ESP Currently Unavailable Mercedes: Troubleshooting Guide
Here’s a detailed guide on what to do when you encounter the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message in your Mercedes-Benz. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand how frustrating these issues can be, and we’re here to provide solutions. This comprehensive guide covers potential causes, diagnostic steps, and fixes to help you resolve this issue and keep your Mercedes running smoothly. Explore effective troubleshooting and repair solutions for your Mercedes-Benz ESP system with insights from CARDIAGTECH.NET, focusing on diagnostic tools and expert advice.
1. Understanding ESP and Its Importance
Electronic Stability Program (ESP) is a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles, especially in Mercedes-Benz cars. It helps prevent skidding and loss of control by selectively applying brakes to individual wheels and adjusting engine power. When the ESP system is functioning correctly, it enhances vehicle stability, particularly in adverse driving conditions such as wet, icy, or snowy roads.
1.1 How ESP Works
ESP works by continuously monitoring several factors:
- Steering Angle: The angle of the steering wheel as determined by the driver.
- Vehicle Speed: How fast the car is moving.
- Yaw Rate: The rate at which the car is turning.
- Lateral Acceleration: The force pushing the car sideways.
Using these inputs, the ESP module compares the driver’s intended path with the vehicle’s actual movement. If a discrepancy is detected—for example, if the car begins to skid—the ESP system intervenes by applying the brakes to one or more wheels and reducing engine power to help the driver maintain control.
1.2 Why ESP is Essential
ESP is more than just a convenience; it’s a critical safety system. Studies have shown that ESP can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, particularly those involving skidding or loss of control. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ESP can reduce single-vehicle crashes by as much as 32%. This makes ESP an indispensable feature, especially for drivers who frequently encounter challenging road conditions.
1.3 Common ESP Issues in Mercedes-Benz Vehicles
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are known for their advanced technology and safety features, but like any complex system, the ESP can experience issues. Some common problems that may trigger the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message include:
- Faulty wheel speed sensors
- Steering angle sensor malfunction
- Low battery voltage
- Problems with the ESP control module
- Brake light switch failure
Addressing these issues promptly is essential not only for restoring the functionality of the ESP system but also for ensuring the safety of the vehicle’s occupants. For reliable diagnostic tools and repair solutions, consider exploring resources at CARDIAGTECH.NET, where quality meets expertise in automotive care.
2. Diagnosing the “ESP Currently Unavailable” Message
When the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message appears on your Mercedes-Benz dashboard, it indicates that the ESP system has detected a fault or malfunction. To accurately diagnose the issue, a systematic approach is required. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you pinpoint the problem:
2.1 Initial Steps
-
Read the Owner’s Manual: Consult your Mercedes-Benz owner’s manual for specific information related to the ESP system and troubleshooting tips. The manual may provide insights into common causes and recommended actions.
-
Restart the Vehicle: Sometimes, the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message may appear due to a temporary glitch. Turn off the engine, wait a few minutes, and then restart the car. If the message disappears, it may have been a transient issue.
-
Check the ESP Button: Ensure that the ESP system hasn’t been accidentally turned off. Locate the ESP button (usually marked with the ESP symbol) and make sure it is engaged.
