ESP Off Mercedes: Diagnose, Reset, and Drive Safely
Esp Off Mercedes: Understanding the ESP system, what the warning light means, common causes for it illuminating, and how to properly diagnose and address the issue is crucial for Mercedes-Benz owners. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides solutions for diagnosing Mercedes-Benz vehicles to ensure your safety and the optimal performance of your vehicle’s stability systems. Learn about electronic stability control, Mercedes-Benz diagnostics, and automotive repair.
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz ESP® System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP®) in your Mercedes-Benz is a crucial safety feature designed to maintain control in critical driving situations. According to Mercedes-Benz, ESP® monitors driving dynamics and intervenes when it detects a loss of control, such as skidding. It works by selectively braking individual wheels to help steer the vehicle back on course. ESP® integrates with other systems like ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and BAS (Brake Assist System) to provide comprehensive stability enhancement.
1.1 How ESP® Enhances Vehicle Stability
ESP® uses sensors to monitor several factors, including steering angle, wheel speed, and lateral acceleration. If these sensors detect a discrepancy between the driver’s intended direction and the vehicle’s actual path, ESP® activates. This intervention is often so subtle that the driver may not even notice it, but it can make a significant difference in preventing accidents. Modern ESP® systems can apply braking force to one or more wheels independently, and in some cases, even adjust engine torque to help maintain control.
ESP® technology has been proven to significantly reduce accidents. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has conducted studies showing that ESP® can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 33%. This highlights the importance of ensuring that your ESP® system is functioning correctly.
1.2 The Role of ABS and BAS in ESP® Functionality
ESP® relies on the capabilities of both the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) and the Brake Assist System (BAS) to function effectively. ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. BAS, on the other hand, detects emergency braking situations and applies maximum braking force more quickly than a driver might be able to on their own.
These systems work together to provide a safety net in challenging driving conditions. For instance, if you need to brake suddenly on a slippery surface, ABS will prevent wheel lockup, BAS will ensure maximum braking force is applied, and ESP® will help keep the vehicle stable and on course.
2. Decoding the ESP Off Mercedes Warning Light
The ESP warning light in your Mercedes-Benz serves as a vital indicator of the system’s status. It can appear in different forms, each signaling a specific condition. Understanding these signals is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s safety and performance. The ESP light typically looks like a car with skid marks behind it. This symbol is universal across most makes and models, making it easy to recognize.
2.1 ESP® Light: Flashing vs. Solid Illumination
A flashing ESP light indicates that the system is actively engaged and working to stabilize the vehicle. This typically occurs when the car detects a loss of traction, such as during hard acceleration on a slippery surface or when cornering aggressively. When the light is flashing, ESP® is intervening to prevent skidding and maintain control.
A solidly illuminated ESP light indicates that the system is either disabled or experiencing a malfunction. In this case, ESP® is not actively working to stabilize the vehicle, and the driver should exercise extra caution. It’s important to address the underlying cause of a solid ESP light as soon as possible to ensure that the system is available when needed.
2.2 Common Causes for the ESP® Light to Illuminate
Several factors can cause the ESP light to illuminate, ranging from simple fixes to more complex issues. Here are some of the most common causes:
- ESP® System Malfunction: A fault within the ESP system itself, such as a sensor failure or a problem with the control module, can trigger the light.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Issues: ESP® relies on accurate wheel speed data to function correctly. If one or more wheel speed sensors are faulty or dirty, the system may not work properly.
- Steering Angle Sensor Problems: The steering angle sensor provides information about the driver’s intended direction. A malfunctioning sensor can disrupt ESP® functionality.
- Low Tire Pressure: ESP® uses tire pressure data as part of its calculations. Low tire pressure can affect the system’s accuracy and trigger the warning light.
- Alignment Issues: Improper wheel alignment can also interfere with ESP® functionality, as it affects the vehicle’s handling and stability.
2.3 The Relationship Between ESP® and BAS/ABS Lights
In some cases, the ESP® light may illuminate in conjunction with the ABS or BAS lights. This often indicates a problem that affects multiple systems, such as a faulty wheel speed sensor that impacts both ABS and ESP®. When multiple warning lights are illuminated, it’s particularly important to have the vehicle diagnosed by a qualified technician to identify the root cause of the issue.
