |
| Clock Spring | Enables the steering wheel to turn while maintaining an electrical connection to the airbag and other systems. | Airbag warning light, horn malfunction, cruise control problems, ESP light on. |
Potential issues related to steering angle sensor are:
- Misalignment: The steering angle sensor may need recalibration following a wheel alignment or suspension work.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor itself can fail due to electrical problems or internal damage.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring connecting the steering angle sensor to the ESP system can also cause communication errors and trigger the ESP light.
3. Diagnosing “Luz ESP Mercedes”: A Step-by-Step Guide
When you see the “luz ESP Mercedes” light on your dashboard, it’s essential to diagnose the problem accurately. This step-by-step guide will help you troubleshoot the issue:
3.1. Preliminary Checks
Before diving into more complex diagnostics, start with these simple checks:
- Check the ESP Button: Ensure that the ESP system hasn’t been accidentally deactivated. Look for an “ESP OFF” button on your dashboard and make sure it’s not pressed.
- Restart Your Vehicle: Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve temporary glitches. Turn off your engine, wait a few minutes, and then restart your vehicle.
- Inspect Tire Pressure: Verify that all tires are inflated to the recommended pressure. Use a tire pressure gauge to check each tire and inflate or deflate as necessary.
- Examine Wheel Size: Ensure that all wheels are the same size and that they match the specifications for your Mercedes-Benz model.
- Brake Lights Check: Ask someone to stand behind your vehicle while you press the brake pedal. Confirm that all brake lights are functioning correctly.
3.2. Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner can provide valuable insights into the cause of the ESP light. Here’s how to use it:
- Locate the OBD-II Port: Find the OBD-II port in your Mercedes-Benz. It’s typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Interpret the Codes: Research the codes to identify the potential issues. Common codes related to the ESP system include those associated with the ABS module, wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and brake light switch.
3.3. Visual Inspection
A visual inspection can help you identify obvious issues:
- Check Wiring: Inspect the wiring harnesses and connectors associated with the ABS module, wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and brake light switch. Look for damaged, corroded, or loose connections.
- Inspect Sensors: Visually inspect the wheel speed sensors for damage or debris.
- Examine the ABS Module: Look for any signs of physical damage to the ABS module.
3.4. Testing Components
Testing individual components can help you pinpoint the source of the problem:
- Brake Light Switch Test: Use a multimeter to test the brake light switch for continuity. The switch should show continuity when the brake pedal is pressed and no continuity when the pedal is released.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Test: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of each wheel speed sensor. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Steering Angle Sensor Test: Use a diagnostic scan tool to monitor the steering angle sensor’s output. Verify that the sensor is providing accurate readings as you turn the steering wheel.
4. Repairing “Luz ESP Mercedes”: Solutions and Procedures
Once you’ve diagnosed the cause of the “luz ESP Mercedes,” you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here are some common solutions:
4.1. Replacing a Faulty Brake Light Switch
Replacing a faulty brake light switch is a relatively straightforward repair that can often be done at home. Here’s how:
- Locate the Brake Light Switch: The brake light switch is typically located near the brake pedal assembly.
- Disconnect the Electrical Connector: Disconnect the electrical connector from the switch.
- Remove the Old Switch: Twist or unclip the old switch to remove it from its mounting.
- Install the New Switch: Install the new switch in the reverse order, ensuring it’s securely mounted.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the switch.
- Test the Switch: Verify that the brake lights function correctly when you press the brake pedal.
4.2. Addressing ABS Module Issues
ABS module issues can be more complex and may require professional assistance. Here are some common solutions:
- Replacing a Wheel Speed Sensor: If a wheel speed sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one. Ensure that the new sensor is compatible with your Mercedes-Benz model.
- Repairing Wiring: Repair any damaged or corroded wiring associated with the ABS module or wheel speed sensors.
- Replacing the ABS Module: If the ABS module itself is faulty, it may need to be replaced. This typically requires programming the new module to your vehicle.
4.3. Rectifying Traction Control Module Problems
Traction control module problems may also require professional attention. Here are some potential solutions:
- Replacing a Wheel Speed Sensor: As with ABS issues, a faulty wheel speed sensor can also cause traction control problems. Replace the sensor if necessary.
