ESP Unavailable Mercedes: Expert Solutions & Repair Guide
Is your Mercedes displaying the dreaded “ESP Unavailable” message? CARDIAGTECH.NET offers expert insights and repair guidance to resolve this issue, helping you restore your vehicle’s safety and performance. Discover potential causes, diagnostic steps, and effective solutions for your Mercedes-Benz.
1. Understanding ESP and Its Importance in Your Mercedes
Electronic Stability Program (ESP), also known as Electronic Stability Control (ESC), is a critical safety system in your Mercedes-Benz. It helps prevent skidding and loss of control by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power. When the “ESP Unavailable” message appears, it signifies a malfunction in this system, potentially compromising your safety, especially in adverse driving conditions. The ESP system integrates with the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and traction control to provide comprehensive stability assistance. A malfunctioning ESP system can affect braking performance and overall vehicle handling.
1.1 The Role of ESP in Preventing Accidents
ESP actively monitors various sensors, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, and yaw rate sensors, to detect when the vehicle is deviating from the driver’s intended path. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%. By intervening to correct oversteer or understeer, ESP helps drivers maintain control in emergency situations, contributing to a safer driving experience.
1.2 How ESP Works in Conjunction with Other Safety Systems
ESP works in harmony with other safety systems, such as ABS and traction control, to provide a comprehensive safety net. ABS prevents wheel lockup during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control, while traction control limits wheel spin during acceleration, improving grip on slippery surfaces. ESP integrates these functions and adds another layer of protection by actively intervening to correct skids and maintain stability.
2. Common Causes of “ESP Unavailable” on Mercedes Vehicles
Several factors can trigger the “ESP Unavailable” message on your Mercedes. Identifying the root cause is the first step toward resolving the issue. Here are some of the most common culprits:
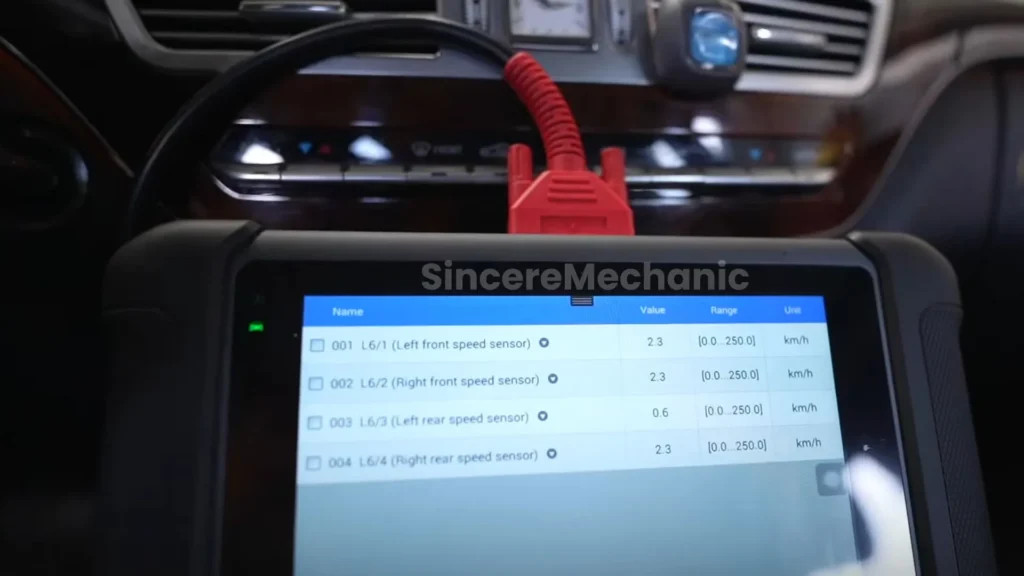
- Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and provide data to the ESP system. A malfunctioning sensor can send incorrect information, causing the ESP to disengage.
- Steering Angle Sensor Issues: The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel, which is crucial for the ESP system to determine the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunctions: The yaw rate sensor measures the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis. This information is essential for detecting skids and initiating corrective actions.
- Brake Light Switch Problems: A faulty brake light switch can disrupt the ESP system, as it relies on this switch to determine when the brakes are applied.