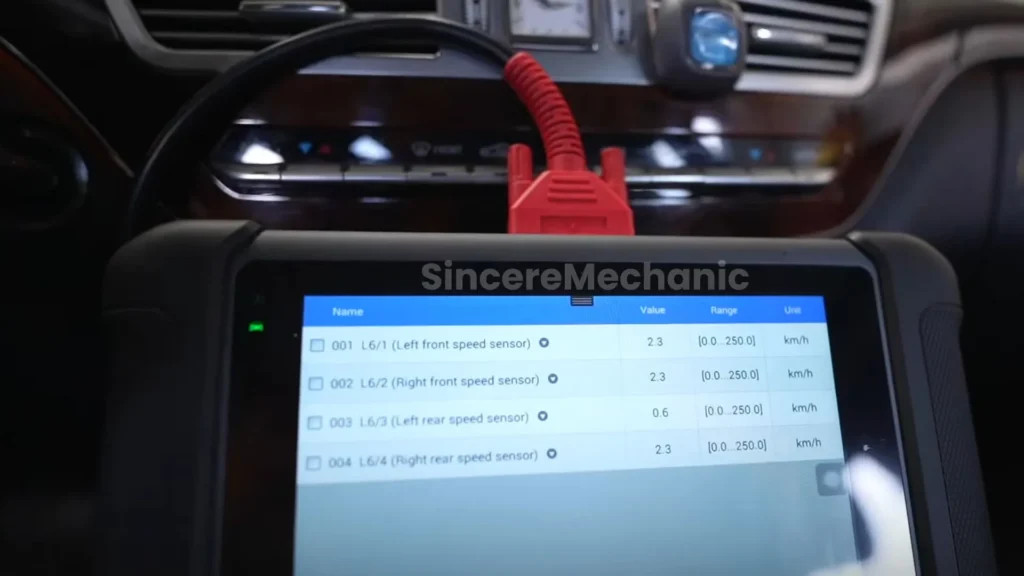
2.2 Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanner is an essential tool for diagnosing automotive issues. It allows you to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer, providing valuable clues about the problem.
-
Connect the Scanner: Plug the OBD-II scanner into the diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard near the steering column.
-
Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
-
Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read the stored diagnostic trouble codes. Note down any codes related to the ESP system, ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), wheel speed sensors, or steering angle sensor.
-
Interpret the Codes: Consult a reliable source, such as a repair manual or online database, to interpret the meaning of the diagnostic trouble codes. This will help you identify the specific component or system that is causing the issue.
-
Clear the Codes: After noting the codes, you can clear them using the scanner. Start the engine and drive the car to see if the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message reappears. If it does, the underlying problem still exists.
2.3 Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Here are some common diagnostic trouble codes associated with ESP issues in Mercedes-Benz vehicles:
| Code | Description | Possible Cause |
|---|---|---|
| C1000 | ESP Control Unit Faulty | Faulty ESP control module, wiring issues |
| C1100-C1103 | Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring problems, reluctor ring damage |
| C1140 | Steering Angle Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty steering angle sensor, incorrect calibration |
| C1200 | Brake Light Switch Circuit Malfunction | Faulty brake light switch, wiring issues |
| C1400 | Low Voltage at Control Unit | Low battery voltage, faulty alternator, wiring problems |
2.4 Advanced Diagnostics
If the basic diagnostic steps do not reveal the cause of the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message, advanced diagnostics may be necessary. This may involve using a more sophisticated diagnostic tool, such as a Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system, to perform detailed tests and inspections.
- Live Data Monitoring: Monitor live data from the ESP system, including wheel speed sensor readings, steering angle sensor data, and brake pressure. This can help identify intermittent faults or abnormalities.
- Component Testing: Perform individual component tests to verify the functionality of sensors, actuators, and control modules.
- Wiring Inspection: Inspect the wiring harness and connectors associated with the ESP system for damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
For specialized diagnostic tools and expert guidance, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our team can assist you in identifying the root cause of ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz and provide effective solutions.
3. Potential Causes of “ESP Currently Unavailable”
The “ESP Currently Unavailable” message in a Mercedes-Benz can stem from various underlying issues. Identifying these potential causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair. Here are some of the most common reasons why this message might appear:
3.1 Wheel Speed Sensor Issues
Wheel speed sensors are vital for the ESP system, as they provide data on the rotational speed of each wheel. If one or more of these sensors malfunction, the ESP system may become disabled, triggering the warning message.
- Faulty Sensor: The sensor itself may be damaged or worn out, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Wiring Problems: The wiring connecting the sensor to the ESP module could be damaged, corroded, or disconnected.
- Reluctor Ring Damage: The reluctor ring (also known as the tone ring) is a toothed ring that the wheel speed sensor reads. If it’s damaged or dirty, it can disrupt the sensor’s ability to accurately measure wheel speed.
