Esp Inoperative Mercedes C Class: Diagnosis And Solutions
Is your Mercedes-Benz C-Class displaying an “ESP Inoperative” warning? Don’t worry. This comprehensive guide from CARDIAGTECH.NET provides expert insights into the causes, troubleshooting steps, and solutions to resolve this issue, ensuring your driving experience remains safe and enjoyable. Learn how to diagnose the problem, understand the role of the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), and explore potential fixes. Let’s dive in to ensure your Mercedes maintains its stability and performance with cutting-edge diagnostic tools.
1. Understanding the Mercedes-Benz ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) in your Mercedes-Benz is a critical safety feature designed to prevent skidding and maintain control during challenging driving conditions. It integrates various sensors and systems to monitor the vehicle’s direction and stability, intervening when it detects a loss of traction or potential instability. This system helps maintain vehicle control, especially in adverse weather conditions or during sudden maneuvers.
1.1. The Role of ESP in Vehicle Stability
ESP works by monitoring wheel speed, steering angle, and yaw rate to detect deviations from the driver’s intended path. If it senses the vehicle is beginning to skid, it selectively applies brakes to individual wheels and reduces engine power to help the driver regain control. ESP enhances stability and prevents accidents, making it an essential safety feature. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 35%.
1.2. Components of the ESP System
The ESP system comprises several key components, including:
- Wheel Speed Sensors: These sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and transmit data to the ESP control unit.
- Steering Angle Sensor: This sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the driver’s intended direction.
- Yaw Rate Sensor: This sensor detects the vehicle’s rotation around its vertical axis.
- Lateral Acceleration Sensor: This sensor measures the vehicle’s sideways acceleration.
- ESP Control Unit: This unit processes data from the sensors and determines when and how to intervene to maintain stability.
1.3. How ESP Prevents Accidents
ESP uses data from various sensors to identify potential loss of control situations. For instance, if the system detects oversteer (the rear of the car sliding out), it might apply the brake to the outer front wheel to create a counteracting force. Similarly, if it detects understeer (the front wheels losing grip), it might apply the brake to the inner rear wheel. By selectively braking individual wheels and reducing engine power, ESP helps the driver maintain control and prevent accidents.
2. Decoding the “ESP Inoperative” Warning
When the “ESP Inoperative” warning appears on your Mercedes-Benz C-Class dashboard, it indicates that the ESP system has been disabled or is malfunctioning. This means the vehicle’s stability control features are not functioning, increasing the risk of losing control in challenging driving conditions.
2.1. Understanding the Warning Message
The “ESP Inoperative” warning is typically accompanied by a symbol on the dashboard, often depicting a car skidding. This warning indicates that the ESP system is not actively monitoring and correcting the vehicle’s stability. Driving without ESP can be particularly dangerous in wet, icy, or snowy conditions.
2.2. Immediate Actions to Take
Upon seeing the “ESP Inoperative” warning, it’s crucial to take the following steps:
- Reduce Speed: Drive at a slower speed than usual, especially in adverse weather conditions.
- Increase Following Distance: Maintain a greater distance from the vehicle ahead to allow more time to react to unexpected situations.
- Avoid Sudden Maneuvers: Refrain from making sudden turns or braking abruptly, as this can increase the risk of losing control.
- Schedule a Diagnostic Check: Visit CARDIAGTECH.NET or a trusted mechanic for a thorough diagnostic check to identify and resolve the underlying issue.
2.3. Potential Risks of Driving with ESP Inoperative
Driving with ESP inoperative increases the risk of losing control, particularly in adverse weather conditions or during emergency maneuvers. Without ESP, the vehicle is more susceptible to skidding, which can lead to accidents. Additionally, it may affect other safety systems that rely on ESP data, such as ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and traction control.
3. Common Causes of ESP Malfunctions in Mercedes C-Class
Several factors can trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning in your Mercedes-Benz C-Class. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective troubleshooting and repair.
3.1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors monitor the speed of each wheel and transmit data to the ESP control unit. If one or more of these sensors fail, the ESP system may not receive accurate information, leading to the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
- Symptoms: ABS light on, traction control light on, speedometer malfunction, rough shifting.