- Repairing Wiring: Repair any damaged or corroded wiring associated with the traction control module or wheel speed sensors.
- Replacing the Traction Control Module: If the traction control module itself is faulty, it may need to be replaced and programmed to your vehicle.
4.4. Resolving Low Battery Voltage Issues
Resolving low battery voltage issues is crucial for maintaining the proper functioning of your ESP system. Here’s how:
- Check Battery Connections: Ensure that the battery terminals are clean and securely connected.
- Charge the Battery: If the battery is low, use a battery charger to bring it back to full charge.
- Replace the Battery: If the battery is old or failing, replace it with a new one that meets the specifications for your Mercedes-Benz model.
- Test the Alternator: Have the alternator tested to ensure that it’s charging the battery correctly. If the alternator is faulty, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
4.5. Correcting Wheel Size and Tire Pressure
Ensuring that your Mercedes-Benz has the correct wheel size and tire pressure is essential for optimal ESP system performance. Here’s what to do:
- Verify Wheel Size: Check the specifications for your Mercedes-Benz model to determine the correct wheel size. Ensure that all wheels on your vehicle match those specifications.
- Adjust Tire Pressure: Use a tire pressure gauge to check the pressure in each tire. Inflate or deflate the tires to the recommended pressure, which can be found on the sticker inside the driver’s side doorjamb or in your owner’s manual.
4.6. Cleaning the Throttle Body
Cleaning the throttle body can help resolve ESP issues related to airflow problems. Here’s how:
- Locate the Throttle Body: The throttle body is typically located near the air intake manifold.
- Disconnect the Air Intake Hose: Disconnect the air intake hose from the throttle body.
- Spray Throttle Body Cleaner: Use a throttle body cleaner to spray the throttle body, removing carbon deposits and debris.
- Wipe Clean: Use a clean cloth to wipe the throttle body clean.
- Reconnect the Air Intake Hose: Reconnect the air intake hose to the throttle body.
4.7. Addressing Steering Angle Sensor Issues
Addressing steering angle sensor issues may require professional assistance. Here are some potential solutions:
- Recalibrate the Sensor: Use a diagnostic scan tool to recalibrate the steering angle sensor.
- Replace the Sensor: If the sensor is faulty, replace it with a new one that’s compatible with your Mercedes-Benz model.
- Repair Wiring: Repair any damaged or corroded wiring associated with the steering angle sensor.
5. Maintaining Your Mercedes ESP System
Preventive maintenance is key to keeping your Mercedes ESP system functioning correctly. Follow these tips:
- Regular Inspections: Have your ESP system inspected regularly by a qualified mechanic.
- Proper Tire Maintenance: Maintain proper tire pressure and ensure that your wheels are correctly aligned.
- Battery Care: Keep your battery in good condition and replace it when necessary.
- Address Issues Promptly: If you notice any warning lights or unusual behavior, address the issue promptly to prevent further damage.
6. When to Seek Professional Help
While some ESP-related issues can be resolved at home, others require professional expertise. Seek professional help if:
- You’re not comfortable performing the necessary repairs.
- You’ve tried the troubleshooting steps and the ESP light is still on.
- You suspect a complex issue, such as an ABS module failure or a traction control module problem.
7. Benefits of a Properly Functioning ESP System
A properly functioning ESP system provides numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Safety: ESP helps prevent skidding and loss of control, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Improved Handling: ESP improves vehicle handling, especially in challenging driving conditions.
- Increased Stability: ESP increases vehicle stability, providing a smoother and more comfortable ride.
8. Choosing the Right Diagnostic Tools
Selecting the right diagnostic tools can significantly streamline the process of identifying and addressing ESP-related issues in your Mercedes-Benz. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality diagnostic tools designed to meet the needs of both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts. Here’s a guide to choosing the right tools:
8.1. OBD-II Scanners
OBD-II scanners are essential for reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and accessing real-time data from your vehicle’s computer. When choosing an OBD-II scanner, consider the following features:
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your Mercedes-Benz model and supports the necessary diagnostic protocols.