3.2 Steering Angle Sensor Malfunction
The steering angle sensor measures the position of the steering wheel and provides this information to the ESP system. A faulty steering angle sensor can prevent the ESP system from functioning correctly.
- Sensor Failure: The sensor may fail due to wear and tear or internal damage.
- Misalignment: The sensor may need to be recalibrated or realigned to provide accurate readings.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the signal from the sensor to the ESP module.
3.3 Low Battery Voltage
Mercedes-Benz vehicles are highly sensitive to voltage fluctuations. Low battery voltage can cause various electronic systems to malfunction, including the ESP system.
- Weak Battery: A battery that is old or not properly charged may not provide sufficient voltage to power the ESP system.
- Faulty Alternator: The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine is running. If it fails, the battery may not receive enough charge, leading to low voltage issues.
- Parasitic Drain: A parasitic drain occurs when an electrical component continues to draw power even when the car is turned off. This can drain the battery over time, leading to low voltage problems.
3.4 ESP Control Module Problems
The ESP control module is the brain of the ESP system. It receives data from various sensors and uses this information to control the braking and engine power.
- Module Failure: The ESP control module itself may fail due to internal damage or software glitches.
- Wiring Issues: The wiring connecting the module to the sensors and actuators could be damaged or corroded.
- Software Issues: The ESP control module’s software may become corrupted or outdated, leading to malfunctions.
3.5 Brake Light Switch Failure
The brake light switch is responsible for activating the brake lights when the brake pedal is pressed. It also provides a signal to the ESP system, indicating when the brakes are being applied.
- Switch Failure: The switch may fail due to wear and tear or internal damage.
- Misadjustment: The switch may need to be adjusted to ensure it is properly aligned with the brake pedal.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt the signal from the switch to the ESP module.
3.6 Other Potential Causes
In addition to the common causes listed above, there are other potential factors that could contribute to the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message:
- ABS System Issues: Since the ESP system relies on the ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), problems with the ABS can also trigger the ESP warning.
- Tire Pressure Issues: Incorrect tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s ability to accurately monitor wheel speed and vehicle stability.
- Aftermarket Modifications: Modifications to the vehicle’s suspension, brakes, or electronic systems can sometimes interfere with the ESP system.
Understanding these potential causes is the first step toward diagnosing and resolving the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message in your Mercedes-Benz. For expert assistance and high-quality diagnostic tools, turn to CARDIAGTECH.NET. We’re dedicated to helping you keep your vehicle running safely and smoothly.
4. Step-by-Step Solutions to Resolve ESP Issues
Once you have identified the potential causes of the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message, you can move on to implementing solutions. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you resolve ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz:
4.1 Inspecting and Replacing Wheel Speed Sensors
-
Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the wheel speed sensors and their wiring. Look for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Pay close attention to the sensor wiring near the wheel hub, as this area is prone to damage from road debris.
-
Testing the Sensors: Use a multimeter to test the resistance of each wheel speed sensor. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for the correct resistance values. If a sensor’s resistance is outside the specified range, it may be faulty.
-
Replacing the Sensor:
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shock.
- Locate the faulty wheel speed sensor. It’s usually mounted near the wheel hub.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the sensor from its mounting bracket. This may involve unscrewing a bolt or clip.
- Install the new wheel speed sensor, ensuring it is securely mounted and properly connected.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
-
Clear Diagnostic Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any diagnostic trouble codes related to the wheel speed sensors.
-
Test Drive: Take the car for a test drive to see if the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message reappears.
4.2 Addressing Steering Angle Sensor Issues
-
Visual Inspection: Inspect the steering angle sensor and its wiring for any signs of damage or loose connections. The sensor is usually located near the steering column.
-
Calibration: The steering angle sensor may need to be recalibrated if it has been replaced or if the vehicle’s alignment has been adjusted. Use a Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system or a similar diagnostic tool to perform the calibration procedure. Follow the tool’s instructions carefully.