- Troubleshooting: Use a diagnostic scanner to identify the faulty sensor. Inspect the sensor and wiring for damage.
- Solution: Replace the faulty wheel speed sensor. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers high-quality replacement sensors to ensure accurate data transmission.
3.2. Steering Angle Sensor Issues
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel and provides data to the ESP system. A malfunctioning steering angle sensor can disrupt the ESP system’s ability to determine the driver’s intended direction.
- Symptoms: ESP light on, difficulty maintaining lane, inaccurate steering response.
- Troubleshooting: Use a diagnostic scanner to check the steering angle sensor’s readings. Perform a steering angle sensor calibration.
- Solution: Replace the steering angle sensor if calibration fails. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides professional-grade diagnostic tools to accurately diagnose and address steering angle sensor issues.
3.3. Low Battery Voltage
The ESP system relies on a stable power supply to function correctly. Low battery voltage can cause the ESP system to malfunction and trigger the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
- Symptoms: ESP light on, difficulty starting the car, dim headlights, slow electrical functions.
- Troubleshooting: Check the battery voltage with a multimeter. Ensure the battery terminals are clean and securely connected.
- Solution: Charge or replace the battery if the voltage is below the recommended level. CARDIAGTECH.NET recommends using a high-quality battery to ensure reliable performance.
3.4. Faulty Brake Light Switch
The brake light switch signals the ESP system when the brakes are applied. A faulty brake light switch can send incorrect signals, causing the ESP system to malfunction.
- Symptoms: ESP light on, brake lights not working, cruise control malfunction.
- Troubleshooting: Check the brake lights to see if they are working. Use a diagnostic scanner to check the brake light switch signal.
- Solution: Replace the faulty brake light switch. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers durable brake light switches that ensure accurate signaling.
3.5. ESP Control Unit Malfunction
The ESP control unit processes data from various sensors and controls the ESP system’s functions. A malfunctioning ESP control unit can cause the “ESP Inoperative” warning.
- Symptoms: ESP light on, ABS light on, traction control light on, multiple ESP-related error codes.
- Troubleshooting: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for error codes related to the ESP control unit.
- Solution: Replace the ESP control unit. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides access to advanced diagnostic tools that can help pinpoint control unit issues.
 Mercedes ESP Wheel Speed Sensor
Mercedes ESP Wheel Speed Sensor
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing ESP Issues
Diagnosing ESP issues requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to identify the root cause of the “ESP Inoperative” warning in your Mercedes-Benz C-Class.
4.1. Initial Inspection
Begin by visually inspecting the vehicle for any obvious issues.
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are properly inflated.
- Inspect Wheel Speed Sensors: Look for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Check Brake Lights: Verify that all brake lights are functioning correctly.
- Inspect Wiring: Check for damaged or corroded wiring related to the ESP system.
4.2. Using a Diagnostic Scanner
A diagnostic scanner is essential for accurately diagnosing ESP issues.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard.
- Read Error Codes: Retrieve any stored error codes related to the ESP system, ABS, or traction control.
- Interpret Error Codes: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource to understand the meaning of the error codes.