- Low Battery Voltage: Insufficient battery voltage can cause various electronic systems, including ESP, to malfunction.
- Wiring and Connector Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring and connectors can disrupt the communication between the ESP components and the control unit.
- ESP Control Unit Failure: In rare cases, the ESP control unit itself may fail, requiring replacement.
3. Diagnostic Steps to Identify the “ESP Unavailable” Issue
Diagnosing the “ESP Unavailable” issue requires a systematic approach. Here are the steps you can take to pinpoint the problem:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the wheel speed sensors, wiring, and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any DTCs stored in the ESP control unit. These codes can provide valuable clues about the source of the problem.
- Check Wheel Speed Sensor Readings: Use a scan tool to monitor the wheel speed sensor readings while driving. Compare the readings from each sensor to identify any discrepancies.
- Inspect the Steering Angle Sensor: Check the steering angle sensor reading to ensure it is accurate and consistent.
- Evaluate the Yaw Rate Sensor: Verify that the yaw rate sensor is functioning correctly and providing accurate data.
- Test the Brake Light Switch: Ensure that the brake light switch is working properly and sending the correct signal to the ESP system.
- Check Battery Voltage: Verify that the battery voltage is within the specified range.
- Inspect the ESP Control Unit: Examine the ESP control unit for any signs of damage or corrosion.
4. Resolving “ESP Unavailable” Issues: Step-by-Step Guide
Once you have identified the cause of the “ESP Unavailable” issue, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to resolving common problems:
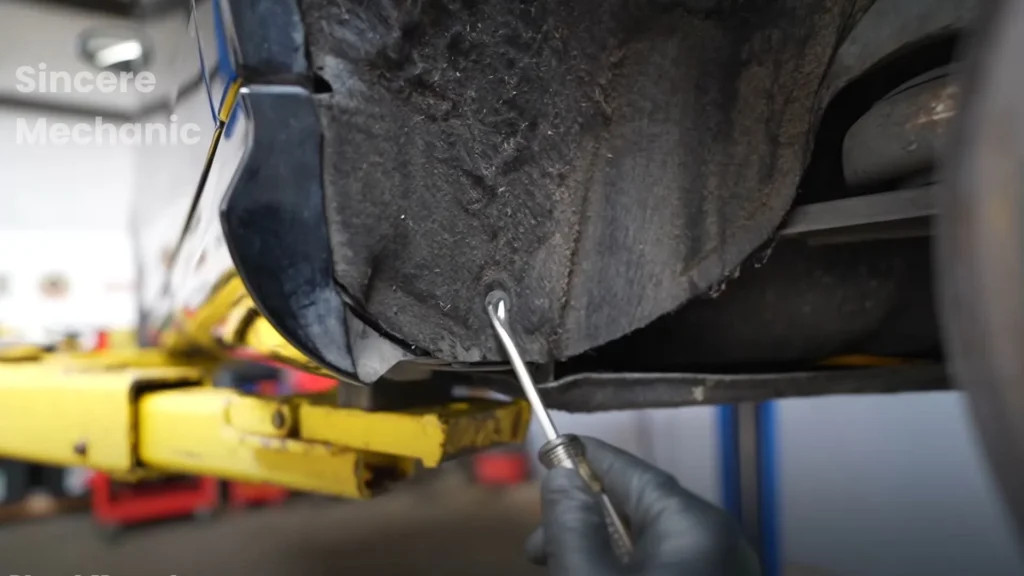
4.1 Addressing Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Step 1: Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor. This can be determined by reading DTCs or monitoring sensor data with a scan tool.
Step 2: Disconnect the sensor from the wiring harness.
Step 3: Remove the sensor from the wheel hub. This may involve removing a bolt or clip.
Step 4: Install the new wheel speed sensor.
Step 5: Reconnect the sensor to the wiring harness.
Step 6: Clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
Ensure accurate data transmission with a functioning Mercedes wheel speed sensor.
4.2 Correcting Steering Angle Sensor Problems
Step 1: Locate the steering angle sensor. This is typically located near the steering column.
Step 2: Disconnect the sensor from the wiring harness.
Step 3: Remove the sensor from its mounting bracket.
Step 4: Install the new steering angle sensor.
Step 5: Reconnect the sensor to the wiring harness.
