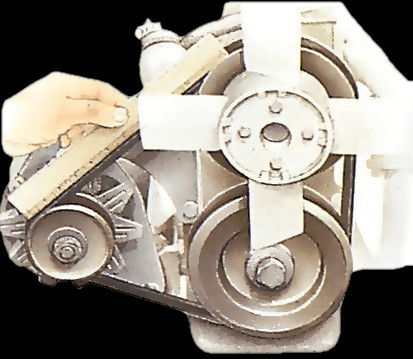
What Is the Operating Principle of a Torque Converter?

CARDIAGTECH.NET sheds light on the operating principle of a torque converter. Unlock peak performance and efficiency in your vehicle’s automatic transmission system. Stay tuned to explore how this innovative device optimizes power delivery for a smoother, more responsive driving experience. Equip yourself with the knowledge to maintain optimal automotive transmission fluid.
1. Understanding the Basics: What is a Torque Converter?
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. It is typically used in automatic transmissions of motor vehicles. At its core, the torque converter bridges the gap between the engine and the transmission, allowing the engine to continue spinning even when the wheels are stationary. This innovative component facilitates smooth starts, prevents engine stalling, and multiplies torque as needed, ensuring optimal performance and driving comfort.
The main functions of a torque converter are:
- Allowing the engine to run even when the wheels are stopped, such as when idling at a traffic light.
- Providing smooth starts and preventing engine stalling.
- Multiplying torque when needed, such as during acceleration or climbing hills.
2. The Key Components of a Torque Converter
A torque converter houses four essential components, each playing a pivotal role in its operation:
- Impeller (Pump): Connected to the engine’s flywheel, the impeller spins at engine speed, acting as a centrifugal pump to propel fluid towards the turbine.
- Turbine: Positioned opposite the impeller, the turbine is connected to the transmission’s input shaft. The fluid from the impeller strikes the turbine blades, causing it to rotate and transfer power to the transmission.
- Stator: Located between the turbine and impeller, the stator redirects fluid flow, multiplying torque by changing the angle at which the fluid re-enters the impeller.
- Transmission Fluid: Specially formulated hydraulic fluid acts as the medium for transferring energy between the impeller and turbine.
 Torque converter diagram showing impeller, turbine, and stator
Torque converter diagram showing impeller, turbine, and stator
3. The Operating Principle: How Does a Torque Converter Work?
The torque converter works through a fascinating interplay of fluid dynamics and mechanical engineering.
- Engine Input: The engine spins the impeller, which acts like a centrifugal pump.
- Fluid Acceleration: The impeller’s curved vanes fling transmission fluid outward, creating a swirling vortex.
- Turbine Engagement: The high-speed fluid strikes the turbine blades, causing it to rotate. The turbine is connected to the transmission input shaft, transferring power to the gearbox.
- Torque Multiplication: As fluid exits the turbine, it flows into the stator, which redirects the fluid’s angle of attack. This redirected flow effectively multiplies torque as it re-enters the impeller, boosting the engine’s power output.
- Continuous Cycle: The fluid circulates continuously between the impeller, turbine, and stator, creating a seamless transfer of power.
4. The Role of the Impeller (Pump)
The impeller, also known as the pump, is directly connected to the engine’s flywheel. As the engine revs, the impeller spins, acting as a centrifugal pump. Its primary function is to generate fluid flow and direct it towards the turbine.
Key features of the impeller:
- Attached to the engine’s flywheel for direct power transfer.
- Designed with curved vanes to accelerate fluid outward.
- Creates a vacuum at its center to draw in more fluid.
 Torque converter pump attached to the housing
Torque converter pump attached to the housing
5. The Role of the Turbine
The turbine is positioned opposite the impeller and is connected to the transmission’s input shaft. As high-speed fluid from the impeller strikes the turbine blades, it forces the turbine to rotate, thus transferring power to the transmission.
Key features of the turbine:
- Connected to the transmission’s input shaft.
- Blades are curved to efficiently capture fluid energy.
- Transfers rotational power to the transmission gears.
6. The Role of the Stator
The stator is a crucial component located between the turbine and impeller. Its primary function is to redirect fluid flow, thereby multiplying torque. By changing the angle at which fluid re-enters the impeller, the stator effectively boosts the engine’s power output, especially during acceleration or when climbing hills.