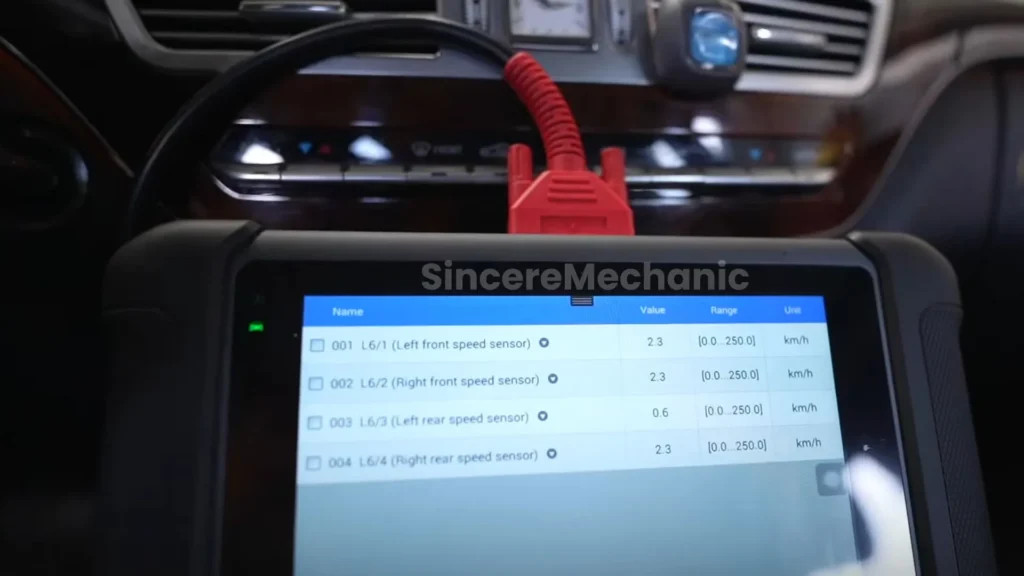
4.3. Testing Wheel Speed Sensors
Test each wheel speed sensor to ensure it is functioning correctly.
- Access Sensor Data: Use the diagnostic scanner to view live data from each wheel speed sensor.
- Compare Readings: Compare the readings from each sensor while driving slowly. The readings should be similar.
- Identify Faulty Sensor: If one sensor shows an erratic or absent reading, it is likely faulty and needs replacement.
4.4. Checking the Steering Angle Sensor
Verify the steering angle sensor’s accuracy using a diagnostic scanner.
- Access Steering Angle Data: Use the diagnostic scanner to view the steering angle sensor’s readings.
- Turn the Steering Wheel: Slowly turn the steering wheel from lock to lock and observe the readings.
- Verify Accuracy: The readings should correspond accurately to the steering wheel’s position. If the readings are erratic or inaccurate, the sensor may need calibration or replacement.
4.5. Evaluating Battery Voltage
Ensure the battery voltage is within the recommended range.
- Use a Multimeter: Connect a multimeter to the battery terminals.
- Check Voltage: Measure the battery voltage with the engine off and with the engine running.
- Compare Readings: The voltage should be around 12.6 volts with the engine off and between 13.7 and 14.7 volts with the engine running. If the voltage is outside these ranges, the battery or charging system may need attention.
5. Repairing ESP Malfunctions: A DIY Guide
Once you’ve identified the cause of the ESP malfunction, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to common ESP repairs.
5.1. Replacing a Wheel Speed Sensor
Replacing a faulty wheel speed sensor is a straightforward process.
- Gather Tools: You’ll need a wrench, socket set, and a new wheel speed sensor from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Loosen the Wheel: Loosen the lug nuts on the wheel with the faulty sensor.
- Jack Up the Car: Safely jack up the car and secure it with jack stands.
- Remove the Wheel: Remove the wheel to access the wheel speed sensor.
- Disconnect the Sensor: Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the Sensor: Remove the bolt securing the sensor and carefully remove the sensor.
- Install the New Sensor: Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly seated and secured.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the sensor.
- Reinstall the Wheel: Reinstall the wheel and tighten the lug nuts.
- Lower the Car: Lower the car and torque the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Test the System: Use a diagnostic scanner to clear any error codes and verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
5.2. Calibrating the Steering Angle Sensor
Calibrating the steering angle sensor requires a diagnostic scanner.
- Connect the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD-II port.
- Access Calibration Function: Navigate to the steering angle sensor calibration function in the scanner’s menu.
- Follow Instructions: Follow the on-screen instructions to calibrate the sensor. This typically involves turning the steering wheel to specific positions.
- Verify Calibration: After calibration, verify that the sensor readings are accurate.
5.3. Replacing the Brake Light Switch
Replacing the brake light switch is a simple task.
- Locate the Switch: The brake light switch is typically located near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the Switch: Disconnect the electrical connector from the switch.
- Remove the Switch: Remove the switch by twisting or unscrewing it.
- Install the New Switch: Install the new switch, ensuring it is properly seated and secured.
- Reconnect the Electrical Connector: Reconnect the electrical connector to the switch.