It is important to note, a Mercedes equipped with a 4MATIC system will also show a warning light if it detects a problem with the all-wheel-drive system.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing ESP® Issues
Diagnosing ESP® issues requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause of the problem. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot ESP®-related warning lights:
3.1 Initial Inspection: Checking for Obvious Issues
Begin by visually inspecting the vehicle for any obvious issues. Check tire pressure to ensure it is within the recommended range. Examine the wheel speed sensors for any signs of damage or contamination. Also, inspect the brake system for any visible problems, such as leaks or worn brake pads.
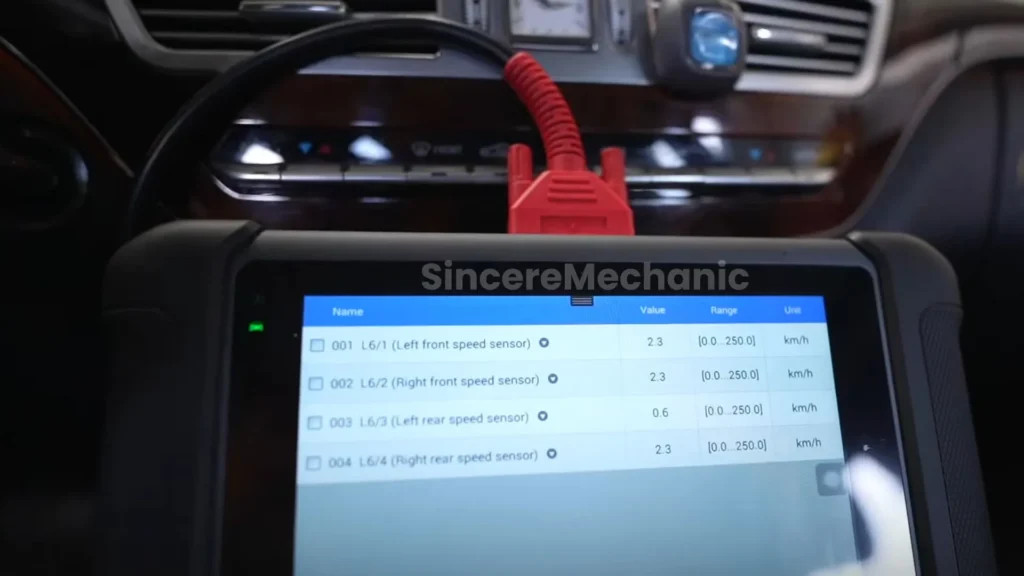
3.2 Using an OBD-II Scanner to Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Next, use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) stored in the vehicle’s computer. DTCs can provide valuable information about the nature and location of the problem. Connect the scanner to the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard, and follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve the codes.
If you’re looking for a reliable OBD-II scanner, CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools designed to help you accurately identify and resolve automotive issues. These tools are essential for both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert guidance on choosing the right tool for your needs.
3.3 Interpreting Common ESP®-Related DTCs
Once you have retrieved the DTCs, research their meaning to understand the potential causes of the problem. Some common ESP®-related DTCs include:
- C1000: Control Module Faulty
- C1100: Wheel Speed Sensor Front Right Circuit Malfunction
- C1120: Steering Angle Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- C1140: BAS Solenoid Valve Circuit Malfunction
These codes can provide valuable clues about the source of the ESP® issue. For example, a C1100 code suggests a problem with the front right wheel speed sensor, while a C1120 code indicates a potential issue with the steering angle sensor.
3.4 Advanced Diagnostic Procedures: Using a Multimeter and Scan Tool
For more complex ESP® issues, advanced diagnostic procedures may be necessary. This can involve using a multimeter to test the electrical circuits of the wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, and other components. Additionally, a more advanced scan tool may be required to perform live data monitoring and component testing.
Live data monitoring allows you to observe the real-time values of various sensors and components while the vehicle is in operation. This can help you identify intermittent problems or subtle deviations from normal values. Component testing, on the other hand, allows you to activate individual components, such as ABS solenoids, to verify their functionality.
4. Resetting the ESP Off Mercedes Light: A Comprehensive Guide
After addressing the underlying cause of the ESP® warning light, it may be necessary to reset the system to clear the light and restore normal operation. Here’s a comprehensive guide to resetting the ESP® light on your Mercedes-Benz:
4.1 Manual Reset Procedure: When and How to Perform It
In some cases, the ESP® light may clear automatically after the issue has been resolved. However, in other cases, a manual reset may be required. To perform a manual reset, follow these steps:
- Turn off the ignition.
- Locate the “ESP Off” button (if equipped) and press it.
- Start the engine and drive the vehicle for a short distance.
- The ESP® light should turn off.
If the ESP® light does not turn off after performing these steps, you may need to use a scan tool to clear the DTCs and reset the system.