Key features of the stator:
- Positioned between the turbine and impeller.
- Redirects fluid flow to optimize torque multiplication.
- Enhances engine power output during demanding conditions.
- One-way clutch to prevent counter-rotation, ensuring efficient fluid redirection.
7. Torque Multiplication Explained
Torque multiplication is a key advantage of torque converters. It occurs when the stator redirects fluid flow, increasing the force exerted on the impeller. This boost in force translates to higher torque output, enabling the vehicle to accelerate more quickly and efficiently.
Factors affecting torque multiplication:
- Stator design: The angle and curvature of the stator vanes directly impact torque multiplication.
- Fluid viscosity: The type and condition of the transmission fluid affect its ability to transfer energy efficiently.
- Engine speed: Torque multiplication is most pronounced at lower engine speeds, providing extra power when needed.
8. Fluid Dynamics in a Torque Converter
Understanding fluid dynamics is essential for comprehending how a torque converter operates. The transmission fluid acts as the medium for transferring kinetic energy between the impeller and turbine.
Key principles of fluid dynamics:
- Fluid viscosity: Affects the efficiency of energy transfer.
- Fluid velocity: Influences the amount of force exerted on the turbine blades.
- Fluid pressure: Impacts the overall performance of the torque converter.
- Bernoulli’s Principle: Explains the relationship between fluid velocity and pressure, crucial for understanding fluid flow within the converter.
9. Efficiency and Slip
While torque converters offer numerous benefits, they are not perfectly efficient. Some energy is lost due to fluid friction and turbulence, resulting in “slip.” Slip refers to the difference in rotational speed between the impeller and turbine.
Factors influencing efficiency and slip:
- Torque converter design: Advanced designs minimize slip and maximize efficiency.
- Fluid condition: Clean, high-quality transmission fluid reduces friction and improves efficiency.
- Operating conditions: High-load conditions can increase slip and reduce efficiency.
- Lock-up clutch: A lock-up clutch can eliminate slip by mechanically connecting the engine and transmission.
10. Lock-Up Clutch: Enhancing Efficiency
To mitigate slip and enhance fuel efficiency, many modern torque converters incorporate a lock-up clutch. This clutch mechanically connects the engine and transmission, eliminating fluid coupling and achieving a 1:1 gear ratio.
Benefits of a lock-up clutch:
- Eliminates slip, improving fuel efficiency.
- Reduces heat generation within the torque converter.
- Provides a more direct and responsive driving experience.
- Engages at cruising speeds to optimize performance.
11. Torque Converter Applications
Torque converters are widely used in various applications, primarily in the automotive industry. They are essential components in automatic transmissions, providing smooth and efficient power transfer.
Common applications:
- Passenger vehicles: Cars, trucks, and SUVs with automatic transmissions.
- Heavy-duty vehicles: Buses, construction equipment, and agricultural machinery.
- Industrial equipment: Forklifts, cranes, and other heavy machinery.
- Marine applications: Boats and ships with automatic transmissions.
12. Advantages of Using a Torque Converter
Torque converters offer several advantages over other types of power transmission systems.
Key benefits:
- Smooth Starts: Provides seamless acceleration from a standstill.
- Stall Prevention: Prevents the engine from stalling under heavy loads.
- Torque Multiplication: Boosts engine power output for improved performance.
- Vibration Damping: Reduces vibrations from the engine, enhancing driving comfort.
- Durability: Robust design ensures long-lasting performance.
13. Disadvantages of Using a Torque Converter
Despite their advantages, torque converters also have some drawbacks.
Potential drawbacks:
- Efficiency Losses: Some energy is lost due to fluid friction and slip.
- Heat Generation: Can generate heat, requiring a cooling system.
- Complexity: More complex than manual transmissions, potentially increasing maintenance costs.
- Weight: Adds weight to the vehicle, potentially affecting fuel economy.
14. Maintaining Your Torque Converter
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of your torque converter.
Essential maintenance tasks:
- Regular Fluid Checks: Monitor transmission fluid levels and condition.
- Fluid Changes: Replace transmission fluid at recommended intervals.
- Cooling System Maintenance: Ensure the cooling system is functioning properly to prevent overheating.