Step 6: Calibrate the steering angle sensor using a scan tool.
Step 7: Clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
4.3 Fixing Yaw Rate Sensor Malfunctions
Step 1: Locate the yaw rate sensor. This is often located under the driver’s seat or in the trunk.
Step 2: Disconnect the sensor from the wiring harness.
Step 3: Remove the sensor from its mounting bracket.
Step 4: Install the new yaw rate sensor.
Step 5: Reconnect the sensor to the wiring harness.
Step 6: Clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
4.4 Repairing Brake Light Switch Issues
Step 1: Locate the brake light switch. This is typically located near the brake pedal.
Step 2: Disconnect the switch from the wiring harness.
Step 3: Remove the switch from its mounting bracket.
Step 4: Install the new brake light switch.
Step 5: Reconnect the switch to the wiring harness.
Step 6: Adjust the switch as needed.
Step 7: Clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
4.5 Addressing Low Battery Voltage
Step 1: Check the battery voltage with a multimeter. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
Step 2: If the battery voltage is low, charge the battery with a battery charger.
Step 3: If the battery is old or damaged, replace it with a new one.
Step 4: Clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
4.6 Repairing Wiring and Connector Issues
Step 1: Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
Step 2: Repair any damaged wiring by splicing in new wires and using heat shrink tubing to protect the connections.
Step 3: Clean any corroded connectors with a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner.
Step 4: Apply dielectric grease to the connectors to prevent future corrosion.
Step 5: Clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
4.7 Replacing the ESP Control Unit
Step 1: Locate the ESP control unit. This is typically located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment.
Step 2: Disconnect the control unit from the wiring harness.
Step 3: Remove the control unit from its mounting bracket.
Step 4: Install the new ESP control unit.
Step 5: Reconnect the control unit to the wiring harness.
Step 6: Program the new control unit with the correct vehicle information using a scan tool.
Step 7: Clear the DTCs and test the ESP system.
5. Tools and Equipment Needed for ESP Repairs
Performing ESP repairs requires a variety of tools and equipment. Here’s a list of essential items:
- OBD-II Scanner: To read and clear DTCs.
- Multimeter: To check battery voltage and test electrical circuits.
- Socket Set: To remove and install sensors and other components.
- Wrench Set: To tighten and loosen bolts and nuts.
- Screwdriver Set: To remove and install screws.
- Wire Strippers and Crimpers: To repair damaged wiring.
- Electrical Contact Cleaner: To clean corroded connectors.
- Dielectric Grease: To protect connectors from corrosion.
- Scan Tool with ESP Calibration Capabilities: To calibrate the steering angle sensor and program the ESP control unit.
- Safety Glasses and Gloves: To protect your eyes and hands.
6. Preventative Measures to Avoid ESP Problems
Preventing ESP problems is always better than dealing with them after they occur. Here are some preventative measures you can take to keep your ESP system in good working order:
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Follow your Mercedes-Benz’s recommended maintenance schedule, including regular inspections of the braking system, suspension, and tires.
- Proper Tire Inflation: Maintain proper tire inflation to ensure optimal traction and stability.
- Avoid Harsh Driving: Avoid aggressive driving maneuvers that can put excessive stress on the ESP system.
- Check for Water Leaks: Inspect your vehicle for water leaks, especially in the trunk and under the seats, as moisture can damage the ESP components.
- Keep the Battery in Good Condition: Ensure that your battery is properly charged and in good condition.
- Address Warning Lights Promptly: If you notice any warning lights on your dashboard, such as the ABS or ESP light, have them checked out immediately.
7. Understanding Mercedes-Benz Specific ESP Issues
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are known for their advanced technology, but they can also be prone to certain ESP-related issues. Here are some common problems specific to Mercedes-Benz models:
- C-Class (W204) ESP Problems: The W204 C-Class is known for issues with the steering angle sensor and wheel speed sensors.
- E-Class (W211) ESP Problems: The W211 E-Class can experience problems with the yaw rate sensor and brake light switch.
- S-Class (W221) ESP Problems: The W221 S-Class is susceptible to issues with the ESP control unit and wiring harness.