- Features: Look for features such as code reading, code clearing, live data streaming, and freeze frame data.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
8.2. Multimeters
Multimeters are versatile tools that can be used to test various electrical components, such as the brake light switch, wheel speed sensors, and wiring harnesses. When selecting a multimeter, consider the following:
- Accuracy: Choose a multimeter with high accuracy for precise measurements.
- Features: Look for features such as voltage measurement, resistance measurement, continuity testing, and diode testing.
- Durability: Select a multimeter that’s built to withstand the rigors of automotive use.
8.3. Diagnostic Scan Tools
Diagnostic scan tools offer advanced capabilities for diagnosing and repairing complex automotive systems, including the ESP system. These tools typically provide features such as:
- Advanced Code Reading: Diagnostic scan tools can read and interpret manufacturer-specific codes, providing more detailed information about the issue.
- Live Data Streaming: These tools allow you to monitor real-time data from various sensors and components, helping you pinpoint the source of the problem.
- Bi-Directional Control: Some diagnostic scan tools offer bi-directional control, allowing you to activate and test individual components.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What does the ESP light mean on my Mercedes?
The ESP light indicates that the Electronic Stability Program is either active, deactivated, or experiencing a malfunction. - Can I drive with the ESP light on?
You can drive with the ESP light on, but it’s not recommended. The ESP system may not function correctly, which can compromise your safety. - How do I reset the ESP light on my Mercedes?
Sometimes, you can reset the ESP light by restarting your vehicle. However, if the light persists, you’ll need to diagnose and repair the underlying issue. - What are the common causes of the ESP light coming on?
Common causes include a faulty brake light switch, ABS module issues, traction control module problems, low battery voltage, incorrect wheel size or tire pressure, throttle body issues, and steering angle sensor failure. - How much does it cost to fix the ESP system on a Mercedes?
The cost to fix the ESP system can vary widely depending on the cause of the problem. A simple repair, such as replacing a brake light switch, may cost less than $100, while more complex repairs, such as replacing an ABS module, can cost several hundred dollars or more. - Can a bad wheel alignment cause the ESP light to come on?
Yes, a bad wheel alignment can cause the ESP light to come on. If your vehicle’s wheels are not properly aligned, it can affect the steering angle sensor and trigger the ESP light. - Is it safe to drive my Mercedes in the snow with the ESP light on?
It’s not recommended to drive your Mercedes in the snow with the ESP light on. The ESP system is designed to help prevent skidding and loss of control in slippery conditions. If the ESP system is not functioning correctly, it can compromise your safety. - Where can I find a reliable mechanic to fix my Mercedes ESP system?
You can find a reliable mechanic to fix your Mercedes ESP system by asking for recommendations from friends or family, searching online for reputable repair shops, or contacting a Mercedes-Benz dealership. - Can I disable the ESP system on my Mercedes?
Some Mercedes-Benz models allow you to disable the ESP system. However, it’s generally not recommended to disable the ESP system unless you’re driving in specific conditions, such as deep snow or mud. - How often should I have my Mercedes ESP system inspected?
It’s recommended to have your Mercedes ESP system inspected at least once a year, or more frequently if you notice any warning lights or unusual behavior.
10. Need Assistance? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET
Experiencing the “luz ESP Mercedes” warning light can be unsettling, but understanding the potential causes and taking appropriate action can help you resolve the issue effectively. From preliminary checks to advanced diagnostics and repairs, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of the ESP system in your Mercedes-Benz. Remember, proper maintenance and timely repairs are essential for ensuring your safety and the longevity of your vehicle.
If you’re facing challenges with your Mercedes-Benz ESP system or need expert advice, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to help. Our team of experienced technicians can provide accurate diagnostics, reliable repairs, and top-quality diagnostic tools to keep your vehicle running smoothly. Don’t hesitate to contact us for assistance:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Let CARDIAGTECH.NET be your trusted partner for all your Mercedes-Benz diagnostic and repair needs. Contact us today to schedule a consultation or explore our wide range of diagnostic tools.