- Professional Inspections: Have your torque converter inspected by a qualified technician periodically.
15. Common Torque Converter Problems
Several issues can arise with torque converters, affecting their performance.
Common problems:
- Slipping: Reduced power transfer and poor acceleration.
- Stalling: Engine stalls when the vehicle comes to a stop.
- Vibration: Excessive vibration during operation.
- Overheating: Can lead to fluid breakdown and component damage.
- Noise: Unusual noises, such as whining or grinding, may indicate a problem.
16. Diagnosing Torque Converter Issues
Identifying torque converter problems early can prevent further damage.
Diagnostic steps:
- Check Fluid Levels: Low fluid levels can indicate a leak.
- Inspect Fluid Condition: Dark or burnt fluid suggests overheating or contamination.
- Listen for Unusual Noises: Whining, grinding, or clunking sounds.
- Monitor Performance: Slipping, stalling, or vibration.
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Scan tools can provide valuable data and error codes.
17. Torque Converter Repair vs. Replacement
When a torque converter fails, you must decide whether to repair or replace it.
Factors to consider:
- Severity of Damage: Minor issues may be repairable, while severe damage may require replacement.
- Cost: Compare the cost of repair versus replacement.
- Vehicle Age: For older vehicles, replacement may be more cost-effective.
- Warranty: Check if the torque converter is still under warranty.
18. Upgrading Your Torque Converter
For performance enthusiasts, upgrading the torque converter can significantly enhance vehicle performance.
Benefits of upgrading:
- Higher Stall Speed: Allows the engine to rev higher before engaging the transmission.
- Increased Torque Multiplication: Improves acceleration and low-end power.
- Improved Efficiency: Some aftermarket converters offer improved efficiency.
- Custom Tuning: Allows for fine-tuning of the transmission’s performance characteristics.
19. Aftermarket Torque Converters
The aftermarket offers a wide range of torque converters designed for various applications and performance levels.
Types of aftermarket converters:
- High-Stall Converters: For performance vehicles needing quicker acceleration.
- Heavy-Duty Converters: For trucks and SUVs used for towing.
- Performance Converters: Optimized for street and track use.
- Custom-Built Converters: Tailored to specific engine and transmission setups.
20. Installation Tips for Torque Converters
Proper installation is crucial for ensuring the correct operation of a new or rebuilt torque converter.
Installation steps:
- Preparation: Ensure all necessary tools and parts are available.
- Inspection: Inspect the new torque converter for any damage.
- Alignment: Align the torque converter properly with the transmission.
- Secure Fastening: Tighten all bolts to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Fluid Fill: Fill the transmission with the correct type and amount of fluid.
- Testing: Perform a test drive to ensure proper operation.
21. The Future of Torque Converter Technology
Torque converter technology continues to evolve, with advancements aimed at improving efficiency, performance, and reliability.
Emerging trends:
- Advanced Materials: Use of lightweight and durable materials.
- Electronic Controls: Integration of electronic controls for precise operation.
- Hybrid Systems: Development of torque converters for hybrid vehicles.
- Improved Designs: Innovative designs to minimize slip and maximize torque multiplication.
- Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs): Integration with CVTs for seamless power delivery.
22. How to Choose the Right Torque Converter for Your Vehicle
Selecting the correct torque converter is vital for optimal performance and reliability.
Factors to consider:
- Vehicle Type: Different vehicles require different torque converters.
- Engine Specifications: Match the torque converter to the engine’s power output.
- Transmission Type: Ensure compatibility with the transmission.
- Driving Style: Consider your driving habits and performance needs.
- Towing Requirements: If you tow, choose a heavy-duty converter.
- Professional Advice: Consult with a qualified technician for expert guidance.
23. Understanding Stall Speed
Stall speed is a critical parameter of a torque converter, referring to the engine speed at which the torque converter begins to transfer power efficiently.
Key aspects of stall speed:
- Definition: The engine RPM at which the turbine starts to spin effectively.
- Impact on Performance: Higher stall speeds improve acceleration but may reduce fuel economy.
- Matching Stall Speed: Choose a stall speed that matches your engine’s power band.
- Adjustable Converters: Some converters offer adjustable stall speeds for customized performance.