7.1 Recalls and Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
Stay informed about any recalls or TSBs related to the ESP system on your Mercedes-Benz. These notices can provide valuable information about potential problems and solutions. You can check for recalls and TSBs on the NHTSA website or through your local Mercedes-Benz dealer.
7.2 Common Error Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common ESP error codes can help you diagnose problems more effectively. Here are some examples:
| Error Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | ESP Control Unit Faulty | ESP control unit failure, wiring issues |
| C1100 | Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues |
| C1200 | Steering Angle Sensor Signal Implausible | Faulty steering angle sensor, calibration issue |
| C1300 | Yaw Rate Sensor Signal Implausible | Faulty yaw rate sensor, wiring issues |
| C1400 | Brake Light Switch Malfunction | Faulty brake light switch, wiring issues |
8. The Importance of Professional Assistance
While some ESP repairs can be performed by experienced DIYers, others require specialized knowledge and equipment. If you are not comfortable working on your vehicle’s ESP system, it is best to seek professional assistance. A qualified Mercedes-Benz technician can accurately diagnose the problem and perform the necessary repairs safely and effectively.
8.1 Finding a Qualified Mercedes-Benz Technician
To find a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician, consider the following:
- Look for ASE Certification: ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) certification indicates that the technician has met certain standards of competence.
- Check Online Reviews: Read online reviews to see what other customers have to say about the technician’s work.
- Ask for Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or other Mercedes-Benz owners for recommendations.
- Verify Experience: Ensure that the technician has experience working on Mercedes-Benz vehicles, particularly the model you own.
8.2 When to Seek Professional Help
You should seek professional help for ESP issues if:
- You are not comfortable working on your vehicle’s ESP system.
- You have tried to diagnose the problem yourself but have been unsuccessful.
- The ESP problem is complex or requires specialized equipment.
- You are concerned about your safety or the safety of others.
9. Cost of ESP Repairs for Mercedes-Benz
The cost of ESP repairs for your Mercedes-Benz can vary depending on the cause of the problem, the parts required, and the labor rate of the repair shop. Here are some approximate costs for common ESP repairs:
| Repair | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement | $200 – $400 per sensor |
| Steering Angle Sensor Replacement | $300 – $600 |
| Yaw Rate Sensor Replacement | $400 – $800 |
| Brake Light Switch Replacement | $100 – $200 |
| ESP Control Unit Replacement | $1,000 – $2,000 |
| Wiring Repair | $100 – $500 |
These are just estimates, and the actual cost of your repair may vary. It is always a good idea to get a written estimate from a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician before proceeding with any repairs.
10. Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz ESP System with CARDIAGTECH.NET
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the importance of maintaining your Mercedes-Benz ESP system. We offer a wide range of diagnostic tools, replacement parts, and technical support to help you keep your ESP system in top condition. Whether you are a professional technician or a DIY enthusiast, we have the resources you need to diagnose and repair ESP problems on your Mercedes-Benz.
10.1 High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
We offer a variety of high-quality OBD-II scanners and scan tools with ESP calibration capabilities. Our tools are designed to provide accurate and reliable diagnostic information, helping you pinpoint the source of ESP problems quickly and efficiently.
10.2 Genuine Mercedes-Benz Parts
We carry a comprehensive selection of genuine Mercedes-Benz parts, including wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensors, yaw rate sensors, brake light switches, and ESP control units. Our parts are manufactured to the highest standards of quality and are guaranteed to fit and perform correctly in your Mercedes-Benz.
10.3 Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert technical support. Whether you need help diagnosing an ESP problem or installing a new part, we are here to assist you every step of the way.
10.4 Order Your ESP Repair Tools Today
Don’t let ESP problems compromise your safety and driving experience. Order your ESP repair tools and parts from CARDIAGTECH.NET today and restore your Mercedes-Benz to its optimal performance. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to learn more. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
Explore CARDIAGTECH.NET for advanced tools and parts essential for Mercedes-Benz ESP system maintenance and repair.
11. Advanced Diagnostics and Calibration
For more complex ESP issues, advanced diagnostics and calibration may be necessary. This typically involves using specialized scan tools and software to analyze the ESP system’s performance and make precise adjustments.
11.1 Using Mercedes-Benz Diagnostic Software
Mercedes-Benz offers its own diagnostic software, such as XENTRY and DAS, which provides in-depth access to the ESP system. This software allows technicians to perform advanced diagnostics, calibration, and programming.