4.2 Using a Scan Tool to Clear DTCs and Reset the ESP® System
A scan tool can be used to clear the DTCs that triggered the ESP® light and reset the system. Connect the scan tool to the OBD-II port and follow the instructions to clear the codes. After clearing the codes, the ESP® light should turn off.
It’s important to note that simply clearing the codes without addressing the underlying cause of the problem will only result in the ESP® light turning on again. Therefore, it’s essential to diagnose and repair the issue before attempting to reset the system.
4.3 Addressing Recurring ESP® Light Issues
If the ESP® light continues to reappear after being reset, it indicates that the underlying problem has not been fully resolved. In this case, further diagnosis and repair may be necessary. Consult a qualified technician to identify the root cause of the recurring ESP® light issue and perform the necessary repairs.
5. Preventative Maintenance to Avoid ESP® Problems
Preventative maintenance is key to avoiding ESP® problems and ensuring the long-term reliability of your Mercedes-Benz. Here are some preventative maintenance tips to keep in mind:
5.1 Regular Tire Pressure Monitoring and Maintenance
Proper tire pressure is essential for ESP® functionality. Check your tire pressure regularly and maintain it at the recommended level. Low tire pressure can affect ESP® accuracy and trigger the warning light.
5.2 Wheel Alignment and Balancing Best Practices
Improper wheel alignment and balancing can also interfere with ESP® functionality. Have your wheels aligned and balanced regularly to ensure optimal handling and stability.
5.3 Inspecting and Cleaning Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are critical to ESP® operation. Inspect them regularly for any signs of damage or contamination. Clean the sensors as needed to ensure accurate readings.
5.4 Brake System Maintenance: Pads, Rotors, and Fluid
Proper brake system maintenance is also important for ESP® functionality. Replace worn brake pads and rotors as needed. Flush and replace brake fluid regularly to maintain optimal braking performance.
6. When to Seek Professional Help: Finding the Right Mechanic
While some ESP® issues can be resolved with DIY troubleshooting and repair, others may require professional help. Here are some situations where it’s best to seek the assistance of a qualified mechanic:
6.1 Identifying Complex and Intermittent Issues
Complex and intermittent ESP® issues can be difficult to diagnose without specialized tools and expertise. If you’re unable to identify the root cause of the problem, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic.
6.2 Working with Advanced Diagnostic Equipment
Advanced diagnostic equipment, such as scan tools with live data monitoring and component testing capabilities, may be required to diagnose certain ESP® issues. If you don’t have access to this equipment, a professional mechanic can help.
6.3 Ensuring Proper Repairs and System Calibration
Proper repairs and system calibration are essential for ESP® functionality. If you’re not confident in your ability to perform the necessary repairs and calibrations, it’s best to leave it to a professional.
6.4 How CARDIAGTECH.NET Can Assist with Your Diagnostic Needs
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the challenges of diagnosing and repairing modern vehicles. That’s why we offer a wide range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you get the job done right. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, we have the tools you need to accurately diagnose and resolve ESP® issues.
Our selection includes advanced scan tools, OBD-II scanners, multimeters, and other diagnostic equipment. We also offer expert technical support to help you troubleshoot and resolve complex automotive issues. Contact us today via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 to learn more about our products and services.
7. The Dangers of Driving with ESP® Disabled
Driving with ESP® disabled can be dangerous, especially in challenging driving conditions. Here are some of the risks associated with driving without ESP®:
7.1 Increased Risk of Skidding and Loss of Control
ESP® is designed to prevent skidding and maintain control in emergency situations. Without ESP®, the risk of losing control of the vehicle is significantly increased, especially on slippery surfaces or during sudden maneuvers.
7.2 Reduced Stability in Emergency Maneuvers
ESP® helps to stabilize the vehicle during emergency maneuvers, such as sudden braking or evasive steering. Without ESP®, the vehicle may be more prone to instability and rollover in these situations.
7.3 Potential for Accidents and Injuries
The increased risk of skidding and loss of control can lead to accidents and injuries. ESP® is a vital safety feature that can help prevent accidents and protect drivers and passengers.
7.4 Why ESP® Should Always Be Enabled (Except in Very Specific Scenarios)
ESP® should always be enabled, except in very specific scenarios. One such scenario is when driving in deep snow or mud, where wheel spin may be necessary to maintain momentum. However, in most other driving conditions, ESP® should be enabled to provide maximum safety and stability.