24. How Torque Converters Impact Fuel Efficiency
Torque converters can impact fuel efficiency due to slip, which wastes energy.
Strategies to improve fuel efficiency:
- Lock-Up Clutch: Use a torque converter with a lock-up clutch to eliminate slip.
- Proper Maintenance: Keep the transmission fluid clean and at the correct level.
- Efficient Driving: Avoid aggressive acceleration and maintain a steady speed.
- Lightweight Components: Use lightweight components to reduce vehicle weight.
25. Torque Converter vs. Fluid Coupling
While both torque converters and fluid couplings use fluid to transmit power, they differ in their capabilities.
Key differences:
- Torque Multiplication: Torque converters can multiply torque, while fluid couplings cannot.
- Stator: Torque converters have a stator to redirect fluid flow, while fluid couplings do not.
- Efficiency: Torque converters are generally less efficient than fluid couplings due to slip.
- Applications: Torque converters are used in automatic transmissions, while fluid couplings are used in simpler applications.
26. Symptoms of a Failing Torque Converter
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing torque converter can help you address the problem before it causes significant damage.
Common symptoms:
- Slipping Transmission: The transmission slips or hesitates during acceleration.
- Rough Shifting: Shifts are harsh or erratic.
- Stalling: The engine stalls when coming to a stop.
- Unusual Noises: Whining, humming, or rattling sounds from the transmission.
- Overheating: The transmission overheats easily.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: A noticeable drop in fuel efficiency.
- Check Engine Light: The check engine light may illuminate.
27. Step-by-Step Guide to Testing a Torque Converter
Testing a torque converter involves several steps to diagnose potential issues.
Testing procedure:
- Visual Inspection: Check for leaks, damage, and fluid condition.
- Stall Test: Perform a stall test to check torque converter performance.
- Input Shaft Play: Check for excessive play in the input shaft.
- Pressure Test: Measure transmission fluid pressure.
- Scan Tool Diagnostics: Use a scan tool to check for error codes.
- Fluid Analysis: Analyze the transmission fluid for contaminants.
28. Tools Needed for Torque Converter Repair
Repairing a torque converter requires specific tools and equipment.
Essential tools:
- Socket Set: For removing and installing bolts.
- Wrench Set: For tightening and loosening nuts and bolts.
- Torque Wrench: For tightening bolts to the correct specifications.
- Pliers: For various tasks, such as removing clips and hoses.
- Screwdrivers: For removing and installing screws.
- Transmission Jack: For supporting the transmission.
- Scan Tool: For diagnosing electronic issues.
- Fluid Pump: For adding transmission fluid.
- Safety Glasses: For eye protection.
- Gloves: For hand protection.
29. Safety Precautions When Working on Torque Converters
Working on torque converters can be hazardous, so it’s essential to take safety precautions.
Safety guidelines:
- Disconnect Battery: Disconnect the battery before working on the transmission.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear safety glasses and gloves.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job.
- Support Vehicle Properly: Use jack stands to support the vehicle.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for repair and maintenance.
- Handle Fluids Carefully: Dispose of used fluids properly.
30. The Impact of Torque Converter on Vehicle Performance
The torque converter significantly impacts a vehicle’s overall performance, affecting acceleration, fuel efficiency, and driving comfort.
Performance aspects:
- Acceleration: Improves acceleration, especially from a standstill.
- Fuel Efficiency: Can impact fuel efficiency due to slip.
- Smoothness: Provides smooth and seamless power transfer.
- Towing Capacity: Affects towing capacity, especially in trucks and SUVs.
- Driving Comfort: Reduces vibrations and harshness, improving driving comfort.
- Overall Drivability: Enhances overall drivability and responsiveness.
31. Understanding Torque Converter Stall Speed and Its Impact on Performance
The stall speed of a torque converter is a crucial factor that significantly influences a vehicle’s performance characteristics. It directly affects acceleration, responsiveness, and overall driving experience. A properly matched stall speed optimizes the engine’s power output, ensuring peak performance in various driving conditions.
Optimizing stall speed for enhanced performance:
- Matching Engine Characteristics: Select a stall speed that aligns with the engine’s power band to maximize torque output.
- Improved Acceleration: A higher stall speed can enhance acceleration, allowing the engine to reach its peak power range more quickly.