-
Replacing the Sensor:
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Remove the steering wheel and any associated trim pieces to access the steering angle sensor.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Remove the sensor from its mounting.
- Install the new steering angle sensor, ensuring it is properly aligned and securely mounted.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reinstall the steering wheel and trim pieces.
- Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
-
Clear Diagnostic Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any diagnostic trouble codes related to the steering angle sensor.
-
Test Drive: Take the car for a test drive to see if the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message reappears.
4.3 Resolving Low Battery Voltage Problems
-
Battery Testing: Use a multimeter or a battery load tester to check the battery’s voltage and condition. A fully charged battery should have a voltage of around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is significantly lower, the battery may need to be replaced.
-
Charging the Battery: If the battery is low but still in good condition, try charging it using a battery charger. Follow the charger’s instructions carefully.
-
Alternator Testing: Use a multimeter to check the alternator’s output voltage while the engine is running. The voltage should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts. If the voltage is outside this range, the alternator may be faulty and need to be replaced.
-
Parasitic Drain Testing: To check for a parasitic drain, follow these steps:
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Connect a multimeter between the negative terminal of the battery and the negative battery cable. Set the multimeter to measure current (amps).
- Wait for a few minutes to allow the car’s electronic systems to go to sleep.
- Check the current reading on the multimeter. A normal parasitic drain should be less than 50 milliamps (0.05 amps).
- If the current reading is higher than 50 milliamps, start disconnecting fuses one at a time to identify the circuit that is causing the drain.
- Once you have identified the circuit, investigate the components on that circuit to find the source of the parasitic drain.
4.4 Addressing ESP Control Module Issues
-
Visual Inspection: Inspect the ESP control module and its wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion. The module is usually located in the engine compartment or under the dashboard.
-
Software Update: Check if there are any software updates available for the ESP control module. Use a Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system or a similar diagnostic tool to perform the update, if necessary.
-
Replacing the Module:
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Locate the ESP control module.
- Disconnect the electrical connectors from the module.
- Remove the module from its mounting.
- Install the new ESP control module, ensuring it is properly connected and securely mounted.
- Reconnect the electrical connectors.
- Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
-
Coding the Module: The new ESP control module may need to be coded to match the vehicle’s specifications. Use a Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system or a similar diagnostic tool to perform the coding procedure.
-
Clear Diagnostic Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any diagnostic trouble codes related to the ESP control module.
-
Test Drive: Take the car for a test drive to see if the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message reappears.
4.5 Correcting Brake Light Switch Problems
-
Testing the Switch: Use a multimeter to test the brake light switch for continuity. The switch should show continuity when the brake pedal is pressed and no continuity when the pedal is released.
-
Adjusting the Switch: Some brake light switches are adjustable. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for instructions on how to adjust the switch.
-
Replacing the Switch:
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Locate the brake light switch. It’s usually mounted near the brake pedal.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the switch.
- Remove the switch from its mounting.
- Install the new brake light switch, ensuring it is properly aligned and securely mounted.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
-
Clear Diagnostic Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to clear any diagnostic trouble codes related to the brake light switch.
-
Test Drive: Take the car for a test drive to see if the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message reappears.
4.6 Additional Tips
- Consult a Professional: If you are not comfortable performing these repairs yourself, or if the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message persists after trying these solutions, consult a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing components, use high-quality parts from a reputable supplier to ensure proper fit and function. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic tools and replacement parts for Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Follow Safety Precautions: Always follow proper safety precautions when working on your vehicle, including wearing safety glasses and gloves, and disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery before performing any electrical work.
By following these step-by-step solutions, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve ESP issues in your Mercedes-Benz, ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. For reliable diagnostic tools and expert advice, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET. We’re here to support you in keeping your Mercedes-Benz in top condition.