8. Exploring the Mercedes-Benz BAS ESP® Light
The Mercedes-Benz BAS ESP® light indicates a problem with the Brake Assist System (BAS) and Electronic Stability Program (ESP®). BAS enhances braking force during emergency stops, while ESP® prevents skidding. When this light illuminates, it suggests an issue affecting both systems.
8.1 Understanding the Combined Functionality of BAS and ESP®
BAS and ESP® work in tandem to provide optimal safety. BAS detects emergency braking and applies maximum braking force, while ESP® prevents wheel lockup and maintains stability. Together, they reduce stopping distances and enhance control.
8.2 Common Causes for the BAS ESP® Light to Illuminate
Several factors can trigger the BAS ESP® light, including:
- Faulty wheel speed sensors
- Steering angle sensor issues
- Brake light switch malfunction
- Hydraulic unit problems
8.3 Diagnostic Steps Specific to the BAS ESP® Light
Diagnosing the BAS ESP® light involves:
- Checking brake fluid level
- Inspecting brake light switch
- Scanning for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Testing wheel speed sensors
8.4 Solutions and Repairs for BAS ESP® Light Issues
Possible solutions include:
- Replacing faulty sensors
- Repairing wiring issues
- Replacing the brake light switch
- Flushing brake fluid
9. Advanced ESP® Features in Modern Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles incorporate advanced ESP® features that enhance safety and performance.
9.1 Adaptive ESP®: Adjusting to Different Driving Conditions
Adaptive ESP® adjusts its intervention based on driving conditions, such as road surface and vehicle load. It optimizes stability control for varying scenarios.
9.2 Curve Dynamic Assist: Enhancing Cornering Stability
Curve Dynamic Assist applies targeted braking to the inside wheels during cornering, reducing understeer and improving stability.
9.3 Crosswind Assist: Counteracting Strong Winds
Crosswind Assist detects and compensates for strong crosswinds, preventing the vehicle from drifting out of its lane.
9.4 Load Adaptive Control: Optimizing Stability Based on Vehicle Load
Load Adaptive Control adjusts ESP® parameters based on vehicle load, ensuring optimal stability regardless of cargo or passenger weight.
9.5 How These Features Contribute to Overall Safety and Performance
These advanced features provide an additional layer of safety and enhance driving confidence in various conditions. They minimize the risk of accidents and improve vehicle handling.
10. CARDIAGTECH.NET Solutions for Mercedes-Benz Diagnostics
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you accurately diagnose and resolve Mercedes-Benz ESP® issues.
10.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Tools for ESP®-Related Problems
We provide advanced scan tools, OBD-II scanners, and multimeters designed for comprehensive diagnostics.
10.2 Expert Technical Support for Troubleshooting and Repairs
Our expert technical support team assists with troubleshooting complex issues and provides guidance on repairs.
10.3 High-Quality Replacement Parts for ESP® Components
We offer high-quality replacement parts for ESP® components, including sensors, control modules, and hydraulic units.
10.4 Contact Information: Address, WhatsApp Number, and Website
Contact us at:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Let CARDIAGTECH.NET be your partner in maintaining the safety and performance of your Mercedes-Benz. Reach out today for expert advice and top-quality diagnostic solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What does the ESP® light mean on my Mercedes-Benz?
The ESP® light indicates the Electronic Stability Program is either actively working to stabilize the vehicle (flashing) or is disabled (solid).
-
Can I drive with the ESP® light on?
If the light is flashing, drive carefully. If solid, ESP® is disabled, reducing stability control.
-
How do I reset the ESP® light on my Mercedes-Benz?
Try turning the steering wheel lock-to-lock or use a scan tool to clear codes.
-
What causes the ESP® light to come on?
Common causes include sensor failures, steering angle issues, or system malfunctions.
-
Is it dangerous to drive with ESP® disabled?
Yes, it reduces stability, increasing the risk of accidents, especially in adverse conditions.
-
How do I diagnose ESP® issues?
Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve DTCs and inspect sensors and wiring.
-
What is BAS ESP® light, and what does it indicate?
It indicates a problem with both the Brake Assist System and Electronic Stability Program.
-
What are some advanced ESP® features in modern Mercedes-Benz vehicles?
Adaptive ESP®, Curve Dynamic Assist, and Crosswind Assist are some advanced features.
-
How can CARDIAGTECH.NET help with ESP® diagnostics?
We offer diagnostic tools, technical support, and high-quality replacement parts.
-
Why is preventative maintenance important for the ESP® system?
It helps avoid ESP® problems, ensuring long-term reliability and safety.
By addressing these questions, drivers can better understand and maintain their ESP® system for safer driving.