- Enhanced Responsiveness: A well-chosen stall speed provides improved throttle response, making the vehicle more agile and responsive.
- Customizable Driving Experience: Adjustable stall speed converters offer the flexibility to fine-tune performance based on individual driving preferences and needs.
32. The Science Behind Torque Converter Efficiency
Torque converter efficiency is a critical aspect that affects fuel economy and overall performance. Understanding the factors influencing efficiency can help optimize the system for maximum power transfer and minimal energy loss. Advanced designs and high-quality fluids contribute to improved efficiency.
Factors influencing torque converter efficiency:
- Fluid Dynamics: Efficient fluid flow within the converter minimizes energy losses due to turbulence and friction.
- Stator Design: The stator’s design and angle play a crucial role in redirecting fluid flow for optimal torque multiplication.
- Lock-Up Clutch: Engaging the lock-up clutch eliminates slip, resulting in a direct mechanical connection and improved efficiency.
- Fluid Viscosity: Using the correct transmission fluid with optimal viscosity ensures efficient energy transfer.
33. How to Identify the Right Torque Converter for Different Driving Conditions
Selecting the appropriate torque converter for specific driving conditions is essential for achieving optimal performance and reliability. Different converters are designed to excel in various scenarios, such as city driving, highway cruising, or heavy-duty towing. Matching the converter to the driving conditions ensures maximum efficiency and responsiveness.
Choosing the right torque converter for different driving conditions:
- City Driving: A lower stall speed converter provides smooth starts and efficient low-speed operation.
- Highway Cruising: A lock-up converter enhances fuel efficiency by eliminating slip at cruising speeds.
- Heavy-Duty Towing: A heavy-duty converter offers increased torque multiplication and durability for demanding towing tasks.
- Performance Driving: A higher stall speed converter maximizes acceleration and responsiveness for performance applications.
34. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Torque Converter Problems
Diagnosing torque converter issues requires advanced techniques to pinpoint the root cause of the problem accurately. Using specialized tools and procedures ensures a thorough evaluation, leading to effective repairs.
Advanced diagnostic techniques:
- Pressure Testing: Measuring fluid pressure at various points in the system helps identify leaks or blockages.
- Stall Testing: Evaluating the converter’s performance under load reveals potential slipping or stalling issues.
- Vibration Analysis: Analyzing vibrations can detect internal damage or imbalance.
- Fluid Analysis: Examining the transmission fluid for contaminants or degradation provides valuable insights.
- Scan Tool Diagnostics: Utilizing scan tools to read error codes and monitor sensor data aids in identifying electronic or mechanical faults.
35. The Importance of Using High-Quality Transmission Fluid in Torque Converters
The quality of transmission fluid significantly impacts the performance and longevity of torque converters. High-quality fluids provide optimal lubrication, cooling, and protection against wear and corrosion, ensuring reliable operation.
Benefits of using high-quality transmission fluid:
- Optimal Lubrication: Reduces friction and wear on internal components.
- Effective Cooling: Dissipates heat, preventing overheating and fluid breakdown.
- Corrosion Protection: Prevents rust and corrosion, extending the lifespan of the converter.
- Consistent Performance: Maintains stable viscosity and properties over a wide temperature range.
- Extended Lifespan: Prolongs the lifespan of the torque converter and transmission.
36. The Role of Torque Converters in Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Torque converters play a crucial role in hybrid and electric vehicles, contributing to smooth starts, torque multiplication, and overall efficiency. They are often integrated with electric motors and sophisticated control systems to optimize power delivery.
Torque converters in hybrid and electric vehicles:
- Smooth Starts: Provide seamless acceleration from a standstill.
- Torque Multiplication: Enhance torque output for improved performance.
- Efficiency Optimization: Integrated with electric motors to maximize energy efficiency.
- Regenerative Braking: Contribute to regenerative braking systems, capturing and storing energy.
- Advanced Control Systems: Integrated with electronic controls for precise and efficient operation.
37. Tips for Extending the Life of Your Torque Converter
Extending the lifespan of a torque converter requires proactive maintenance and careful driving habits. Following these tips ensures reliable performance and minimizes the risk of costly repairs.
Tips for extending torque converter life:
- Regular Fluid Checks: Monitor transmission fluid levels and condition.