11.2 Steering Angle Sensor Calibration
Steering angle sensor calibration is often required after replacing the sensor or performing certain repairs. This process ensures that the ESP system accurately interprets the steering wheel’s position. Calibration typically involves using a scan tool to reset the sensor and then performing a series of steering maneuvers.
11.3 Yaw Rate Sensor Calibration
Yaw rate sensor calibration may be necessary after replacing the sensor or if the vehicle has been involved in an accident. This process ensures that the ESP system accurately measures the vehicle’s rotation. Calibration typically involves using a scan tool to reset the sensor and then performing a series of driving maneuvers.
12. Case Studies: Real-World ESP Repair Examples
To illustrate the process of diagnosing and repairing ESP problems, here are a few case studies based on real-world examples:
12.1 Case Study 1: C-Class (W204) with “ESP Unavailable” Message
Problem: A customer brought in a W204 C-Class with the “ESP Unavailable” message displayed on the dashboard. The customer reported that the message appeared intermittently, especially in wet weather.
Diagnosis: The technician scanned the vehicle and found a DTC for a faulty front right wheel speed sensor. The technician also noticed that the sensor wiring was corroded.
Solution: The technician replaced the front right wheel speed sensor and repaired the corroded wiring. The technician then cleared the DTC and tested the ESP system, which functioned correctly.
12.2 Case Study 2: E-Class (W211) with ABS and ESP Lights On
Problem: A customer brought in a W211 E-Class with both the ABS and ESP lights illuminated on the dashboard. The customer reported that the lights came on after hitting a pothole.
Diagnosis: The technician scanned the vehicle and found a DTC for a faulty yaw rate sensor. The technician also noticed that the sensor was loose in its mounting bracket.
Solution: The technician replaced the yaw rate sensor and secured it properly in its mounting bracket. The technician then cleared the DTC and tested the ESP system, which functioned correctly.
12.3 Case Study 3: S-Class (W221) with “ESP Malfunction” Message
Problem: A customer brought in a W221 S-Class with the “ESP Malfunction” message displayed on the dashboard. The customer reported that the message appeared after the car had been sitting for several days.
Diagnosis: The technician scanned the vehicle and found a DTC for low battery voltage. The technician also noticed that the battery was old and weak.
Solution: The technician replaced the battery with a new one. The technician then cleared the DTC and tested the ESP system, which functioned correctly.
13. DIY vs. Professional Repair: Making the Right Choice
Deciding whether to attempt ESP repairs yourself or seek professional help is a personal decision. Here are some factors to consider:
13.1 Assessing Your Skill Level
Be honest about your automotive repair skills and experience. If you have limited experience working on cars, it is best to leave ESP repairs to a professional.
13.2 Evaluating the Complexity of the Repair
Some ESP repairs, such as replacing a wheel speed sensor or brake light switch, are relatively straightforward and can be performed by experienced DIYers. However, other repairs, such as replacing the ESP control unit or calibrating the steering angle sensor, are more complex and require specialized knowledge and equipment.
13.3 Considering the Potential Risks
Improperly performed ESP repairs can compromise your safety and the safety of others. If you are not confident in your ability to perform the repair correctly, it is best to seek professional help.
13.4 The Benefits of DIY Repairs
Performing ESP repairs yourself can save you money on labor costs and give you a sense of accomplishment. However, it is important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks before attempting any repairs.
14. Optimizing ESP Performance for Enhanced Safety
In addition to repairing ESP problems, there are steps you can take to optimize ESP performance for enhanced safety:
14.1 Tire Maintenance and Alignment
Proper tire maintenance, including regular inflation and rotation, is essential for optimal ESP performance. Worn or improperly inflated tires can reduce traction and compromise the ESP system’s ability to maintain control. Regular wheel alignments can also help ensure that the tires are properly aligned, which improves handling and stability.
14.2 Suspension System Inspection
A properly functioning suspension system is crucial for ESP performance. Worn or damaged suspension components can affect the vehicle’s handling and stability, reducing the effectiveness of the ESP system. Have your suspension system inspected regularly by a qualified technician.