- Test the Brake Lights: Verify that the brake lights are functioning correctly.
5.4. Addressing Low Battery Voltage
Addressing low battery voltage involves charging or replacing the battery.
- Charge the Battery: Use a battery charger to charge the battery to the recommended voltage.
- Test the Battery: After charging, test the battery to ensure it holds a charge.
- Replace the Battery: If the battery fails to hold a charge, replace it with a new battery from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Check the Charging System: Ensure the alternator is functioning correctly and charging the battery while the engine is running.
6. Advanced Diagnostic Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of advanced diagnostic tools to help you accurately diagnose and repair ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz C-Class.
6.1. OBD-II Scanners
Our OBD-II scanners provide comprehensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Features: Read and clear error codes, view live data, perform component testing.
- Benefits: Accurate diagnostics, easy to use, cost-effective.
6.2. ABS/ESP Diagnostic Tools
Specialized tools for diagnosing ABS and ESP systems.
- Features: ABS bleeding, ESP calibration, sensor testing.
- Benefits: Precise diagnostics, advanced functionality, reliable performance.
6.3. Multimeters
Essential tools for electrical testing.
- Features: Voltage testing, continuity testing, current testing.
- Benefits: Accurate measurements, durable construction, easy to use.
6.4. Battery Testers
Ensure your battery is in optimal condition.
- Features: Battery voltage testing, charging system testing, load testing.
- Benefits: Quick and accurate results, easy to use, essential for battery maintenance.
7. Preventive Maintenance for ESP Systems
Preventive maintenance can help avoid ESP malfunctions and ensure the system functions correctly.
7.1. Regular Inspections
Regularly inspect the ESP system components.
- Check Wheel Speed Sensors: Look for damage or loose connections.
- Inspect Wiring: Check for damaged or corroded wiring.
- Verify Tire Pressure: Ensure all tires are properly inflated.
- Check Brake Lights: Verify that all brake lights are functioning correctly.
7.2. Battery Maintenance
Maintain the battery in good condition.
- Keep Terminals Clean: Clean the battery terminals regularly to prevent corrosion.
- Check Voltage: Check the battery voltage periodically.
- Replace as Needed: Replace the battery when it reaches the end of its service life.
7.3. Proper Tire Care
Ensure proper tire care.
- Maintain Correct Pressure: Keep tires inflated to the recommended pressure.
- Regularly Rotate Tires: Rotate tires to ensure even wear.
- Replace Worn Tires: Replace tires when they are worn to ensure optimal traction.
7.4. Routine Diagnostic Scans
Perform routine diagnostic scans.
- Check for Error Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for any stored error codes.
- Address Issues Promptly: Address any issues promptly to prevent them from escalating.
8. The Importance of Professional Assistance
While many ESP issues can be resolved with DIY repairs, some situations require professional assistance.
8.1. When to Seek Professional Help
Seek professional help in the following situations:
- Complex Issues: If you are unable to diagnose the issue or the repair is beyond your skill level.
- Persistent Problems: If the “ESP Inoperative” warning persists after attempting DIY repairs.
- Safety Concerns: If you are concerned about the safety of driving the vehicle.
8.2. Benefits of Professional Service
Professional service offers several benefits.
- Expert Diagnostics: Trained technicians can accurately diagnose complex issues.
- Specialized Tools: Professional mechanics have access to specialized tools and equipment.
- Quality Repairs: Professional repairs are performed to a high standard, ensuring reliability and safety.
8.3. Finding a Trusted Mechanic
Finding a trusted mechanic is essential for quality service.
- Check Reviews: Look for online reviews and ratings.
- Ask for Referrals: Ask friends, family, or colleagues for referrals.
- Verify Certifications: Ensure the mechanic is certified and experienced in Mercedes-Benz repairs.
9. Real-World Scenarios: ESP Troubleshooting
Let’s examine some real-world scenarios and how to troubleshoot ESP issues.
9.1. Scenario 1: ESP Light After Battery Replacement
Problem: The “ESP Inoperative” light comes on after replacing the battery.
Possible Causes:
- Steering angle sensor needs calibration.
- Faulty wheel speed sensor.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for error codes.