5. Maintaining Your ESP System
Maintaining your Mercedes-Benz ESP (Electronic Stability Program) system is crucial for ensuring its reliability and effectiveness. Regular maintenance can help prevent issues and keep your vehicle running safely. Here are some essential maintenance tips to keep your ESP system in optimal condition:
5.1 Regular Inspections
-
Wheel Speed Sensors: Periodically inspect the wheel speed sensors for any signs of damage, dirt, or corrosion. Clean the sensors and reluctor rings as needed to ensure accurate readings.
-
Steering Angle Sensor: Ensure the steering angle sensor is properly calibrated, especially after any alignment adjustments or suspension work.
-
Brake System: Regularly inspect the brake system, including brake pads, rotors, and brake lines. Ensure the brake light switch is functioning correctly.
-
Tires: Maintain proper tire pressure and ensure your tires are in good condition. Uneven tire wear or incorrect tire pressure can affect the ESP system’s performance.
-
Battery: Check the battery’s voltage and condition regularly. A weak or failing battery can cause various electronic systems to malfunction, including the ESP system.
5.2 Proper Tire Maintenance
Tires play a critical role in the ESP system’s ability to maintain vehicle stability. Here are some tire maintenance tips:
- Maintain Correct Tire Pressure: Check and adjust tire pressure at least once a month and before long trips. Refer to the vehicle’s owner’s manual or the sticker on the driver’s side doorjamb for the recommended tire pressure.
- Regular Tire Rotation: Rotate your tires every 5,000 to 7,000 miles to ensure even wear. This helps maintain consistent grip and handling.
- Inspect Tire Tread: Regularly inspect your tires for wear and damage. Replace tires when the tread depth reaches the minimum legal limit (usually 2/32 inch).
- Use Recommended Tires: Use tires that meet the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications. Using non-recommended tires can affect the ESP system’s performance.
5.3 Brake System Maintenance
The brake system is closely linked to the ESP system, so maintaining it properly is essential:
- Check Brake Pads and Rotors: Inspect brake pads and rotors regularly for wear and damage. Replace them as needed to ensure optimal braking performance.
- Flush Brake Fluid: Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, which can reduce its effectiveness. Flush and replace brake fluid every two years or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Inspect Brake Lines: Check brake lines for leaks, cracks, or corrosion. Replace any damaged brake lines immediately.
- Test Brake Light Switch: Ensure the brake light switch is functioning correctly. The brake lights should illuminate when the brake pedal is pressed.
5.4 Battery Maintenance
Maintaining a healthy battery is crucial for the proper functioning of the ESP system:
- Regular Voltage Checks: Check the battery’s voltage regularly using a multimeter. A fully charged battery should have a voltage of around 12.6 volts.
- Clean Battery Terminals: Clean battery terminals regularly to remove corrosion. Use a wire brush and a baking soda solution to clean the terminals.
- Secure Battery Connections: Ensure battery connections are tight and secure. Loose connections can cause voltage drops and affect the ESP system’s performance.
- Battery Load Testing: Have the battery load tested periodically to assess its ability to hold a charge under load.
5.5 Professional Servicing
Schedule regular servicing with a qualified Mercedes-Benz technician. During the service, the technician can perform a comprehensive inspection of the ESP system and other critical components.
- Diagnostic Scans: Technicians can use diagnostic tools to scan for any hidden issues or fault codes that may not trigger a warning light on the dashboard.
- Software Updates: Technicians can update the ESP control module’s software to the latest version, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
- Component Testing: Technicians can perform individual component tests to verify the functionality of sensors, actuators, and control modules.
5.6 Driving Habits
Your driving habits can also impact the ESP system’s performance. Avoid aggressive driving maneuvers, such as sudden acceleration, hard braking, and sharp turns, which can put excessive strain on the system.
- Smooth Driving: Practice smooth and controlled driving techniques to minimize the ESP system’s interventions.
- Adjust to Road Conditions: Adjust your driving style to suit the road conditions. Reduce speed and increase following distance in wet, icy, or snowy conditions.