- Timely Fluid Changes: Replace transmission fluid at recommended intervals.
- Proper Cooling System Maintenance: Ensure the cooling system is functioning correctly.
- Avoid Overloading: Avoid towing or carrying loads beyond the vehicle’s capacity.
- Smooth Driving Habits: Avoid aggressive acceleration and harsh braking.
- Professional Inspections: Have the torque converter inspected by a qualified technician periodically.
38. Understanding Torque Converter Lock-Up Clutch Operation and Benefits
The lock-up clutch is a critical component that enhances fuel efficiency and performance by mechanically connecting the engine and transmission. Understanding its operation and benefits can help optimize vehicle performance.
Key aspects of lock-up clutch operation and benefits:
- Eliminates Slip: Engages to eliminate slip, providing a direct mechanical connection.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Reduces energy losses, resulting in better fuel economy.
- Reduced Heat Generation: Minimizes heat buildup within the torque converter.
- Enhanced Responsiveness: Provides a more direct and responsive driving experience.
- Optimal Cruising Performance: Engages at cruising speeds to maximize efficiency.
39. How to Troubleshoot Common Torque Converter Noises
Troubleshooting common torque converter noises requires careful listening and systematic diagnosis. Identifying the source and nature of the noise can help pinpoint the underlying problem.
Common torque converter noises and troubleshooting tips:
- Whining Noise: May indicate low fluid level, worn bearings, or a failing pump.
- Humming Noise: Could be caused by cavitation or fluid aeration.
- Rattling Noise: May suggest loose components or internal damage.
- Clunking Noise: Could indicate worn gears or a damaged stator.
Troubleshooting steps:
- Listen Carefully: Identify the type and location of the noise.
- Check Fluid Level and Condition: Ensure the fluid is at the correct level and in good condition.
- Perform a Visual Inspection: Look for leaks, damage, or loose components.
- Use a Scan Tool: Check for error codes or sensor data.
- Consult a Technician: Seek professional assistance if the problem persists.
40. The Impact of Torque Converter Design on Overall Transmission Performance
The design of a torque converter significantly affects the overall performance of the transmission, influencing shift quality, torque multiplication, and efficiency.
Design considerations:
- Stator Vane Angle: Affects torque multiplication and efficiency.
- Impeller and Turbine Blade Design: Influences fluid flow and energy transfer.
- Converter Size and Weight: Impacts vehicle weight and fuel economy.
- Lock-Up Clutch Integration: Enhances efficiency and responsiveness.
Impact on transmission performance:
- Shift Quality: Well-designed converters provide smooth and seamless shifts.
- Torque Multiplication: Enhances torque output for improved acceleration.
- Efficiency: Maximizes energy transfer, improving fuel economy.
- Overall Performance: Optimizes the transmission’s performance characteristics for various driving conditions.
Do you find yourself grappling with persistent torque converter issues, unsure of the best course of action? Are you seeking reliable solutions to enhance your vehicle’s performance and efficiency? Look no further. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States or call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Our team of expert technicians is ready to provide tailored advice and premium tools to address your specific needs. Let CARDIAGTECH.NET be your trusted partner in automotive excellence. Visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
FAQ: Torque Converters
-
What is a torque converter?
A torque converter is a fluid coupling in automatic transmissions that transfers engine power to the wheels.
-
How does a torque converter work?
It uses fluid to transmit rotational energy from the engine to the transmission, multiplying torque as needed.
-
What are the main components of a torque converter?
The main components include the impeller, turbine, and stator.
-
What is the purpose of the stator?
The stator redirects fluid flow, multiplying torque for improved performance.
-
What is stall speed?
Stall speed is the engine RPM at which the torque converter starts to transfer power efficiently.
-
How does a lock-up clutch improve efficiency?
It eliminates slip by mechanically connecting the engine and transmission, enhancing fuel economy.
-
What are common signs of a failing torque converter?
Common signs include slipping, stalling, and unusual noises.
-
How often should I change my transmission fluid?
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals for fluid changes.
-
Can I upgrade my torque converter for better performance?
Yes, aftermarket converters can enhance acceleration and torque multiplication.
-
What is the role of a torque converter in hybrid vehicles?
It provides smooth starts, torque multiplication, and contributes to regenerative braking systems.