- Calibrate the steering angle sensor.
- Test wheel speed sensors.
Solution: Calibrate the steering angle sensor. If the issue persists, replace any faulty wheel speed sensors.
9.2. Scenario 2: ESP Light in Wet Weather
Problem: The “ESP Inoperative” light comes on in wet weather.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty wheel speed sensor.
- Corroded wiring.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect wheel speed sensors for damage.
- Check wiring for corrosion.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for error codes.
Solution: Replace any faulty wheel speed sensors and repair or replace corroded wiring.
9.3. Scenario 3: ESP Light During Hard Braking
Problem: The “ESP Inoperative” light comes on during hard braking.
Possible Causes:
- Faulty brake light switch.
- ABS malfunction.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check brake lights for proper function.
- Use a diagnostic scanner to check for error codes related to the ABS system.
- Test the brake light switch.
Solution: Replace the faulty brake light switch or address any ABS malfunctions.
10. Conclusion: Maintaining Your Mercedes-Benz C-Class ESP System
The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a critical safety feature in your Mercedes-Benz C-Class. Understanding how it works, recognizing the signs of a malfunction, and performing regular maintenance can help ensure your vehicle remains safe and reliable. Whether you choose to perform DIY repairs or seek professional assistance, CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to provide the tools, knowledge, and support you need to keep your Mercedes-Benz C-Class running smoothly.
Prioritize your safety and your vehicle’s well-being. By addressing ESP issues promptly and maintaining the system effectively, you can continue to enjoy a secure and confident driving experience. Remember, a well-maintained ESP system not only enhances safety but also preserves the performance and value of your Mercedes-Benz C-Class.
Don’t let ESP malfunctions compromise your driving experience. With the right knowledge, tools, and resources, you can confidently diagnose and resolve ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz C-Class. Trust CARDIAGTECH.NET to provide top-quality diagnostic tools and expert guidance to keep your vehicle performing at its best.
Ready to take control of your Mercedes-Benz C-Class maintenance? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and high-quality diagnostic tools to keep your ESP system functioning flawlessly. Your safety is our priority, and we’re here to help you maintain a secure and enjoyable driving experience.
Contact us today!
Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
Embrace the road ahead with confidence, knowing that your Mercedes-Benz C-Class is equipped with a fully functional ESP system. Let CARDIAGTECH.NET be your trusted partner in maintaining the safety and performance of your vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What does the “ESP Inoperative” warning mean?
The “ESP Inoperative” warning indicates that the Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is disabled or malfunctioning, meaning the vehicle’s stability control features are not functioning.
2. Can I drive with the “ESP Inoperative” light on?
It is not recommended to drive with the “ESP Inoperative” light on, as it increases the risk of losing control, especially in adverse weather conditions.
3. What are the common causes of ESP malfunctions?
Common causes include faulty wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor issues, low battery voltage, a faulty brake light switch, and ESP control unit malfunctions.
4. How can I diagnose ESP issues?
You can diagnose ESP issues by performing a visual inspection, using a diagnostic scanner to read error codes, testing wheel speed sensors, checking the steering angle sensor, and evaluating battery voltage.
5. What tools do I need to diagnose and repair ESP issues?
Essential tools include a diagnostic scanner, multimeter, socket set, wrench, and replacement parts from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
6. How do I reset the ESP system after a repair?
After performing a repair, use a diagnostic scanner to clear any error codes and verify that the ESP system is functioning correctly.
7. Can low tire pressure cause the ESP light to come on?
Yes, low tire pressure can affect the ESP system and cause the warning light to illuminate. Ensure all tires are properly inflated.
8. Is it safe to disable ESP?
Disabling ESP is generally not recommended, as it reduces the vehicle’s stability control. However, it may be necessary in certain situations, such as driving in deep snow.
9. How often should I have my ESP system checked?
You should have your ESP system checked during routine maintenance, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles.
10. Where can I find high-quality replacement parts for my ESP system?
You can find high-quality replacement parts for your ESP system at CARDIAGTECH.NET. We offer a wide range of sensors, switches, and control units to ensure your Mercedes-Benz C-Class performs at its best.