- Avoid Overloading: Avoid overloading the vehicle, as this can affect its handling and stability.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help keep your Mercedes-Benz ESP system in optimal condition, ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. For high-quality diagnostic tools and expert advice, trust CARDIAGTECH.NET. We’re dedicated to helping you maintain your vehicle to the highest standards.
6. Real-World Scenarios and Case Studies
To further illustrate the importance of understanding and addressing the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message in your Mercedes-Benz, let’s examine some real-world scenarios and case studies:
6.1 Case Study 1: Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz C-Class owner experienced the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message on the dashboard. The car also exhibited erratic braking behavior and occasional ABS activation during normal driving conditions.
Diagnosis: Using an OBD-II scanner, the technician retrieved a diagnostic trouble code indicating a fault with the left front wheel speed sensor. Further inspection revealed that the sensor was damaged due to road debris.
Solution: The technician replaced the faulty wheel speed sensor and cleared the diagnostic trouble code. After a test drive, the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message disappeared, and the car’s braking behavior returned to normal.
Lesson Learned: This case highlights the importance of regularly inspecting wheel speed sensors for damage and addressing any issues promptly.
6.2 Case Study 2: Low Battery Voltage
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz E-Class owner noticed the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message appearing intermittently on the dashboard. The message usually appeared after the car had been sitting for a few days without being driven.
Diagnosis: The technician performed a battery voltage test and found that the battery voltage was low, especially after the car had been sitting for a while. Further testing revealed that the battery was old and not holding a charge properly.
Solution: The technician replaced the old battery with a new one. After the replacement, the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message no longer appeared, and the car’s electronic systems functioned correctly.
Lesson Learned: This case emphasizes the importance of maintaining a healthy battery and replacing it when necessary to prevent electronic system malfunctions.
6.3 Case Study 3: Steering Angle Sensor Miscalibration
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz S-Class owner experienced the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message after having the car’s alignment adjusted. The car also exhibited a tendency to pull to one side during driving.
Diagnosis: The technician performed a steering angle sensor calibration using a Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system. The calibration procedure revealed that the steering angle sensor was misaligned after the alignment adjustment.
Solution: The technician recalibrated the steering angle sensor using the diagnostic tool. After the calibration, the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message disappeared, and the car’s handling returned to normal.
Lesson Learned: This case highlights the importance of ensuring proper steering angle sensor calibration after any alignment adjustments or suspension work.
6.4 Scenario 4: Brake Light Switch Failure
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz CLK owner noticed the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message appearing on the dashboard along with the ABS warning light. Additionally, the cruise control system stopped working.
Diagnosis: The technician inspected the brake light switch and found that it was not functioning correctly. The brake lights were not illuminating when the brake pedal was pressed.
Solution: The technician replaced the faulty brake light switch. After the replacement, the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message and the ABS warning light disappeared, and the cruise control system functioned correctly.
Lesson Learned: This case demonstrates the interconnectedness of various electronic systems in modern vehicles and how a seemingly minor component like the brake light switch can affect multiple systems.
6.5 Scenario 5: Aftermarket Modifications
Scenario: A Mercedes-Benz SLK owner experienced the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message after installing aftermarket suspension components.
Diagnosis: The technician inspected the suspension components and found that they were interfering with the ESP system’s sensors.
Solution: The technician adjusted the aftermarket suspension components to ensure they were not interfering with the ESP system’s sensors. After the adjustment, the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message disappeared.
Lesson Learned: This case highlights the potential for aftermarket modifications to interfere with the ESP system and the importance of ensuring compatibility before making any modifications.
These real-world scenarios and case studies illustrate the diverse range of issues that can trigger the “ESP Currently Unavailable” message in a Mercedes-Benz. By understanding these scenarios and the solutions implemented, you can better diagnose and address ESP issues in your vehicle. For professional diagnostic tools and expert assistance, visit CARDIAGTECH.NET. We’re dedicated to helping you keep your Mercedes-Benz running safely and smoothly.