14.3 Brake System Maintenance
The ESP system relies on the braking system to function properly. Worn brake pads, rotors, or calipers can reduce braking performance and compromise the ESP system’s ability to control the vehicle. Have your brake system inspected and maintained regularly.
15. ESP and Winter Driving: Tips for Enhanced Safety
ESP is especially valuable during winter driving conditions, when roads are slippery and traction is limited. Here are some tips for using ESP effectively in winter:
15.1 Understanding ESP Limitations
While ESP can help you maintain control in slippery conditions, it is not a substitute for safe driving practices. Always drive at a safe speed, maintain a safe following distance, and avoid sudden maneuvers.
15.2 Using Winter Tires
Winter tires provide significantly better traction than all-season tires in snow and ice. Consider using winter tires during the winter months to improve your vehicle’s handling and stability.
15.3 Adjusting Driving Style
Adjust your driving style to suit the winter conditions. Accelerate, brake, and steer smoothly and gradually. Avoid sudden movements that can upset the vehicle’s balance.
15.4 Knowing How to React to Skids
If your vehicle does start to skid, remain calm and steer gently in the direction you want to go. Avoid slamming on the brakes or making sudden steering corrections.
16. The Future of ESP Technology
ESP technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being developed all the time. Here are some trends to watch for in the future:
16.1 Integration with Autonomous Driving Systems
ESP is likely to play an increasingly important role in autonomous driving systems. As vehicles become more autonomous, ESP will be used to provide a safety net in case of system failures or unexpected events.
16.2 Enhanced Sensor Technology
New sensor technologies, such as advanced radar and lidar systems, will provide ESP with more accurate and detailed information about the vehicle’s surroundings. This will allow ESP to react more quickly and effectively to potential hazards.
16.3 Over-the-Air Updates
Over-the-air updates will allow manufacturers to improve ESP performance and add new features without requiring drivers to visit a service center.
17. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About ESP Unavailable Mercedes
Q1: What does “ESP Unavailable” mean on my Mercedes?
A1: It indicates a malfunction in the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), a safety system that helps prevent skidding and loss of control.
Q2: Can I drive my Mercedes with the “ESP Unavailable” message on?
A2: While you can drive, it’s not recommended. The ESP system is compromised, reducing stability and safety, especially in adverse conditions. Get it checked ASAP.
Q3: What are the common causes of “ESP Unavailable”?
A3: Faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, yaw rate sensor malfunctions, brake light switch problems, low battery voltage, or wiring issues.
Q4: How can I diagnose the “ESP Unavailable” issue?
A4: Start with a visual inspection, then use an OBD-II scanner to check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). Further diagnostics may be needed.
Q5: Can I fix the “ESP Unavailable” issue myself?
A5: Some repairs, like replacing a wheel speed sensor, are DIY-friendly. More complex issues require professional expertise.
Q6: How much does it cost to repair the “ESP Unavailable” issue?
A6: Costs vary widely, from a few hundred dollars for a sensor replacement to over a thousand for control unit repairs.
Q7: How can I prevent ESP problems?
A7: Regular vehicle maintenance, proper tire inflation, avoiding harsh driving, checking for water leaks, and maintaining a healthy battery.
Q8: Are there specific ESP issues common to Mercedes-Benz models?
A8: Yes, certain models like the C-Class (W204), E-Class (W211), and S-Class (W221) have known ESP-related problems.
Q9: Where can I find a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician?
A9: Look for ASE certification, check online reviews, ask for recommendations, and verify their experience with Mercedes vehicles.
Q10: What tools do I need for ESP repairs?
A10: An OBD-II scanner, multimeter, socket set, wrench set, screwdriver set, wire strippers, and possibly a scan tool with ESP calibration capabilities.
18. Conclusion: Prioritizing Safety with a Functional ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a vital safety system in your Mercedes-Benz, helping you maintain control in challenging driving situations. Addressing the “ESP Unavailable” message promptly is crucial for your safety and the safety of others. By understanding the potential causes of ESP problems, following the diagnostic steps outlined in this guide, and seeking professional assistance when needed, you can ensure that your ESP system is functioning optimally. Remember, CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner for all your Mercedes-Benz diagnostic and repair needs. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to learn more. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.