7. The Importance of Professional Diagnostic Tools
When troubleshooting complex automotive systems like the ESP in a Mercedes-Benz, professional diagnostic tools are indispensable. These tools provide a level of accuracy and insight that is simply not achievable with basic diagnostic methods. Here’s why professional diagnostic tools are essential for resolving ESP issues:
7.1 Accurate Code Reading
Professional diagnostic tools can accurately read and interpret diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the vehicle’s computer. These codes provide valuable clues about the nature and location of the fault.
- Enhanced Code Definitions: Professional tools often provide more detailed and specific code definitions than generic OBD-II scanners. This can help you pinpoint the exact component or system that is causing the problem.
- Subcode Reading: Some professional tools can read subcodes, which provide even more detailed information about the fault.
- Historical Data: Professional tools can often access historical data, such as past fault codes and freeze frame data, which can help identify intermittent issues.
7.2 Live Data Monitoring
Professional diagnostic tools allow you to monitor live data from various sensors and systems in real-time. This can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent faults or abnormalities.
- Sensor Readings: Monitor live data from wheel speed sensors, steering angle sensor, brake pressure sensor, and other relevant sensors to identify any inconsistencies or malfunctions.
- System Parameters: Monitor live data from the ESP control module, ABS module, and other related modules to assess their performance.
- Graphing Capabilities: Some professional tools offer graphing capabilities, which allow you to visualize live data and identify trends or patterns.
7.3 Component Testing
Professional diagnostic tools often include component testing capabilities, which allow you to activate and test individual components to verify their functionality.
- Actuator Testing: Activate actuators, such as ABS solenoids, to verify that they are functioning correctly.
- Sensor Simulation: Simulate sensor signals to test the response of the ESP control module.
- Wiring Tests: Perform wiring tests to check for continuity, shorts, and opens in the wiring harness.
7.4 Calibration and Programming
Some professional diagnostic tools can perform calibration and programming functions, which are necessary for certain repairs.
- Steering Angle Sensor Calibration: Calibrate the steering angle sensor after replacement or alignment adjustments.
- ESP Control Module Programming: Program the ESP control module after replacement to match the vehicle’s specifications.
- ABS Module Programming: Program the ABS module after replacement to ensure proper integration with the ESP system.
7.5 Mercedes-Benz Specific Tools
For Mercedes-Benz vehicles, specialized diagnostic tools like the Mercedes-Benz Star Diagnosis system are particularly valuable. These tools offer advanced features and capabilities that are specifically tailored to Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- Dealer-Level Diagnostics: The Star Diagnosis system provides dealer-level diagnostic capabilities, allowing you to perform the same tests and procedures as a Mercedes-Benz technician.
- Access to Technical Information: The Star Diagnosis system provides access to technical information, such as repair manuals, wiring diagrams, and technical service bulletins.
- Software Updates: The Star Diagnosis system allows you to update the software of various control modules, including the ESP control module, to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
7.6 Choosing the Right Tool
When selecting a professional diagnostic tool, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure the tool is compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Features: Choose a tool that offers the features and capabilities you need, such as code reading, live data monitoring, component testing, and calibration.
- Ease of Use: Select a tool that is easy to use and has a user-friendly interface.
- Support: Choose a tool from a reputable manufacturer that offers good customer support and technical assistance.
Investing in professional diagnostic tools is a wise decision for anyone who wants to maintain and repair their Mercedes-Benz vehicle. These tools can save you time and money by helping you accurately diagnose and resolve issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of professional diagnostic tools for Mercedes-Benz vehicles. Visit our website or contact us today to learn more.
8. Preventive Measures to Avoid ESP Problems
Preventing ESP (Electronic Stability Program) problems in your Mercedes-Benz involves a combination of proactive maintenance, careful driving habits, and timely attention to potential issues. By taking these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of ESP malfunctions and ensure your vehicle’s safety and performance.
8.1 Regular Maintenance
-
Wheel Speed Sensor Maintenance:
- Inspect wheel speed sensors regularly for damage, dirt, or corrosion.
- Clean the sensors and reluctor rings as needed to ensure accurate readings.
- Replace faulty wheel speed sensors promptly.
-
Steering Angle Sensor Calibration:
- Ensure the steering angle sensor is properly calibrated, especially after any alignment adjustments or suspension work.
- Recalibrate the steering angle sensor if necessary.
-
Brake System Maintenance:
- Inspect brake pads, rotors, and brake lines regularly.
- Replace worn brake pads and rotors promptly.
- Flush and replace brake fluid every two years or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Ensure the brake light switch is functioning correctly.
-
Tire Maintenance:
- Maintain proper tire pressure.
- Rotate tires every 5,000 to 7,000 miles to ensure even wear.
- Inspect tires regularly for wear and damage.
- Replace tires when the tread depth reaches the minimum legal limit.
- Use tires that meet the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Battery Maintenance:
- Check the battery’s voltage regularly.
- Clean battery terminals to remove corrosion.
- Ensure battery connections are tight and secure.
- Have the battery load tested periodically.
- Replace weak or failing batteries promptly.
8.2 Careful Driving Habits
-
Smooth Driving:
- Practice smooth and controlled driving techniques to minimize the ESP system’s interventions.
- Avoid sudden acceleration, hard braking, and sharp turns.
-
Adjust to Road Conditions:
- Adjust your driving style to suit the road conditions.
- Reduce speed and increase following distance in wet, icy, or snowy conditions.
-
Avoid Overloading:
- Avoid overloading the vehicle, as this can affect its handling and stability.
8.3 Timely Attention to Potential Issues
-
Pay Attention to Warning Lights:
- Pay close attention to any warning lights that appear on the dashboard, especially those related to the ESP system, ABS system, or brake system.
- Investigate the cause of any warning lights promptly.
-
Address Performance Issues:
- Address any performance issues, such as erratic braking, pulling to one side, or unusual handling behavior, promptly.
- Have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician if you notice any of these issues.
-
Regular Diagnostic Scans:
- Schedule regular diagnostic scans with a qualified technician to check for any hidden issues or fault codes.
- Address any identified issues promptly.
8.4 Avoid Aftermarket Modifications
- Careful Modifications:
- Be cautious when making aftermarket modifications to the vehicle, especially to the suspension, brakes, or electronic systems.
- Ensure any modifications are compatible with the ESP system.
- Have modifications installed by a qualified technician.
8.5 Use Quality Parts
- Quality Replacements:
- When replacing components, use high-quality parts from a reputable supplier to ensure proper fit and function.
- Avoid using cheap or generic parts, as they may not meet the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of ESP problems and ensure your Mercedes-Benz vehicle’s safety and performance. For high-quality diagnostic tools and expert advice, trust CARDIAGTECH.NET. We’re dedicated to helping you maintain your vehicle to the highest standards.
9. Choosing the Right Repair Shop
Selecting the right repair shop for your Mercedes-Benz is crucial, especially when dealing with complex systems like the ESP (Electronic Stability Program). A qualified and experienced repair shop can accurately diagnose and resolve ESP issues, ensuring your vehicle’s safety and performance. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a repair shop:
9.1 Expertise and Experience
-
Mercedes-Benz Specialization:
- Look for a repair shop that specializes in Mercedes-Benz vehicles.
- A shop with Mercedes-Benz expertise is more likely to have the knowledge, tools, and experience needed to properly diagnose and repair ESP issues.
-
Technician Qualifications:
- Inquire about the qualifications and certifications of the technicians working at the shop.
- Look for technicians who are certified by organizations like the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE).
-
Experience with ESP Systems:
- Ask about the shop’s experience with diagnosing and repairing ESP systems.
- A shop with extensive experience is more likely to be familiar with the common causes of ESP problems and the most effective solutions.
9.2 Equipment and Tools
- Diagnostic Tools:
- Ensure the repair shop has professional diagnostic tools